Optimization for Economics, a Visual Approach
Mike Carr
Contents
0 Calculus Reference 3
0.1 Graphs of Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
0.2 Limits and Derivatives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
0.3 Multivariable Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1 Unconstrained Optimization 31
1.1 Single-Variable Optimization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
1.2 Concavity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
1.3 Multivariable Optimization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
2 Constrained Optimization 89
2.1 Equality Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
2.2 Inequality Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
2.3 The Kuhn-Tucker Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
3 Comparative Statics 135
3.1 The Implicit Function Theorem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
3.2 The Envelope Theorem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
4 Sufficient Conditions 163
4.1 The Extreme Value Theorem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
4.2 The Bordered Hessian . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
4.3 Separation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
4.4 Concave Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
4.5 Quasiconcavity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
1
Note to the Reader
For the last several years I have taught a course in optimization at Emory University for seniors
majoring in mathematics and economics. While mathematics and economics is the standard preparation
for a doctoral program in economics, the vast majority of students in this course are bound for careers
in finance. One of the challenges in designing this course has been balancing the interests and needs
of students on both tracks. These notes have evolved from my own teaching materials. Their goal is
to present methods for optimization and the reasoning behind them. This reasoning makes students
resilient to the myriad modifications that these tools endure at the hands of economists.
As an outsider to economics education, I was impressed to see the extent to which economics has
embraced visual methods of instruction. More than any other field whose foundation lies in mathematics,
the standard economics curriculum provides students not only with descriptions and formulas, but with
diagrams to depict core principles. Microeconomics students are inundated with supply curves, budget
lines, indifference curves, and graphs in marginal space. This is certainly a lifeline for visual learners,
but I suspect it produces deeper understanding for all.
As a geometer, my first inclination is to lean heavily upon visual reasoning when presenting the
methods of optimization. In our efforts to find a textbook for our admittedly niche curriculum, we have
not found a economics-focused text that takes this approach. I have made these notes available in the
hope that this visual viewpoint can become an effective supplement to existing techniques. Like with
the graphical arguments in undergraduate microeconomics, I think it can bring a complete and rigorous
understanding of optimization methods to a broader set of learners.
The audience for this text is anyone who wants to understand the mathematical methods for finding
maximizers in economic theory. The best-prepared reader will have mastered the techniques of differ-
entiation, including partial derivatives. They will also be familiar with the foundations of mathematical
logic: set notation, functions, and methods of proof like contradiction and the contrapostive. Finally,
they will need a basic proficiency in vector and matrix operations: sums, products and determinants. A
competent high-school treatment may suffice for this requirement.
Anyone who sets out to teach or learn the methods of optimization from this text should be aware
of its limitations. It does not contain the economic applications that my economist colleagues present
each semester. These must be provided in order to create genuine enthusiasm for the material. This is
a deficiency that I would like to rectify eventually, if there is some consensus about which examples to
include.
We have used one widely-available source of economic examples: Optimization for Economic Theory
by Avinash Dixit. This excellent book has a rigorous, traditional treatment of most of the material here
and good explanations of some advanced applications. Dixit’s book has proved too difficult for all but the
strongest undergraduates to read independently, but the examples are compelling and comprehensible
with some extra exposition.
Finally I would like to acknowledge my economist colleagues Blake Allison and Teddy Kim who were
essential partners in developing this course. Three students, Alexia Witthaus, Jacob Sugarmann and
Aarya Aamer, carefully read my early drafts and asked many questions. Their feedback allowed me to
identify the most opaque exposition (and clarify it, I hope). There is still a long road of revision and
improvement ahead for this document. I would appreciate any feedback you have.
Mike Carr
May 2023
Chapter 0
Calculus Reference
0.1
Graphs of Functions
Goals:
1 Graph algebraic functions.
2 Graph transformations of functions.
0.1.1
Graphs of Basic Functions
Definition 0.1
The graph of a function f(x) is the set of points (x, y) whose coordinates satisfy the equation y = f(x).
In this section we review several basic functions and their graphs. These will be important as examples
and counterexamples for our methods of optimization. In addition, knowing the shape of a graph is an
efficient way to memorize the behavior of functions that appear frequently in economic models.
Definition 0.2
Linear functions can be written in slope-intercept form:
f(x) = mx + b.
The graph of a linear function is a line.
m is the slope, which is the change in y over the change in x between any two points on the line.
(0, b) is the y intercept.
If we have the slope and a known point (a, b) on a line. We can write its equation in point-slope
form.
y − b = m(x − a)
4
Definition 0.3
A monomial is a function of the form:
f(x) = x
n
where n is an integer greater than 0.
For n ≥ 2 the graph y = x
n
curves upward over the positive values of x.
Greater values of n have lower values of f(x) when 0 < x < 1 but higher values when x > 1.
For even values of n the graph is symmetric across the y-axis, curving up when x is negative.
For odd values of n the graph curves down when x is negative. It is anti-symmetric across the
x = 0.
x
2
x
4
x
6
x
y
Figure 1: Graphs of even-powered
monomials
x
x
3
x
5
x
y
Figure 2: Graphs of odd-powered
monomials
Monomials of Negative Power
Monomials of negative power have the form f (x) = x
−n
. They are also commonly written
f(x) =
1
x
n
.
The graph y =
1
x
n
has a vertical asymptote at x = 0.
The graph approaches the x-axis, y = 0 as x gets large.
For even values of n, the graph is above the x-axis.
For odd values of n, the graph is above the x-axis for positive x and below it for negative x.
A greater choice of n makes the function approach the x-axis more quickly.
5
0.1.1
Graphs of Basic Functions
x
y
Figure 3: Graphs of y = x
−2
, y = x
−4
and y = x
−6
x
y
Figure 4: Graphs of y = x
−1
, y = x
−3
and y = x
−5
Definition 0.4
A root function is a function of the form:
f(x) =
n
√
x
where n is an integer greater than 0.
The domain of
n
√
x is [0, ∞) if n is even and all real numbers if n is odd.
The x and y intercept of y =
n
√
x is at (0, 0).
Root functions are increasing. At x = 0, they travel straight up.
√
x
3
√
x
x
y
Figure 5: Graphs of root functions
6
Definition 0.5
An exponential function has the form:
f(x) = a
x
where a is a number greater than 0.
a is called the base of the exponential function.
The graph y = a
x
passes through (0, 1).
If a > 1 then f(x) increases quickly as x takes on positive values. Greater values of a give a
steeper increase. f(x) approaches 0 as x goes to −∞. Greater values of a give a faster approach.
The graph does not touch or cross the x-axis.
If a < 1, then the above is reversed.
e is a commonly used base. e is approximately 2.718.
x
y
Figure 6: Graphs of y = 2
x
, y = e
x
and y = 3
x
Definition 0.6
A logarithmic function has the form:
f(x) = log
a
x
where the base a is a number greater than 1. log
a
x is the number b such that a
b
= x. The natural
logarithm is the logarithm with base e. It is denoted f (x) = ln x.
a
b
can never be 0 or less. The domain of f(x) = log
a
x is (0, ∞).
As x approaches 0, log
a
x goes to −∞.
y = log
a
x has an x intercept at (1, 0).
7
0.1.1
Graphs of Basic Functions
y = log
a
x grows more and more slowly as x increases. This effect is more pronounced for larger
values of a.
x
y
Figure 7: Graphs of y = log
2
x, y = ln x and y = log
10
x
Logarithms and exponents are inverse functions. We solve exponential equations by applying a
logarithm to both sides. We solve logarithm equations by exponentiating both sides.
a
x
= c x = log
a
c
log
a
x = c x = a
c
0.1.2
Graphs of Transformations
Suppose we would like to transform the graph y = f(x). Here are four ways we can.
The graph of y = af(x) is stretched by a factor of a in the y direction.
The graph of y = f(x) + b is shifted by b in the positive y direction.
The graph of y = f(cx) is compressed by a factor of c in the x direction.
The graph of y = f(x + d) is shifted by d in the negative x direction.
We can perform multiple transformations on a single function.
8
Figure 8: The graph of y = f (x) and its transformation y = af (cx + d) + b
9
0.2
Limits and Derivatives
Goals:
1 Verify that a function is continuous.
2 Compute derivatives.
3 Use derivatives to understand graphs and vice versa.
0.2.1
The Limit of A Function
Calculus is the study of change. Our most important rate of change cannot be computed directly,
but exists only as a limit of rates.
Definition 0.7
The limit as x approaches a (or x → a) of a function f(x) is denoted lim
x→a
f(x).
lim
x→a
f(x) = L means that we can make f(x) arbitrarily close to L by restricting x to a small
enough neighborhood surrounding a.
If there is no L such that lim
x→a
f(x) = L, we say that lim
x→a
f(x) does not exist.
Remark
arbitrarily close means any amount of closeness demanded. We need to be able to make f(x)
within
1
10
of L, within
1
1000
of L, within
1
10000000
of L and so on. When proving that a limit
exists, mathematicians traditionally model this closeness with the variable ϵ. We indicate or verify
arbitrary closeness with the inequality |f (x) − L| < ϵ.
By a neighborhood we mean an open interval that contains a. The set {a} is not a neighborhood.
If it were, then every function would limit to f(a) as x → a. Mathematicians generally restrict to
neighborhoods of the form (a − δ, a + δ), then they need a way to produce a valid, positive δ for
any given positive ϵ.
10
Figure 9: A neighborhood of a that keeps f(x) within ϵ of L
0.2.2
Continuity
Limits give us a formal approach to defining continuity. Many of our results will rely on the fact that
a function is continuous.
Definition 0.8
A function f(x) is continuous at a, if
lim
x→a
f(x) = f(a).
f(x) can also be continuous on an interval or other set of points if it is continuous at each a in that
set. If it is continuous on R, we say f(x) is a continuous function.
Proving that a function is continuous requires us to verify its limit at every point a. This is too
much work for a case-by-case basis. Instead mathematics adopts a constructive approach. First we show
that a few basic functions are continuous. Next we prove that sums, differences, products and other
combinations preserve continuity.
11
0.2.2
Continuity
Theorem 0.9
The following functions are continuous on their domains
1 Constant functions
2 Linear functions
3 Polynomials
4 Roots
5 Exponential functions
6 Logarithms
7 Trigonometric functions
8 f(x) = |x|
Theorem 0.10
If f(x) and g(x) are continuous on their domains, then the following are also continuous on their
domains
1 f(x) + g(x)
2 f(x) − g(x)
3 f(x)g(x)
4
f(x)
g(x)
(note that any x where g(x) = 0 is not in the domain)
5 f(x)
g(x)
as long as f(x) > 0
6 f(g(x))
We can use these theorems together to argue that complicated functions are continuous.
12
Example
The function f(x) =
4
√
3x
2
− 17x + 2 −
e
x
log
5
x
is the difference of two functions. The first is a compo-
sition of a root function and polynomial (both continuous on their domains). The second is a quotient
of an exponential and a logarithm (both continuous on their domains). Thus f(x) is the difference of
two continuous functions and is continuous on its domain.
Remark
Just about any function we can write using algebraic expressions is continuous on its domain. This does
not mean it is continuous everywhere. f(x) =
1
x
is not continuous at x = 0, for example.
0.2.3
The Intermediate Value Theorem
One early intuition for continuity is that the graph of a continuous function can be drawn without
any breaks. There are many ways to formalize this idea. One of the most important is the following
theorem.
Theorem 0.11 [The Intermediate Value Theorem]
If f is a continuous function on [a, b] and K is a number between f(a) and f (b), then there is some
number c between a and b such that f(c) = K.
Intuitively, a continuous graph cannot get from one side of the line y = K to the other without
intersecting y = K. Notice that this theorem does not say exactly where this intersection must occur,
only that it must occur somewhere in the interval (a, b). It also does not rule out the possibility of more
than one such c existing.
Example
Show that f (x) = e
x
− 3x has a root between 0 and 1.
13
0.2.3 The Intermediate Value Theorem
Solution
A root is a number c such that f(c) = 0. To prove such a root exists, we check the conditions of the
intermediate value theorem.
f(x) is a sum of continuous functions, so it is continuous on its domain.
f(0) = 1
f(1) = e − 3 < 0
0 is between f(0) and f(1)
We conclude there is some c between 0 and 1 such that f (c) = 0.
−1
1 2
−1
1
2
y = e
x
− 3x
(0, 1)
(1, 3 − e)
c
x
y
Figure 10: A root of y = e
x
− 3x
0.2.4
The Derivative
The derivative is a method for measuring the rate of change of a function.
14
Definition 0.12
Given a function f(x), the derivative of f(x) at a is the number
lim
h→0
f(a + h) − f (a)
h
.
The derivative function of f(x) is the function
lim
h→0
f(x + h) − f (x)
h
.
Here are two different notations for the derivative at a.
1
df
dx
(a) (Leibniz)
2 f
′
(a) (Lagrange)
The ratio
f(a + h) − f (a)
h
can be interpreted two ways
1 The average rate of change of f between a and a + h
2 The slope of a secant line of y = f(x) from (a, f(a)) to (a + h, f(a + h))
Since the derivative is the limit of these, we interpret f
′
(a) as
1 The instantaneous rate of change of f at a
2 The slope of a tangent line to y = f(x) at (a, f(a))
Figure 11: A secant line and a tangent line to y = f (x)
15
0.2.4
The Derivative
We can take higher order derivatives by taking derivatives of derivatives. The derivative function
of f in this context is called the first derivative. Its derivative function is the second derivative. The
second derivative’s derivative function is the third derivative and so on.
Notation
The following notations are used for higher order derivatives
name Lagrange notation Leibniz notation
first derivative f
′
(x)
df
dx
second derivative f
′′
(x)
d
2
f
dx
2
third derivative f
′′′
(x)
d
3
f
dx
3
fourth derivative f
(4)
(x)
d
4
f
dx
4
fifth derivative f
(5)
(x)
d
5
f
dx
5
The sign of a higher order derivative tells us how the derivative of one order lower is changing. For
example if
d
5
f
dx
5
< 0, then
d
4
f
dx
4
is decreasing.
0.2.5
Computing Derivatives
The limit definition of a derivative is too unwieldy to use every time. Instead calculus students learn
the derivatives of some basic functions. They then use theorems to compute derivatives when those
functions are combined.
16
Derivatives of Basic Functions
d
dx
c = 0 (derivative of a constant is 0)
d
dx
x
n
= nx
n−1
for any n = 0 (The Power Rule)
d
dx
e
x
= e
x
d
dx
a
x
= a
x
ln a for a > 0
d
dx
ln x =
1
x
d
dx
log
a
x =
1
x ln a
The following rules allow us to differentiate functions made of simpler functions whose derivative we
already know.
Differentiation Rules
Sum Rule: (f(x) + g(x))
′
= f
′
(x) + g
′
(x)
Constant Multiple Rule: (cf(x))
′
= cf
′
(x)
Product Rule: (f(x)g(x))
′
= f
′
(x)g(x) + g
′
(x)f(x)
Quotient Rule:
f(x)
g(x)
′
=
f
′
(x)g(x)−g
′
(x)f(x)
(g(x))
2
unless g(x) = 0
Chain Rule: (f(g(x))
′
= f
′
(g(x))g
′
(x)
0.2.6
Computing a Derivative
Compute
d
2
dx
2
(4
√
75 − 3x
2
+ 10)
17
0.2.6
Computing a Derivative
Solution
We begin by computing the first derivative. We use the chain rule with 4x
1/2
+ 10 as the outer function
and 75 − 3x
2
as the inner function.
d
dx
(4
p
75 − 3x
2
+ 10) = 2(75 − 3x
2
)
−1/2
(−6x)
= −
12x
√
75 − 3x
2
We compute the second derivative by differentiating the first derivative. We use the quotient rule. We
need the chain rule again when we differentiate the denominator.
d
2
dx
2
(4
p
75 − 3x
2
+ 10) = −
d
dx
12x
√
75 − 3x
2
= −
d
dx
(12x)
√
75 − 3x
2
−
d
dx
(
√
75 − 3x
2
)(12x)
(
√
75 − 3x
2
)
2
= −
12
√
75 − 3x
2
+
3x
√
75−3x
2
(12x)
75 − 3x
2
= −
12
√
75 − 3x
2
+
36x
2
√
75−3x
2
75 − 3x
2
We can obtain a common denominator to simplify this expression.
d
2
dx
2
(4
p
75 − 3x
2
+ 10) = −
12(
√
75−3x
2
)
2
√
75−3x
2
+
36x
2
√
75−3x
2
75 − 3x
2
= −
12(75 − 3x
2
) + 36x
2
(75 − 3x
2
)
3/2
= −
900
(75 − 3x
2
)
3/2
18
0.3
Multivariable Functions
Goals:
1 Compute partial derviatives.
2 Recognize continuous multivariable functions.
3 Apply the chain rule to compositions of multivariable functions.
0.3.1
Multi-Variable Functions
Most interesting phenomena are not described by a single variable. We will need to develop methods
for optimizing multivariable functions. There are many ways to denote multivariable domains and the
functions on them. This is how we will denote them.
Notation
An n-vector is an ordered set of n numbers called components. For instance a = (5, −
√
17, 12.31)
is a 3-vector.
We add a vector arrow, as in a, to indicate that a is a vector.
The components of a vector can be denoted abstractly by subscripts: x = (x
1
, x
2
, . . . x
n
). The
x
i
do not have arrows because they are numbers, not vectors.
n-space, the set of all n-dimensional vectors, is denoted R
n
.
0 is the zero vector: (0, 0, 0, . . . , 0). The dimension should be clear from context.
The vectors e
1
, e
2
, . . . , e
n
are the standard basis vectors of R
n
. e
i
has 1 in the ith component
and 0 in the others. For example e
2
= (0, 1, 0, . . . , 0).
An n-variable function f (x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
n
) can be written f(x).
19
0.3.1
Multi-Variable Functions
Remark
Using a common letter with an index variable
x
1
, x
2
, x
3
. . .
is a good choice for a large or an unknown number of variables. We will use this notation when developing
the theory of multivariable optimization. In many economics problems, there is a fixed, small number
of variables. In these problems, it is more convenient to use different letters for each variable, to avoid
keeping track of subscripts.
x, y, z, . . .
Even better, we should try to choose descriptive variable names like q for quantity or p for price.
We visualize functions with their graphs. The height of the graph over a point in the domain
represents the value of the function at that point. This allows us to detect visually where the function
is large or small, increasing or decreasing.
Definition 0.13
Given an n-variable function f(x), the graph of f is the set of points (x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
n
, y) in R
n+1
that
satisfy y = f(x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
n
).
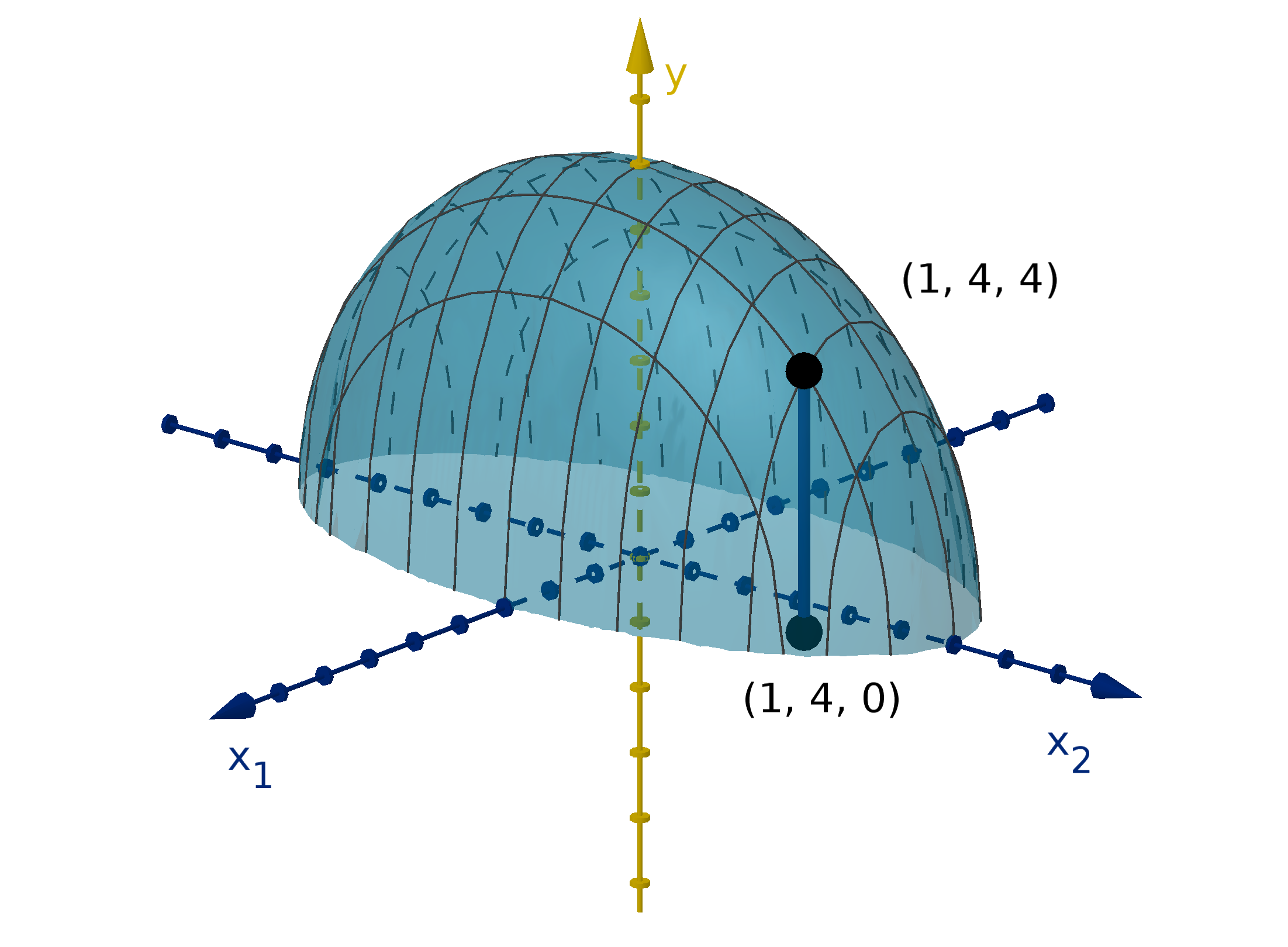
Figure 12: The graph y =
p
36 − 4x
2
1
− x
2
2
and the height showing f(1, 4).
20
Remark
In general, a graph of the form y = f (x
1
, x
2
) will be hard to visualize. For more than three variables,
this visualization becomes impossible. So why bother? Graphs are a useful visual aid to the reasoning
behind our methods. As we progress, it is useful to have an prototypical two-variable graph in your
head. You can apply our methods to that graph, whether or not you have an algebraic expression to go
with it.
0.3.2
Partial Derivatives
Our optimization tools rely on the ability to measure rates of change. For a function of multiple
variables, there are many rates of change, because there are many ways in which the input variables can
change. The simplest are those where only one variable is changing while the others remain fixed.
Definition 0.14
The partial derivative of f with respect to x
i
is a function of x. It measures the rate of change of f
at x as x
i
increases but the other coordinates remain constant. The formula is
lim
h→0
f(x + he
i
) − f (x)
h
Here are two different notations for the partial derivative.
1
∂f
∂x
i
(x) (Leibniz)
2 f
x
1
(x) (Lagrange)
Each has advantages, so we will use both. When it will not cause confusion, we can shorten Lagrange’s
notation from f
x
i
(x) to f
i
(x).
In the two variable case, we can interpret f
1
(x) as the slope of the tangent line to the graph
y = f(x
1
, x
2
) in the x
1
-direction. Higher-dimensional partial derivatives are also slopes, but are harder
to visualize.
21
0.3.2
Partial Derivatives
Figure 13: The tangent line to y = f (x
1
, x
2
) in the x
1
-direction
Computing a partial derivative requires us to treat the non-changing variables as constants. Then
we can perform ordinary single-variable differentiation with the respect to the variable that is changing.
0.3.3
Computing a Partial Derivative
The profit of a firm with a Cobb-Douglas production function might be modeled by
π(L, K) = pL
α
K
β
− wL − rK.
We can compute the partial derivative π
L
(L, K), which measures the marginal effect of hiring more
labor.
Solution
Since π
L
(L, K) is a partial derivative, we can treat K as a constant. That means that neither K
β
nor
rK is changing. We treat K
β
as a constant multiple of the monomial function L
α
. We treat rK as a
constant term with derivative 0.
π
L
(L, K) = pαL
α−1
K
β
− w
22
0.3.4
Multivariable Limits and Continuity
Definition 0.15
A multivariable function f (x) is continuous at a, if
lim
x→a
f(x) = f(a)
In order to verify this limit, we must check that f(x) can be made arbitrarily close to f(a) by
restricting to a sufficiently small neighborhood of a. This neighborhood allows for travel in infinitely
many directions from a, rather than just forwards and backwards like a one-variable limit. This makes
multivariable limits difficult to compute rigorously and multivariable continuity difficult to verify directly.
Fortunately, we can use the same approach we used for single-variable functions.
Variant of Theorem 0.9
The following multivariable functions are continuous on their domains
1 Constant functions
2 Linear functions
3 Polynomials
4 Roots
5 Exponential functions
6 Logarithms
7 Trigonometric functions
23
0.3.4 Multivariable Limits and Continuity
Variant of Theorem 0.10
If f(x) and g(x) are continuous on their domains, and c is a constant, then the following are also
continuous on their domains
1 f(x) + g(x)
2 f(x) − g(x)
3 f(x)g(x)
4
f(x)
g(x)
(note that any x where g(x) = 0 is not in the domain)
5 f(x)
g(x)
as long as f(x) > 0
6 f(g(x)) where f (x) is a one-variable function
Multivariable continuity becomes important when discussing derivatives. Partial derivatives do not
use multivariable limits. They use a limit as a single variable h goes to 0. For this reason, we are not
guaranteed that partial derivatives reliably model the shape of a function.
Example
Consider the function
f(x
1
, x
2
) =
(
0 if x
2
≤ 0
x
1
if x
2
> 0
This function is 0 when x
1
= 0 or x
2
= 0. Thus the partial derivatives at (0, 0) are
f
1
(0, 0) = 0 f
2
(0, 0) = 0
If we increase x
1
while holding x
2
constant or increase x
2
while holding x
1
constant, then the function
stays constant at 0. This does not reflect the fact that if we increase both x
1
and x
2
at (0, 0), the
function will have a positive slope.
Many theorems rely on a function behaving consistently with its partial derivatives no matter which
direction we travel. The following property will usually serve that purpose.
Definition 0.16
A function f(x) is continuously differentiable, if all the partial derivative functions f
i
(x) are continuous
functions. If instead they are all continuous at a point a, we say f(x) is continuously differentiable at
a.
24
0.3.5
The Chain Rule
How do model the change of a multivariable function when more than one input variable is changing?
We write each input variable as a function of a parameter. For instance, if x
1
and x
2
are both changing
we can write each as a function of a parameter t. We can combine these to define a vector function:
x(t) = (x
1
(t), x
2
(t)).
f(x(t)) is a composition of functions. If we have defined x
1
(t) and x
2
(t) to correctly model the change
we want in x
1
and x
2
, then the derivative of f(x(t)) will tell us how f is changing as well. Notice
f(x(t)) is a single variable function. The value of t determines its value completely. The multivariable
chain rule computes its derivative using x(t) and the gradient of f(x).
Definition 0.17
Given a function f(x), the gradient vector of f at x is
∇f(x) = (f
1
(x), f
2
(x), . . . , f
n
(x))
Theorem 0.18 [The Multivariable Chain Rule]
Suppose f(x) is a continuously differentiable, n-variable function. If x(t) is differentiable, then the
derivative of the composition f(x(t)) with respect to t is
df
dt
(t) = ∇f(x(t)) · x
′
(t)
or
df
dt
(t) =
n
X
i=1
f
i
(x(t))x
′
i
(t)
We should avoid using the notations f
′
(t) and f
t
(t) for derivatives of compositions. Instead, we use
Leibniz notation. This makes the variable of differentiation clear without implying that we are computing
a partial derivative.
25
0.3.6
Applying the Chain Rule
Suppose f(x
1
, x
2
) =
ln x
1
x
2
. If x
1
(t) = t
2
and x
2
(t) = e
t
, compute
d
dt
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t)).
Solution
According to the chain rule
d
dt
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t)) = f
x
1
(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))x
′
1
(t) + f
x
2
(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))x
′
2
(t)
=
1
x
1
(t)x
2
(t)
x
′
1
(t) −
ln x
1
x
2
2
x
′
2
(t)
=
1
t
2
e
t
2t −
ln t
2
e
2t
e
t
=
2
te
t
−
ln t
2
e
t
=
2 − t ln t
2
te
t
Remark
The multivariable chain rule is not useful for direct calculations. Substituting the expressions for x
1
(t)
and x
2
(t) would have given us
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t)) =
ln t
2
e
t
.
We can differentiate this using single-variable methods to obtain the same answer. The multivariable
chain rule will instead serve us well in more abstract situations.
0.3.7
Alternate Notations and the Chain Rule
The multivariable chain rule is easiest to state when we give the component functions names that
match the variables of f. When this is not the case, we need to take care with our notation.
26
Example
Let f (x, y) be a continuously differentiable function. Let x and y be defined by differentiable functions
g(t) and h(t) respectively. The chain rule states that
d
dt
f(g(t), h(t)) = f
x
(g(t), h(t))g
′
(t) + f
y
(g(t), h(t))h
′
(t).
We do not write f
g
or f
h
in this example. f is defined as a function of x and y, so those are the only
partial derivatives it has.
Some applications use one of the variables of f as the parameter. The simplest example gives an
alternate formulation for the partial derivative.
Example
Let f(x
1
, x
2
) be a continuously differentiable function. Let x
1
be the identity function of itself and let
x
2
to be a constant function of x
1
.
x
1
= x
1
dx
1
dx
1
= 1
x
2
= c
dc
dx
1
= 0
The rate of change with this parameterization should reflect that x
1
is changing and x
2
is not. That is
exactly what the chain rule tells us.
d
dx
1
f(x
1
, c) = f
x
1
(x
1
, c)
dx
1
dx
1
+ f
x
2
(x
1
, c)
dc
dx
1
= f
x
1
(x
1
, c)(1) + f
x
2
(x
1
, c)(0)
= f
x
1
(x
1
, c)
We will build upon this formulation when we compute comparative statics.
Finally, we should note that the chain rule applies when the x
i
are multivariable functions of a vector
t. In this case, f(x(
t)) is a function of
t and thus we can compute its partial derivatives.
27
0.3.7 Alternate Notations and the Chain Rule
Generalization of Theorem 0.18
Suppose f(x) is a continuously differentiable, n-variable function. If x
i
(
t) are differentiable functions of
the variables t
j
, then the partial derivative of the composition f (x(
t)) with respect to t
k
is
∂f
∂t
k
(
t) = ∇f(x(
t)) · x
k
(
t)
or
∂f
∂t
k
(
t) =
n
X
i=1
f
i
(x(
t))
∂x
i
∂t
k
(
t)
This generalization follows immediately from treating each t
j
except t
k
as a constant.
0.3.8
Proving the Multivariable Chain Rule
The proof of the multivariable chain rule uses the same tools as the single variable chain rule (and
product rule). However, multivariable limits are much more difficult to verify than single variable limits.
To check that lim
x→a
f(x) = L, we have to consider values of x in every direction from a, not just forward
or backwards along a line. We will sketch the proof for the case where f is a two-variable function.
Even the sketch is quite technical. It contains no arguments that are important enough to commit to
memory.
Proof
We apply the definition of a derivative
df
dt
= lim
h→0
f(x(t + h)) − f(x(t))
h
= lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t + h), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))
h
We break up this limit into a sum of two limits by adding and subtracting a term and regrouping the
result (assuming the limit of each summand exists)
= lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t + h), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h)) + f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))
h
= lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t + h), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h))
h
+ lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))
h
28
Next we multiply each limit by 1, represented as a quotient of an expression divided by itself.
= lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t + h), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h))
h
x
1
(t + h) − x
1
(t)
x
1
(t + h) − x
1
(t)
+ lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))
h
x
2
(t + h) − x
2
(t)
x
2
(t + h) − x
2
(t)
Naturally
x
i
(t+h)−x
i
(t)
x
i
(t+h)−x
i
(t)
evaluates to
0
0
when h = 0. This is not a problem for a limit. However, if it
also evaluates to
0
0
at other values of h, no matter how small a neighborhood of h = 0 we choose,
then another approach is needed. In this case, the entire term will limit to 0, but we omit the formal
argument from this sketch. Instead we assume all is well, and we reorganize each product by swapping
denominators.
= lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t + h), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h))
x
1
(t + h) − x
1
(t)
x
1
(t + h) − x
1
(t)
h
+ lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))
x
2
(t + h) − x
2
(t)
x
2
(t + h) − x
2
(t)
h
We break up the result as a product of limits (assuming the limit of each factor exists)
= lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t + h), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h))
x
1
(t + h) − x
1
(t)
lim
h→0
x
1
(t + h) − x
1
(t)
h
+ lim
h→0
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))
x
2
(t + h) − x
2
(t)
lim
h→0
x
2
(t + h) − x
2
(t)
h
The second factor of each product now looks like a derivative. To make first factors look more like
derivatives, we let j = x
1
(t + h) −x
1
(t) and k = x
2
(t + h) −x
2
(t). These quantities go to 0 as h → 0.
Our limits can be rewritten as
= lim
(h,j)→(0,0)
f(x
1
(t) + j, x
2
(t + h)) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h))
j
lim
h→0
x
1
(t + h) − x
1
(t)
h
+ lim
(h,k)→(0,0)
f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t) + k) − f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))
k
lim
h→0
x
2
(t + h) − x
2
(t)
h
At this point we have four limits, each of which looks like the definition of a derivative. We can
replace each one with its derivative notation. In general, we cannot evaluate a multivariable limit by
handling one variable at a time, but the fact that the partial derivatives are continuous allows us to do
so here. The details of this kind of argument are covered in an analysis course.
= lim
h→0
f
1
(x
1
(t), x
2
(t + h))x
′
1
(t) + lim
h→0
f
2
(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))x
′
2
(t)
= f
1
(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))x
′
1
(t) + f
2
(x
1
(t), x
2
(t))x
′
2
(t)
This is the dot product
= ∇f(x(t)) · x
′
(t)
One can adapt this proof to a higher dimension by breaking the limit into more summands. The
theorem we gave is even more general, because applies to an n-variable function. To prove that version,
we would use a proof by induction.
29
0.3.8 Proving the Multivariable Chain Rule
30
Chapter 1
Unconstrained Optimization
1.1
Single-Variable Optimization
Goals:
1 Know the definition of a local or global maximizer.
2 Apply the first- and second-order conditions to calculate maximizers.
3 Distinguish between necessary and sufficient conditions and recognize the role of each in optimiza-
tion.
4 Understand the role of the derivative in proving the first- and second-order conditions.
Some of the most important methods in calculus are those that identify maximizers and minimizers
of functions. This section gives precise theorems to describe those methods. We will also examine
the distinct but complementary roles played by necessary conditions and sufficient conditions. Finally,
we will give a reasonably compact formal basis to prove the theorems of this section and support the
theorems in the sections that follow.
1.1.1
The First-Order Condition
Given a function, we are interested in what inputs of that function will produce the largest or
smallest values of that function. These inputs are called maximizers and minimizers. In order to identify
maximizer and minimizers, we need to have a rigorous definition that we can verify.
Definition 1.1
Suppose a lies in the domain of a function f(x).
1 a is a maximizer of f if f(a) ≥ f(x) for all other x in the domain of f. In this case f(a) is called
the maximum of f.
2 a is a local maximizer of f if f(a) ≥ f(x) for all other x in some neighborhood of a. It is a
strict local maximizer if f (a) > f(x) instead. In either case f(a) is called a local maximum of
f.
3 a is a minimizer of f if f(a) ≤ f(x) for all other x in the domain of f. In this case f(a) is called
the minimum of f.
4 a is a local minimizer of f if f(a) ≤ f (x) for all other x in some neighborhood of a. It is a
strict local minimizer if f(a) < f(x) (than 0) to the left of a and smaller values (than 0) to the
right. Thus, travelinstead. In either case f (a) is called a local minimum of f .
32
Remark
When we are trying to draw a contrast with a local maximizer, sometimes we use global maximizer or
absolute maximizer to refer to a maximizer of a function.
The difficulty in finding maximizers is that the domain has infinitely many points. Using only the
definition, we would need to evaluate them all, one by one, to find a maximizer. This is obviously
impossible. Thankfully, calculus gives us a way to narrow down the search.
Derivatives measure the rate of change of a function. Knowing whether the rate is positive or negative
should tell us how f(a) compares to nearby values. Here is a way to formally state that relationship.
Lemma 1.2
If f
′
(a) > 0, then for all x in some neighborhood of a,
1 f(x) > f(a) if x > a
2 f(x) < f(a) if x < a.
Figure 1.1: The graph y = f (x) and a neighborhood where it stays close to its tangent line
Remark
A lemma is a statement that is not particularly interesting on its own. It is used as a step to proving a
more important result.
We will provide a formal proof for this lemma later. The main argument is that near a, y = f(x)
lies close enough to the tangent line at a to mimic its behavior, attaining larger values for x > a and
33
1.1.1 The First-Order Condition
smaller values for x < a. Notice that this behavior does not need to persist for all x. We cannot say
how long y = f(x) will stay close to its tangent line. It may be that the neighborhood where it does is
quite small.
We can make the same argument for functions with a negative derivative, except the behavior is
backwards. Aside from switching the direction of some inequalities, the proof is identical. Rather than
treat this result as its own lemma, we present it as a variant.
Variant of Lemma 1.2
If f
′
(a) < 0, then for all x in some neighborhood of a,
1 f(x) < f(a) if x > a
2 f(x) > f(a) if x < a.
The existence of nearby x such that f(x) > f (a) is inconsistent with the definition of a local
maximizer. Lemma 1.2 and its variant guarantee such x, so:
If f
′
(a) > 0, then a is not a local maximizer.
If f
′
(a) < 0, then a is not a local maximizer.
We convert these statements to their contrapositives. If a is a local maximizer, then f
′
(a) is neither
positive nor negative. This gives us the following condition.
Theorem 1.3 [The First-Order Condition (FOC)]
Let a be a local maximizer or local minimizer of f(x). Either f
′
(a) does not exist or f
′
(a) = 0.
Definition 1.4
The values of x that satisfy the first-order condition are called critical points.
34
1.1.2
Applying the First-Order Condition
What does the first-order condition tell us about f (x) = 8x
3
− x
4
?
Solution
The first-order condition tells us that a local maximizer or minimizer only occurs where the derivative
is 0 or undefined. The derivative of this function is 24x
2
− 4x
3
. It is defined for all x, so we solve for
where it is 0.
f
′
(x) = 0
24x
2
− 4x
3
= 0
4x
2
(6 − x) = 0
x = 0 or x = 6
This means that no point except x = 0 or x = 6 can be a local maximizer or minimizer.
−4 −2
2 4 6 8 10
−200
200
400
600
y = f(x)
x
y
Figure 1.2: The graph of f(x) = 8x
3
− x
4
Remark
The first-order condition does not tell us that either of x = 0 or x = 6 must a local maximizer or a local
minimizer. In fact, x = 6 is a local maximizer but x = 0 is neither.
35
1.1.3
The Second-Order Condition
As the previous example shows, the first-order condition is limited in its conclusion. Knowing the
value of f
′
(a) is not enough to give us certainty about the shape of the graph near a. For that we need
to know how the first derivative is changing at a. The change in the first derivative is measured by
the second derivative. The second derivative function, denoted f
′′
(x), is the derivative of the function
f
′
(x). The sign of the second derivative allows us to classify some critical points.
Theorem 1.5 [The Second-Order Condition (SOC)]
If f
′
(a) = 0 and f
′′
(a) < 0, then a is a strict local maximizer of f.
−2 −1
1 2 3 4 5
−10
10
20
y = f(x)
y = f
′
(x)
(2, f(2))
y = f(x)
x
y
Figure 1.3: A neighborhood where a = 2 is the maximizer of f (x)
The intuition behind this result relies on the fact that f
′′
(a) is the derivative of f
′
(x) at a. If
f
′′
(a) < 0, then f
′
(a) takes on larger values (than 0) to the left of a and smaller values (than 0) to the
right. Traveling left to right, the function increases until it reaches a. After passing a, it decreases.
Naturally, we have the following variant.
Variant of Theorem 1.5
If f
′
(a) = 0 and f
′′
(a) > 0, then a is a strict local minimizer of f.
Remark
This is sometimes called the local second-order condition, since it gives information about local
maximizers.
We cannot conclude anything, if f
′′
(a) = 0. a may be a maximizer, a minimizer or neither.
36
1.1.4
Applying the Second-Order Condition
What does the second-order condition tell us about f (x) = 8x
3
− x
4
?
Solution
The second-order condition requires f
′
(x) = 0. We’ve already shown that this only occurs at x = 0 and
x = 6. The other part of the condition requires us to compute the second derivative.
f
′
(x) = 24x
2
− 4x
3
f
′′
(x) = 48x − 12x
2
f
′′
(0) = 0
f
′′
(6) = −144 < 0
This means that x = 6 is strict local maximizer. The second-order condition does not tell us anything
about x = 0.
1.1.5
The Global Second-Order Condition
A firm seeking to increase its profits does not have much use for a local maximizer. The excuse:
“Our strategy was superior to all numerically similar strategies” will not impress a board of directors.
Nor would any rational actor settle for a mere local maximizer of their utility function. Utility maximizers
and profit maximizers want to find the global maximizer. If we know more about the second derivative
of the utility function, we can identify such a value.
Theorem 1.6 [The Global Second-Order Condition (GSOC)]
If f
′
(x
∗
) = 0 and f
′′
(x) < 0 for all x, then x
∗
is the only critical point of f and is the unique global
maximizer of f.
37
1.1.5 The Global Second-Order Condition
Remark
Unlike the (local) second-order condition, this theorem requires that the second derivative is
negative everywhere, not just at x
∗
.
In return for a stronger requirement, we obtain a much stronger conclusion.
Economists traditionally use x
∗
to denote a global maximizer. Thus we will use x
∗
to denote a
known maximizer or any point that will imminently be identified as a maximizer.
−2
2 4
−2
−1
1
2
3
(2, f(2))
y = f(x)
y = f
′
(x)
x
y
Figure 1.4: A function and its derivative near a maximizer
Unlike in the local case, we can make some use of a zero second derivative here.
Variants of Theorem 1.6
1 If f
′
(x
∗
) = 0 and f
′′
(x) > 0 for all x, then x
∗
is the only critical point of f and is the global
minimizer of f.
2 If f
′
(x
∗
) = 0 and f
′′
(x) ≤ 0 for all x, then x
∗
is a global maximizer of f (not necessarily unique).
3 If f
′
(x
∗
) = 0 and f
′′
(x) ≥ 0 for all x, then x
∗
is a global minimizer of f (not necessarily unique).
38
1.1.6
Sufficient and Necessary Conditions
The conclusions we draw from the first-order condition are fundamentally different from the con-
clusions that we draw from the second-order conditions. Neither of them allows us to fully answer the
question of which points are local maximizers of f . We can see the difference in their structure
FOC: If a is a local maximizer, then [condition]
SOC: If [condition], then a is a local maximizer
Mathematics has the following vocabulary for describing this difference.
Definition 1.7
Suppose we have a condition P that we are using to detect whether a statement Q is true or false.
1 A statement of the form “If Q then P ” indicates that P is a necessary condition for Q.
2 A statement of the form “If P then Q” indicates that P is a sufficient condition for Q.
Remark
We can find uses for both necessary and sufficient conditions, but we need to be careful to interpret
their conclusions correctly.
If you want to show that Q is true, you need to use a sufficient condition. A necessary condition
will not suffice.
If you want to rule out Q being true, one way is to show that a necessary condition is not satisfied.
Going forward, it is important to identify each new result as being necessary or sufficient (or maybe
both). We can begin by seeing how these terms apply to the first- and second-order conditions.
The first-order condition is a necessary condition. You can not have a local maximizer without
satisfying it. It is not a sufficient condition. A point can satisfy the first-order condition without being
a local maximizer.
Example
Let f(x) = x
3
. The value a = 0 satisfies the FOC but is not a local maximizer (or minimizer).
39
1.1.6
Sufficient and Necessary Conditions
This means that the first-order condition can only rule out values that are not maximizers. We
cannot conclude that a point is a maximizer just by showing that it satisfies the first-order condition.
The second-order condition is a sufficient condition. If f
′
(a) = 0 and f
′′
(a) < 0 then a must be a
local maximizer. It is not a necessary condition: there may be local maximizers that do not satisfy the
second-order condition.
Example
Let f(x) = −x
4
. The local maximizer a = 0 does not satisfy the SOC, because f
′′
(0) = 0.
The global second-order condition is also a sufficient condition and not a necessary one. For example,
a function can have a global maximizer without satisfying it.
−2
2 4
−1
1
2
3
(1, f(1))
y = f(x)
x
y
Figure 1.5: The graph of f(x) =
2
x
2
−2x+2
, which has a global maximizer and unique critical point at
x
∗
= 1, but does not satisfy the GSOC.
Remark
Abstractly, there is no difference between P and Q. There are two ways to view the statement:
If P , then Q.
P is a sufficient condition for Q.
Q is a necessary condition for P
However, we like to think of conditions as statements that we use to test for what we really care about.
So while, abstractly, being a local maximizer is a sufficient condition for f
′
(a) = 0, this does not reflect
the way we use the first-order condition in practice.
Generally we will want to have both necessary and conditions to test for properties that we care about.
With the tools we have so far, we can determine that certain points are local or global maximizers. We
40
can determine that many points are not local maximizers. Still, there may be points that satisfy the first-
order condition but not the second-order condition. We cannot tell whether these are local maximizers
or not.
The best condition would be a condition that is both necessary and sufficient. No such tool exists for
general optimization, so we are on the lookout for additional conditions to apply when the ones we have
are inconclusive. Coming up with new conditions is usually hard work, but we can obtain one easily, if
we exploit the relationship between maximizers and minimizers.
A sufficient condition for a minimizer can be turned into a necessary condition for a maximizer. If
f
′
(a) = 0 and f
′′
(a) > 0 then by a variant of Theorem 1.5, a is a strict local minimizer. Thus it cannot
be a maximizer. On the other hand, if f
′′
(a) exists but f
′
(a) = 0 then a is still not a local maximizer.
This leaves only the following possibilities for the second derivative at a local maximizer a.
Theorem 1.8
If a is a local maximizer of f, then f
′′
(a) ≤ 0 or f
′′
(a) does not exist.
1.1.7
Proving the First-Order Condition
In general, we expect a positive derivative to mean that greater values of x produce greater values
of f(x). The lemma at the heart of the first-order condition described what we can conclude when a
derivative is positive at one point.
The derivative is a limit, so any formal argument needs to start there. Proofs about limits can require
extensive computations and creative problem solving. Fortunately, we will only need the following lemma
about limits.
Lemma 1.9
If lim
x→a
f(x) = L and L > 0, then there is a neighborhood of a on which f is positive.
Proof
Since L is positive, L/2 is also positive. By definition of a limit there is some neighborhood of a in
which f(x) is within L/2 of L. We can express that distance with an absolute value.
|f(x) − L| < L/2
−L/2 < f(x) − L < L/2
L/2 < f(x) < 3L/2
Since L/2 is positive, so is f(x).
41
1.1.7 Proving the First-Order Condition
Variant of Lemma 1.9
If lim
x→a
f(x) = L and L < 0, then there is a neighborhood of a on which f is negative.
We are now in a position to prove Lemma 1.2.
Lemma 1.2
If f
′
(a) > 0, then for all x in some neighborhood of a,
1 f(x) > f(a) if x > a
2 f(x) < f(a) if x < a.
Proof
Since f
′
(a) = lim
h→0
f(a + h) − f (a)
h
> 0, Lemma 1.9 guarantees that there is a neighborhood of h
values near 0 where
f(a+h)−f (a)
h
> 0. Let x = a + h. In the corresponding neighborhood of x values
around a, we can make the following computations.
1 If x > a then h > 0 and
f(a + h) − f (a)
h
> 0
f(x) − f(a)
h
> 0
f(x) − f(a) > 0
f(x) > f(a)
2 If x < a then h < 0 and
f(a + h) − f (a)
h
> 0
f(x) − f(a)
h
> 0
f(x) − f(a) < 0
f(x) < f(a)
42
Remark
This proof uses an earlier lemma. If you are carefully reading this proof to understand the argument,
you may need to look back at the lemma and think about how it is being used here.
Visually, the argument of this proof is that the secant lines from a have positive slope in some
neighborhood of a.
1.1.8
Proving the Second-Order Conditions
In order to prove the second-order condition, we need a stronger conclusion than Lemma 1.2. Calculus
teaches that a function with positive derivatives is increasing, while a function with negative derivatives
is decreasing. In order to make a rigorous argument, we should know formal definitions of increasing
and decreasing.
Definition 1.10
Let f(x) be a function, and let I be an interval in its domain.
f(x) is increasing if for any numbers a < b in the domain of f , f(a) < f(b).
f(x) is decreasing if for any numbers a < b in the domain of f , f(a) > f(b).
43
1.1.8 Proving the Second-Order Conditions
Figure 1.6: The graph of an increasing function
f
′
(a) > 0 is not enough to guarantee that f (x) increases in a neighborhood of a. f(x) may suffer
from oscillations that persist arbitrarily close to a (see Figure 1.1). If we want to use a derivative to show
that a function is increasing, we need to know the derivative is positive at every point on an interval.
Lemma 1.11
If f
′
(x) > 0 for all x on an interval I, then f (x) is increasing on I.
To prove this lemma, we need to show that when f
′
(x) > 0, the function satisfies the formal
definition of increasing that we saw above. This is surprisingly arduous to prove using the definition of
a derivative as our starting point. Here are two deceptively short proofs
Proof
Suppose a < b. Apply the fundamental theorem of calculus: f (b)−f (a) =
Z
b
a
f
′
(x) dx. The integrand
is positive over all of [a, b], so the integral is positive too. Thus f (b) > f(a).
44
Figure 1.7: The fundamental theorem of calculus applied to a positive derivative
Proof
Suppose a < b. Apply the mean value theorem: There is some c between a and b such that
f(b)−f (a)
b−a
=
f
′
(c). Since c ∈ I, we know that f
′
(c) > 0. Thus f(b) > f(a).
Figure 1.8: The point c, whose tangent line has the same slope as the secant from a to b
You should not be satisfied by these proofs. Each raises a new question.
1 How do you prove the fundamental theorem of calculus?
2 How do you prove the mean value theorem?
A satisfactory argument would either prove the missing result or find another method that eliminates
the need for them. Unfortunately, any of these approaches takes us into concepts beyond the scope of
these notes. You can expect to find their formal proofs in an analysis course.
Naturally, this lemma has variants. We can switch the direction of the inequality, but we can also
relax the strictness of the inequality.
45
1.1.8 Proving the Second-Order Conditions
Variants of Lemma 1.11
1 If f
′
(x) < 0 on an interval I, then f (x) is decreasing on I.
2 If f
′
(x) ≥ 0 on an interval I, then f(x) is non-decreasing on I, meaning that if a < b,
f(a) ≤ f(b).
3 If f
′
(x) ≤ 0 on an interval I, then f (x) is non-increasing on I, meaning that if a < b, f(a) ≥
f(b).
Moving forward, we will see strict and non-strict variants so frequently that when we don’t, it is
worth pondering why not.
With these lemmas in hand, we are ready to prove the second-order condition.
Theorem 1.5
If f
′
(a) = 0 and f
′′
(a) < 0, then a is a strict local maximizer of f.
Arguments about the second derivative usually rely on the fact that f
′′
(x) is the derivative of f
′
(x).
We will apply Lemma 1.9, letting f
′
(x) play the role of the original function with f
′′
(x) as its derivative.
We can thus use the sign of f
′′
(a) to compare the values of f
′
(x) and f
′
(a). Here is the formal
argument.
Proof
We suppose f
′
(a) = 0 and f
′′
(a) < 0. f
′′
(x) is the derivative of f
′
(x), and it is negative at a. A
variant of Lemma 1.9 applies. There is some neighborhood I of a where
if x > a, then f
′
(x) < f
′
(a) = 0
if x < a, then f
′
(x) > f
′
(a) = 0.
The second inequality shows, by Lemma 1.11, that f(x) is increasing to the left of x in I. By definition
of increasing this means that f(x) < f(a) for all x < a in I. Similarly, the first inequality shows that
f(x) is decreasing to the right of a in I. By definition of decreasing this means that f(x) < f(a) for
all x > a in I. Thus f(a) > f(x) for all other x in I. This satisfies the definition of a strict local
maximizer, so we conclude that a is a strict local maximizer of f .
The proof of the global second-order condition follows the same logic. The only difference is that
we can apply Lemma 1.11 instead of Lemma 1.9 to get a global statement about the first derivative on
either side of x
∗
. Here is the full text for the sake of completeness.
46
Proof
We suppose f
′
(x
∗
) = 0 and f
′′
(x) < 0 for all x. A variant of Lemma 1.11 tells us that f
′
(x) is
decreasing for all x. This means:
if x > x
∗
, then f
′
(x) < f
′
(x
∗
) = 0
if x < x
∗
, then f
′
(x) > f
′
(x
∗
) = 0.
The second inequality shows, by Lemma 1.11, that f(x) is increasing for all x < x
∗
. By definition of
increasing this means that f (x) < f (x
∗
) for all x < x
∗
. Similarly, the first inequality shows that f(x)
is decreasing for all x > x
∗
. By definition of decreasing this means that f(x) < f(x
∗
) for all x > x
∗
.
Thus f(x
∗
) > f (x) for all other x. This satisfies the definition of a unique maximizer, so we conclude
that x
∗
is a unique maximizer of f.
To show that x
∗
is the only critical point, we simply note that if there were another critical point,
it would also satisfy this condition and be the unique maximizer. Since there can be only one unique
maximizer, no such critical point can exist.
1.1.9
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The first-order condition (Theorem 1.3)
The second-order condition (Theorem 1.5)
The global second-order condition (Theorem 1.6)
Necessary and sufficient conditions (Definition 1.7)
f
′′
(x
∗
) < 0
and f
′
(x
∗
) = 0
f
′′
(x) < 0 for all x
and f
′
(x
∗
) = 0
x
∗
is a
strict local max
x
∗
is the
unique global max and
only critical point
f
′
(x
∗
) = 0 or DNEf
′′
(x
∗
) ≤ 0 or DNE
SOC
GSOC
FOCThm 1.8
Figure 1.9: Relationships between the conditions of single variable optimization
47
1.2
Concavity
Goals:
1 Recognize convex sets.
2 Recognize concave and convex functions visually.
3 Understand the difference between strict and non-strict convexity/concavity.
4 Verify concavity using inequalities, tangent lines or second derivatives as appropriate.
5 Use concavity to find maximizers of a function.
1.2.1
Convex Sets
Our goal is to understand what the shape of a graph tells us about the maximizer(s) of a function.
We would prefer methods that apply to both single-variable and multivariable functions. For this, we
need to be able to describe shapes in any dimension. Most students learn how to recognize a convex
polygon, but we can define convexity in a large variety of shapes. Convex regions can be angular or
smooth. They can exist in any dimension. To see this, we need the formal definition of convexity.
Definition 1.12
A region D ⊆ R
n
is convex, if the line segment between any two points a and
b in D entirely lies in
D.
There is no restriction on the dimension of D. We can even apply it to regions in the real line.
Example
If D is a subset of R
1
, then D is convex if and only if it is connected.
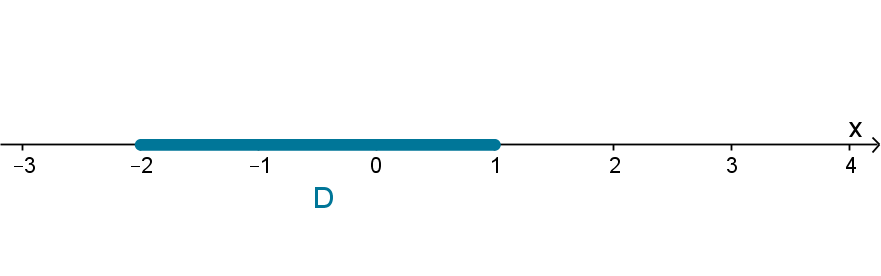
48
For a polygon, this definition should match our previous intuition of convexity. Convince yourself
that any two points in the convex polygons you learned about can be connected with a segment. In a
nonconvex polygon there is at least one pair of points whose line segment leaves the polygon. You can
convince yourself by picking your favorite nonconvex polygon and finding such a segment.
a
b
a
b
Figure 1.10: A convex polygon and a nonconvex polygon
We cannot make a rigorous case for convexity by drawing segments. There are too many to check.
We can instead make convexity more algebraic by parameterizing the line segment from a to
b.
x(t) = (1 − t)a + t
b 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
You can check that this is a line by writing it as
x(t) = a + t(
b −a) 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
x(0) = a. As t increases, x(t) travels in the direction of (
b −a) until arriving at
b when t = 1. To
check for convexity of D, we just need to test that the points of x(t) lie in D.
Figure 1.11: The line segment from a to
b
Furthermore, we do not need to check every a and
b. Any a and
b whose segment leaves D will
leave the at some boundary point c and reenter at some boundary point
d (Figure 1.12). Thus if we
49
1.2.1
Convex Sets
only checked segments between boundary points, the segment between c and
d would be sufficient to
indicate that D is not convex. We summarize this argument in the following theorem.
a
b
c
d
Figure 1.12: A segment that leaves a nonconvex region
Theorem 1.13
A region D is convex if for all a and
b in the boundary of D and all t in [0, 1],
(1 − t)a + t
b ∈ D
We visually identify convex polygons as polygons where every corner “points outward.” However,
the corners of the polygon are the only places that point outward. The rest of the boundary is flat,
pointing neither inward nor outward. With non-polygonal regions, it is possible to have a boundary that
points outward everywhere, not just at a few corners. This will be a useful property to keep track of, so
we have a name for such regions.
Definition 1.14
A region D is strictly convex, if the segment, not including the endpoints, between any two points a
and
b in D entirely lies in the interior of D.
Figure 1.13: Two convex regions, one strictly convex and the other not strictly convex
50
Remark
Every strictly convex region is also convex, but some convex regions are not strictly convex. We say
that strict convexity is a stronger condition and convexity is a weaker condition.
We are often interested in the intersection of two regions. For instance, if one region is the set of
points satisfying one condition, while a second region is the set of points satisfying a second conditions,
then their intersection is the points satisfying both conditions. Convexity behaves well in these situations.
Theorem 1.15
If D
1
and D
2
are convex regions, then D
1
∩ D
2
is convex.
The proof is a good exercise.
1.2.2
Concave Functions
Our next step is to use convexity to describe the shape of functions or, more precisely, their graphs.
Most students encounter convex and concave functions in calculus, though they are sometimes called
concave up and concave down. With a rigorous definition of a convex region, we are now in position to
define what it means to be a convex function.
Definition 1.16
Let f(x) be a function whose domain is convex. We say f(x) is convex, if y ≥ f(x), the region above
its graph, is convex. It is concave if y ≤ f(x), the region below its graph, is convex.
51
1.2.2
Concave Functions
Figure 1.14: A concave function
Remark
Be careful when learning these definitions. Students often expect the definition of concave function to
have something to do with a region being nonconvex (which is sometimes called concave), but it does
not. Nonconvex regions above and below graphs are unremarkable. It is when one of regions is convex
that the graph is special.
Figure 1.15: The graph of a function that is neither concave nor convex and the nonconvex regions
above and below it.
We might ask whether the region above or below y = f (x) is strictly convex, rather than merely
convex. If it is, we can pass the “strictness” onto our description of f.
Definition 1.17
Let f(x) be a function whose domain is convex. f (x) is strictly convex, if the region y ≥ f(x) is
strictly convex. It is strictly concave if the region y ≤ f(x) is strictly convex.
52
Remark
Strict concavity is a stronger condition than concavity. Every strictly concave function is also concave,
but some concave functions are not strictly concave.
Figure 1.16: A function that is concave but not strictly concave
Notice that the region below y = f(x) is a mirror image of the region above y = −f(x). If one is
convex, so is the other. We can make the following connection between a function and its negative.
Lemma 1.18
Let f(x) be a function.
1 f(x) is concave if and only if −f (x) is convex.
2 f(x) is strictly concave if and only if −f (x) is strictly convex.
We will use this lemma as an excuse to ignore convex functions. Any argument about concave
functions becomes an argument about convex functions by introducing a negative sign.
53
1.2.3
The Inequality Test for Concavity
We verify the convexity of the region below y = f (x) by checking line segments between points on
the boundary. The boundary in this case is the graph itself. The line segments are called secants.
Figure 1.17: A secant below the graph of y = 5 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
We take two general points (a, f(a)) and (
b, f(
b)) on y = f(x). We parametrize the secant between
them.
x(t) =(1 − t)a + t
b
y(t) =(1 − t)f(a) + tf(
b)
0 ≤ t ≤ 1
We can write an inequality to express the condition that secant lies below the graph.
Figure 1.18: A secant below the graph of a single-variable function
54
Theorem 1.19
A function is concave, if and only if for all a and
b in its domain and any 0 ≤ t ≤ 1 we have
(1 − t)f (a) + tf(
b)
| {z }
height of secant
≤ f((1 − t)a + t
b)
| {z }
height of y=f (x(t))
0 ≤ t ≤ 1
Remarks
This is an “if and only if” condition. That means it is both necessary and sufficient for establishing
concavity.
Only a function with a convex domain can meet this condition. Otherwise we cannot always
evaluate f((1 − t)a + t
b), because (1 − t)a + t
b may lie outside the domain.
The theorem follows directly from the definitions we have developed so far. Here is a representation
of our reasoning.
(1 − t)f(a) + tf(
b) ≤ f((1 − t)a + t
b)
for all a,
b and t
The secant between any a and
b
lies under the graph y = f(x)
The region below y = f(x) is convex
f is concave
Applying the same reasoning to the definitions of convexity and strict concavity/convexity gives the
following variants. Note that we cannot demand a strict inequality at t = 0 or t = 1 because the secant
will always intersect the graph y = f(x) at a and b.
55
1.2.3 The Inequality Test for Concavity
Variants of Theorem 1.19
1 A function is convex, if and only if for all a and
b in its domain and any 0 ≤ t ≤ 1 we have
(1 − t)f (a) + tf(
b) ≥ f((1 − t)a + t
b) 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
2 A function is strictly concave, if and only if for all a and
b in its domain and any 0 < t < 1 we
have
(1 − t)f (a) + tf(
b) < f((1 − t)a + t
b) 0 < t < 1
3 A function is strictly convex, if and only if for all a and
b in its domain and any 0 < t < 1 we have
(1 − t)f (a) + tf(
b) > f((1 − t)a + t
b) 0 < t < 1
1.2.4
Verifying Concavity with an Inequality
Verify that f (x) = 5 − x
2
is concave using the inequality condition.
Solution
Let a and b be any two real numbers. We need to show that for all t in [0, 1]:
(1 − t)f (a) + tf(b) ≤ f((1 − t)a + tb)
To prove this inequality, we first need the AM-GM (arithmetic mean-geometric mean) inequality from
algebra. Here it is.
(a − b)
2
≥ 0
a
2
− 2ab + b
2
≥ 0
a
2
+ b
2
≥ 2ab
We also note that for t in [0, 1], t(1 − t) ≥ 0. We now prove the required inequality, starting with
the right side.
56
f((1 − t)a + tb) = 5 − ((1 − t)a + tb)
2
definition of f
= 5 − (1 − t)
2
a
2
− 2t(1 − t)ab − t
2
b
2
distribute
≥ 5 − (1 − t)
2
a
2
− t(1 − t)(a
2
+ b
2
) − t
2
b
2
AM-GM
= 5 − (1 − t)
2
a
2
− t(1 − t)a
2
− t(1 − t)b
2
− t
2
b
2
distribute
= 5 − (1 − t)(t + 1 − t)a
2
− t(1 − t + t)b
2
factor
= 5 − (1 − t)a
2
− tb
2
simplify
= 5(1 − t) − (1 − t)a
2
+ 5t − tb
2
break up 5
= (1 − t)(5 − a
2
) + t(5 − b
2
) factor
= (1 − t)f (a) + tf(b) definition of f
The inequality condition is difficult to verify, even for this simple function. It is much worse for a
function involving a square root or an exponential. On the other hand. The inequality condition can be
convenient for abstract results.
Theorem 1.20
If f(x) and g(x) are both concave, then so is their sum: h(x) = f(x) + g(x)
Proof
Let a and
b be in the domain of h. Since the domain of h is the intersections of the domains of f and g,
h has a convex domain (Theorem 1.15). We know from the concavity of f and g that for all t in [0, 1]:
(1 − t)f (a) + tf(
b) ≤ f((1 − t)a + t
b)
(1 − t)g(a) + tg(
b) ≤ g((1 − t)a + t
b)
We now verify that the inequality holds for h:
(1 − t)h(a) + th(
b) = (1 − t)f (a) + (1 − t)g(a) + tf(
b) + tg(
b)
≤ f((1 − t)a + t
b) + g((1 − t)a + t
b)
= h((1 − t)a + t
b)
We conclude that h is concave.
57
1.2.4
Verifying Concavity with an Inequality
Main Idea
The inequality condition is sometimes useful at a theoretical level, but is painful to check for any but
the simplest specific functions. We will want a condition that is easier to check.
1.2.5
Concavity and Tangent Lines
We sought out the idea of concavity because it applies to functions of many variables. Some results
about concave functions are related to their derivatives. We will develop these tools in the setting
that is most comfortable and intuitive: one-variable functions. Once we have presented the theory of
optimization for multivariable functions, we will revisit and generalize these results.
Derivatives tell us about tangent lines, and tangent lines have an interesting relationship to convex
sets. If you draw a nonconvex set, you will be able to find a tangent line that crosses through the set.
A convex set, on the other hand, lies entirely on one side of any of its tangent lines. We will not try
to prove this for general sets, but we will prove it for the strictly convex region below the graph of a
strictly concave function.
Lemma 1.21
If f(x) is a strictly concave function that is differentiable at a, then the rest of the graph y = f(x) lies
below its tangent line at (a, f(a)).
y = f(x)
x
y
Figure 1.19: The graph of a strictly concave function and some of its tangent lines
This lemma describes the relationship between y = f(x) and a single tangent line. It can apply to
a function that is not differentiable at other points in its domain. If the function is differentiable on its
entire domain, we can produce a necessary and sufficient condition on the tangent lines.
58
Theorem 1.22
Let f(x) be a differentiable function on a convex domain. f (x) is strictly concave, if and only if the
graph y = f(x) lies below all of its tangent lines (except at the point on tangency).
The proofs of these results are somewhat technical. We will provide them after we have discussed
applications.
1.2.6
Concavity Conditions for a Maximizer
Our main use of concavity (for now) is to produce sufficient conditions for maximizers. The following
corollary follows from Lemma 1.21.
Corollary 1.23
If f(x) is a strictly concave function and f
′
(x
∗
) = 0, then x
∗
is the unique global maximizer of f.
Proof
The assumption that f
′
(x
∗
) = 0 tells us that f is differentiable at x
∗
, and the tangent line at x
∗
is
horizontal. By Lemma 1.21, the rest of the graph lies below this line. We conclude that x
∗
is the unique
global maximizer.
y = f(x)
(x
∗
, f(x
∗
))
x
y
Figure 1.20: The graph of y = f (x), which lies below the tangent line at x
∗
.
Like in the global second-order condition, we can also argue that x
∗
is the only critical point. If
there were another, then it would also be the unique global maximizer, which is nonsense.
59
1.2.7
A Second Derivative Test for Concavity
We would still like to have a better way to determine when a function is concave. In calculus, we
learn that the sign of the second derivative determines the concavity of a function. We are now in a
position to formally argue this result.
Theorem 1.24
If f is a function on a convex domain D ⊆ R and f
′′
(x) < 0 for all x in D, then f(x) is strictly
concave.
This means that a negative second derivative is a sufficient condition for strict concavity. Is it
necessary? No, consider the following.
Example
Consider f(x) = −x
4
. This function is strictly concave, but f
′′
(0) = 0, so the second derivative is not
always negative.
Putting this with Corollary 1.23 gives a string of conditions. Each is sufficient and neither is necessary,
so the implications can only be followed from left to right.
f
′′
(x) < 0
for all x
f strictly concave
Any x
∗
with f
′
(x
∗
) = 0
is a maximizer
We could claim that Corollary 1.23 and Theorem 1.24 have combined to give an alternate argument
for the global second-order condition. However, proving Theorem 1.24 without the global second-order
condition would require us to redo much of the work that went into that theorem. Instead we will use
the global second-order condition to keep our proof of Theorem 1.24 brief.
Proof
Our goal is to apply Theorem 1.22. Let a be a point in the domain of f. Since f
′′
(x) exists, f
′
(a)
exists. Let y = ℓ(x) be the tangent line to y = f(x) at a. Let g(x) = f(x) − ℓ(x). We know the
following about g:
g
′′
(x) = f
′′
(x) − ℓ
′′
(x) < 0 for all x, since ℓ
′′
(x) = 0.
g
′
(a) = f
′
(a) − ℓ
′
(a) = 0, since the derivative is the slope of the tangent line.
g(a) = 0, since ℓ(a) = f(a).
g and a satisfy the conditions of the global second-order condition. Thus a is the unique maximizer of
g, meaning g(x) < g(a) = 0 for all x = a. Thus y = f (x) lies below y = ℓ(x). This reasoning holds for
the tangent line at any value a. Theorem 1.22 tells us that f is strictly concave.
60
y = f(x)
y = g(x)
(a, f(a))
x
y
Figure 1.21: The graph of f(x), the tangent line at a, and their difference
1.2.8
Verifying Concavity with the Second Derivative
Verify that f (x) = 5 − e
x
is strictly concave.
Solution
f
′′
(x) = −e
x
< 0 for all x. Therefore by Theorem 1.24, f (x) is strictly concave.
Main Idea
The second derivative is an easier test of strict concavity than the inequality we used earlier, but it is
only a sufficient condition. It does not detect every strictly concave function.
1.2.9
Proving the Relationship Between Concavity and Tangent Lines
We will now present the formal reasoning of Lemma 1.21 and Theorem 1.22. We prove Lemma 1.21
by examining the difference between f(x) and its secants.
61
1.2.9 Proving the Relationship Between Concavity and Tangent Lines
Proof
Pick any b = a on the graph y = f (x). The tangent line to y = f (x) at (a, f (a)) has equation
y = f(a) + f
′
(a)(x −a). We will first show that (b, f(b)) does not lie above the tangent line by showing
that f(b) ≤ f(a) + f
′
(a)(b − a).
Consider the case that b > a. Denote the secant from (a, f(a)) to (b, f(b)) by the equation y = s(x)
and let g(x) = s(x) − f(x). The region below y = f(x) is convex, so y = s(x) is below y = f(x)
for any x between a and b. Their difference, g(x), is less than or equal to 0 on this interval. By the
contrapositive of Lemma 1.2 we know g
′
(a) cannot be greater than 0.
s
′
(a) is the slope of the secant:
f(b) − f(a)
b − a
. We substitute this into g
′
(a) ≤ 0 and solve.
g
′
(a) ≤ 0
s
′
(a) − f
′
(a) ≤ 0 (sum rule)
f(b) − f(a)
b − a
− f
′
(a) ≤ 0 (substitute)
f(b) − f(a) − f
′
(a)(b − a) ≤ 0 (b − a > 0)
f(b) ≤ f(a) + f
′
(a)(b − a)
We conclude that (b, f(b)) does not lie above the tangent line.
Now we must also show it does not lie on the tangent line. This is easiest with a contradiction
argument. Suppose some (b, f(b)) lies on the tangent line at a. Then consider any c between a and b.
(c, f(c)) also does not lie above tangent line by the argument we gave for b. However, the secant from
(a, f(a)) to (b, f(b)) is part of the tangent line, and (c, f(c)) lies above this by the definition of strict
concavity. This is a contradiction. Thus there is no (b, f(b)) that lies on the tangent line.
The case where b < a can be proved with a similar argument. We conclude that (b, f(b)) lies below
the tangent line to y = f(x) at (a, f(a)).
y = f(x)
y = s(x)
(a, f(a))
(b, f(b))
x
y
Figure 1.22: A tangent line and a secant to a concave function
Theorem 1.22 is an “if and only if” statement, so it requires two arguments to prove. We must
show that if f is strictly concave, then its graph lies below its tangent lines. We must also show that if
62
its graph lies below its tangent lines, then it is strictly concave. Fortunately, Lemma 1.21 has already
shown that if f (x) is strictly concave, then y = f(x) lies below the tangent line at a.
Proof
Suppose we know f is concave. For each a in the domain of f, Lemma 1.21 states that y = f (x) lies
below its tangent line at a. Since this holds for all a, y = f(x) lies below all of its tangent lines.
Now suppose that we know y = f (x) lies below all its tangent lines. We will verify that the region
under y = f (x) is strictly convex. Let a and b be any points in the domain of f . Let c be any point
between them. We know that (a, f(a)) and (b, f(b)) both lie below the tangent line to y = f(x) at
(c, f(c)). Thus the tangent line lies above the entire secant between (a, f(a)) and (b, f(b)). (c, f(c))
is on this tangent line, so (c, f(c)) is above the secant as well.
Since this argument holds for any such c, we conclude that the entire graph between a and b lies
above the secant. Since this is true for any choice of a and b, we conclude that the region below
y = f(x) is strictly convex and f (x) is a strictly concave function.
y = f(x)
(a, f(a))
(c, f(c))
(b, f(b))
x
y
Figure 1.23: A secant with both endpoints below the tangent line at (c, f(c))
1.2.10
Non-Strict Concavity and Convexity
We have primarily worked with strictly concave functions, because they give the strongest results
about maximizers. The properties of non-strict concavity and convexity give similar results. The results
for convexity are obtained by flipping the directions of inequalities. They are probably not worth mem-
orizing. On the other hand, economists frequently need to work with non-strictly concave functions. It
is worth understanding how utility maximization works for these.
Graphs of non-strictly concave functions can intersect their own tangent lines. For instance, a linear
function is concave, and its graph is identical to its tangent line. While the graph of a concave function
can intersect the tangent lines, it cannot go above them.
63
1.2.10 Non-Strict Concavity and Convexity
Variants of Lemma 1.21
Let f(x) be a function on a convex domain.
1 If f (x) is a concave function that is differentiable at a, then the graph y = f(x) has no points
above its tangent line at (a, f(a)).
2 If f(x) is a strictly convex function that is differentiable at a, then the rest of the graph y = f (x)
lies above its tangent line at (a, f(a)).
3 If f(x) is a convex function that is differentiable at a, then the graph y = f(x) has no points
below its tangent line at (a, f(a)).
The proof for non-strict concavity is identical to the proof for strict concavity, with the contradiction
argument omitted. The necessary and sufficient conditions are unsurprising.
Variants of Theorem 1.22
Let f(x) be a differentiable function on a convex domain.
1 f(x) is concave if and only if the graph y = f(x) has no points above any of its tangent lines.
2 f(x) is strictly convex if and only if the graph y = f(x) lies above each of its tangent lines (except
at the point of tangency).
3 f(x) is convex if and only if the graph y = f(x) has no points below any of its tangent lines.
These results can also be extended to well-behaved non-differentiable functions. For instance, what-
ever “tangent lines” you might reasonably add to the function in Figure 1.16 will not stray below the
graph. Rigorously defining tangent lines in these situations would require a detailed argument involving
limits, so we will not pursue it here.
The variants of Lemma 1.21 give rise to their own corollaries about maximizers and minimizers.
64
Variants of Corollary 1.23
1 If f(x) is a concave function and f
′
(x
∗
) = 0, then x
∗
is a global maximizer (but other points may
be as well).
2 If f(x) is a strictly convex function and f
′
(x
∗
) = 0, then x
∗
is the unique global minimizer of f.
3 If f(x) is a convex function and f
′
(x
∗
) = 0, then x
∗
is a global minimizer (but other points may
be as well).
(x
∗
, f(x
∗
))
x
1
x
2
Figure 1.24: A global but non-unique maximizer of a not strictly concave function
Finally, we can use the Variants of Theorem 1.22 to produce second-derivative tests for the other
forms of concavity and convexity.
Variants of Theorem 1.24
1 If f is a function on a convex domain D ⊂ R and f
′′
(x) ≤ 0 for all x in D, then f(x) is concave.
2 If f is a function on a convex domain D ⊂ R and f
′′
(x) > 0 for all x in D, then f(x) is strictly
convex.
3 If f is a function on a convex domain D ⊂ R and f
′′
(x) ≥ 0 for all x in D, then f(x) is convex.
In the non-strict case, the condition is necessary as well as sufficient.
65
1.2.10 Non-Strict Concavity and Convexity
Corollary 1.25
A twice differentiable function f(x) on a convex domain D is concave, if and only if f
′′
(x) ≤ 0 for all
x in D.
The sufficiency of f
′′
(x) ≤ 0 is found in the preceding variant. We establish necessity with a
contrapositive argument. It should look familiar to anyone who read our proof of Theorem 1.24. Notice
that it is making a local rather than a global argument.
Proof
Suppose f
′′
(x) ≤ 0 for all x. A variant of Theorem 1.24 tells us that f is concave.
On the other hand, suppose f
′′
(a) > 0 for some a. First note than since f
′′
(x) exists, f is a
differentiable function. Let y = ℓ(x) be the tangent line to y = f(x) at a. Consider g(x) = f(x)−ℓ(x).
We know the following about g:
g
′′
(a) = f
′′
(a) − ℓ
′′
(a) > 0, since ℓ
′′
(x) = 0.
g
′
(a) = f
′
(a) − ℓ
′
(a) = 0, since the derivative is the slope of the tangent line.
g(a) = 0, since f(a) = ℓ(a).
Thus by a variant of the (local) second-order condition, Theorem 1.5, a is a strict local minimizer of g,
meaning g(x) > g(a) = 0 for all x in a neighborhood of a. Thus y = f(x) lies above y = ℓ(x) in this
neighborhood. By a variant of Theorem 1.22, f is not concave.
The contrapositive of this argument is that if f is concave, then there is no a such that f
′′
(a) > 0.
Equivalently, f
′′
(x) ≤ 0 for all x.
This result means that we not only have a way to show that f(x) is concave, but also that it is not
concave. If f
′′
(a) > 0 for any a, then f is not a concave function.
1.2.11
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The definition of a (strictly) convex region (Definitions 1.12 and 1.14)
The definition of a (strictly) concave function (Definitions 1.16 and 1.17)
The inequality condition for concave functions (Theorem 1.19)
The tangent line condition for strictly concave functions (Theorem 1.22)
66
The sufficient condition for a maximizer using strict concavity (Corollary 1.23)
The second derivative tests for strictly concave and concave functions (Theorem 1.24 and Corollary
1.25)
Here is a summary of which conditions and statements from this section imply which others. Some
of these conditions only apply to differentiable, or even twice differentiable functions.
If f differentiable
(twice if relevant)
(1 − t)f (a) + tf(b) < f((1 − t)a + tb) (1 − t)f (a) + tf(b) ≤ f((1 − t)a + tb)
f strictly concave f concave
y = f(x) below tangent lines y = f(x) not above tangent lines
f
′′
(x) < 0 f
′′
(x) ≤ 0
critical points are unique maximizers critical points are maximizers
Figure 1.25: Conditions and applications of concave functions
67
1.3
Multivariable Optimization
Goals:
1 Apply the first- and second-order conditions to multivariable functions
2 Calculate the Hessian of a function
3 Understand the definition and significance of positive or negative definite matrices
4 Test whether a matrix is positive or negative definite
5 Show that a multivariable function is strictly concave
1.3.1
Parametrizations and Compositions
In this section we develop conditions to find maximizers of multivariable functions. Our optimization
methods so far rely on using rates of change to compare a potential maximizer to the points around it.
This is a more daunting task in the multivariable situation, because the comparison points can lie in any
direction. The function can be changing differently depending on which direction we travel. We avoid
the need to develop now tools from scratch by considering paths through a potential maximizer a.
A path through a is a function x(t) such that for some t
0
, x(t
0
) = a. We can think of the variable
t as representing time. Then x(t) represents the position on our path at time t.
A path breaks down into coordinate functions
x(t) = (x
1
(t), x
2
(t), . . . , x
n
(t))
If these are differentiable, the derivative
x
′
(t) = (x
′
1
(t), x
′
2
(t), . . . , x
′
n
(t))
represents the instantaneous rate of change in position of x with respect to t. It is tangent to the
path. In physics it is called the velocity vector.
68
Figure 1.26: A path and its tangent vector
We will study a function f(x) by studying compositions of the form f (x(t)). At each value of t, we
compute the corresponding position on the path and then evaluate f at that position. Geometrically,
this is the height of the graph y = f(x) above the curve x(t).
Figure 1.27: The graph of the composition f(x(t)) and the corresponding points in the original graph
y = f(x)
The derivative of f(x(t)) with respect to t is computed using the multivariable chain rule.
69
1.3.1
Parametrizations and Compositions
Theorem 0.18
Suppose f(x) is an continuously differentiable n-variable function. If x(t) is a differentiable path, then
the derivative of the composition f(x(t)) with respect to t is
df
dt
(t) = ∇f(x(t)) · x
′
(t)
or
df
dt
(t) =
n
X
i=1
f
i
(x(t))x
′
i
(t)
As with single-variable optimization, the sign of a derivative is important to our arguments. We can
obtain the sign of
df
dt
visually, using the following fact about dot products.
The Sign of the Dot Product
Given nonzero vectors u and v, the sign of u ·v is
positive if u and v make an acute angle
zero if u and v are orthogonal
negative if u and v make an obtuse angle
The angle between ∇f and x
′
(t) determines the sign of
df
dt
. This indicates whether f(x) increases
or decreases as x travels along the path x(t).
Figure 1.28: The tangent line to the graph y = f (x(t)) and the angle between ∇f (x(t)) and x
′
(t)
70
The value of
df
dt
is realized geometrically as the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the
composition function: y = f (x(t)).
Using compositions to find maximizers has two main consequences. The first is helpful. The second
creates difficulties.
1 f(x(t)) is a one-variable function. No matter the dimension of x, we can graph y = f(x(t)) in
the ty-plane and look for maximizers there.
2 One path will not cover the whole domain of f(x). We have to study many different paths x(t),
if we want to compare a potential maximizer to every other point in the domain.
We could study all paths in the domain of f, but that would be needlessly difficult. Instead we
restrict ourselves to paths that are lines. We will express these lines using the following notation.
Notation
Every line has a direction vector v = (v
1
, v
2
, . . . , v
n
). A line through a in the direction of v has the
equation
x(t) = a + tv
In a convex domain, any two values f (a) and f(
b) can be attained as values of the composition
f(a + tv), where v =
b −a. If we want to compare these values (for instance to argue that a is or is
not a maximizer), we compare f(a + 0v) and f (a + 1v).
Lemma 1.26
Suppose f (x) has a convex domain. A point a is a (local or global) maximizer, if and only if 0 is a
(local or global) maximizer of f(a + tv) for all direction vectors v.
This lemma tells us that a necessary condition for 0 to be a maximizer of f(a + tv) for all v is
a necessary condition for a to be a maximizer of f(x). Similarly, a sufficient condition for 0 to be a
maximizer of f(a + tv) for all v is a sufficient condition for a to be a maximizer of f(x).
The compositions f(a + tv) are realized as cross sections of the graph y = f(x) above the line
x(t) = a + tv.
71
1.3.1
Parametrizations and Compositions
Figure 1.29: The graph of a two-variable function and its cross section over a line
1.3.2
The Multivariable First-Order Condition
Our starting point for multivariable optimization is Lemma 1.26. a is a local maximizer or minimizer
of f (x), if and only if 0 is a local maximizer or minimizer of f(a + tv) for all vectors v. A condition on
the compositions f(a + tv) at t = 0 becomes a condition on a.
The first-order condition on f(a + tv) at t = 0 is
df
dt
(0) = 0
∇f(a + 0v) ·v = 0
∇f(a) ·v = 0
If a is a local maximizer, this must hold for all directions v. There is only one value of ∇f(a) that
satisfies this requirement.
Theorem 1.27 [The Multivariable First-Order Condition]
Suppose a lies in the domain of f (x). If a is a local maximizer or minimizer of f, then either ∇f(a) =
0
or ∇f (a) does not exist.
Like in the single variable case, we call points where ∇f (x) is
0 or undefined critical points. Finding
critical points is often the first step in a multivariable optimization.
72
Remark
If a lies at the boundary of the domain, then it may not be possible to travel in all directions v from
a and still evaluate f(a + tv). Fortunately, the first-order condition still holds. If ∇f(a) exists, then
the partial derivatives f
i
(a) exist. Thus f (a + he
i
) exists for h near 0. That means we can at least
travel in the standard basis directions from a without immediately leaving the domain of f(x). At a
local maximizer, the derivatives in these directions must be 0.
1.3.3
Computing Critical Points
What does the multivariable first-order condition say about f (x
1
, x
2
) = x
4
1
− 4x
1
x
2
+ x
4
2
?
Solution
We compute the gradient vector by taking the partial derivatvies with respect to x
1
and x
2
.
∇f(x) = (f
1
(x), f
2
(x))
= (4x
3
1
− 4x
2
, 4x
1
+ 4x
3
2
)
This is never undefined, so we solve for where it is (0, 0).
4x
3
1
− 4x
2
= 0 −4x
1
+ 4x
3
2
= 0
x
3
1
= x
2
(solve for x
2
)
−4x
1
+ 4x
9
1
= 0 (substitute)
4x
1
(x
8
− 1) = 0 (factor)
x
1
= 0 or ± 1
Subsituting back into x
3
1
= x
2
gives lets us solve for the corresponding values of x
2
. We obtain the
critical points (0, 0), (1, 1) (−1, −1). We conclude that no point other than (0, 0), (1, 1) (−1, −1) can
be a local maximizer or a local minimizer. We cannot conclude whether each of these points is a local
maximizer, a local minimzer or neither.
73
1.3.4
The Second Derivative of a Composition
We would also like to apply the local or global second-order condition along each line. In order to
do this, we need a way to compute
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv). The chain rules allows us to write the first derivative
as a dot product, or a sum. We will write it as a sum.
d
dt
f(a + tv) =
n
X
i=1
f
i
(a + tv)v
i
To obtain the second derivative we differentiate both sides. We differentiate each term of the sum. We
can treat each v
i
as a constant multiple, but f
i
(a + tv) is a composition of functions. The derivative
of each term will need the chain rule. We again write this as a sum, using a different index variable to
avoid ambiguity. The partial derivatives of f
i
are f
ij
.
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) =
d
dt
n
X
i=1
f
i
(a + tv)v
i
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) =
n
X
i=1
d
dt
(f
i
(a + tv)) v
i
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) =
n
X
i=1
n
X
j=1
f
ij
(a + tv)v
j
v
i
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) =
n
X
i=1
n
X
j=1
f
ij
(a + tv)v
j
v
i
We could use this formula to compute the second derivative of a particular composition f(a + tv). We
could test whether it is positive or negative. What we need, though, is to test the sign of the second
derivative for all direction vectors v. While this is possible in small dimensions, leaving the v
i
as variables,
the algebra quickly becomes daunting as n increases.
1.3.5
The Hessian Matrix
A theorem in linear algebra provides a shortcut. To do linear algebra, we need to write our vectors
like matrices.
74
Point Form and Column Form
When we want to emphasize that a vector x represents a point in R
n
, we write it as x = (x
1
, x
2
, . . . x
n
).
If we want to do matrix multiplication, we can write it as a column vector:
x =
x
1
x
2
.
.
.
x
n
The expression
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) =
n
X
i=1
n
X
j=1
f
ij
(a + tv)v
j
v
i
that we obtained can be written as a matrix product.
h
v
1
v
2
··· v
n
i
f
11
(a + tv) f
12
(a + tv) ··· f
1n
(a + tv)
f
21
(a + tv) f
22
(a + tv) ··· f
2n
(a + tv)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
f
n1
(a + tv) f
n2
(a + tv) ··· f
nn
(a + tv)
v
1
v
2
.
.
.
v
n
You may want to convince yourself that this algebra is correct with a 2 or 3 dimensional example.
What do we make of the individual factors in this product? The vectors on either end of this expression
are just v and its transpose (v flipped sideways). The matrix in the middle seems important. We should
have a name for it.
Definition 1.28
Given a function f(x) of n variables, the Hessian is a n ×n matrix function of x whose entries are the
second partial derivatives of f at x. Its formula is
Hf (x) =
f
11
(x) f
12
(x) ··· f
1n
(x)
f
21
(x) f
22
(x) ··· f
2n
(x)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
f
n1
(x) f
n2
(x) ··· f
nn
(x)
Notice that for well-behaved functions, f
ij
= f
ji
. This means the Hessian will be a symmetric
matrix.
75
1.3.6
Negative Definite Matrices
Our Hessian notation allows us to write
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) = v
T
Hf (a + tv)v. The following vocabulary
captures exactly which Hessian matrices will produce a negative (or positive) second derivative in all
directions.
Definition 1.29
A symmetric n × n matrix M is negative definite, if for all nonzero n-vectors v,
v
T
Mv < 0.
It is positive definite, if for all nonzero n-vectors v,
v
T
Mv > 0.
Remark
We may think, based on positive and negative numbers, that most matrices are either positive definite
or negative definite. In fact, a randomly chosen matrix is most likely to be neither. For most matrices,
v
T
Mv is positive for some v and negative for others.
Connecting this back to our original goal, we can apply the definition of negative definite to describe
the sign of the second derivatives of the compositions f(a + tv). For a critical point a, we can draw the
following conclusions.
If Hf(a) is negative definite, then
d
2
f
dt
2
(0) < 0 for all v. Since
df
dt
(0) = 0, t = 0 satisfies the
second-order condition for all v. We conclude a is a strict local maximizer of f.
If Hf (x) is negative definite for all x, then
d
2
f
dt
2
(t) < 0 for all t and all v. Since
df
dt
(0) = 0, t = 0
satisfies the global second-order condition for all v. We conclude a is the unique global maximizer
of f.
Without an efficient way to test whether a matrix is negative definite, we have only managed to
restate the problem. We can say that we are checking whether Hf(a) is negative definite, or we can
say that we are checking whether
n
X
i=1
n
X
j=1
f
ij
(a)v
j
v
i
< 0 for all v
1
, v
2
, . . . , v
n
. The computations are
the same, and they are daunting.
Fortunately, there is an easier way to show that a matrix is negative or positive definite.
76
Theorem 1.30
A symmetric n ×n matrix M is negative definite if the upper left square minors M
i
have determinants
that satisfy the alternating condition:
(−1)
i
|M
i
| > 0 for all 1 ≤ i ≤ n
Example
For a 4 × 4 matrix, here are the M
i
and what we would check to apply Theorem 1.30.
· · · ·
· · · ·
· · · ·
· · · ·
|M
1
| < 0
|M
2
| > 0
|M
3
| < 0
|M
4
| > 0
Variant of Theorem 1.30
A n × n matrix M is positive definite if the upper left square minors have positive determinants.
1.3.7
The Multivariable Second-Order Conditions
Now that we have a check for negative definite and positive definite matrices, it is worth stating
the results of our investigation as theorems. These are our most important sufficient conditions for a
maximizer of a multi-variable function.
77
1.3.7 The Multivariable Second-Order Conditions
Theorem 1.31 [The Multivariable Second-Order Condition]
Given a function f(x) with a it its domain. If
∇f(a) =
0
Hf (a) is negative definite
then a is a strict local maximizer of f.
Theorem 1.32 [The Multivariable Global Second-Order Condition]
Suppose f is a function with a convex domain D and x
∗
is in D. If
∇f(x
∗
) =
0
Hf (x) is negative definite for all x ∈ D.
then x
∗
is the only critical point of f and the unique global maximizer.
We can summarize the reasoning behind the global second-order condition as follows:
Hf (x) is negative definite
for all x
d
2
dt
2
f(x
∗
+ tv) < 0 for
all directions v
∇f(x
∗
) =
0
df
dt
(0) = 0 along
all lines x
∗
+ tv
0 is the global maximizer
of f(x
∗
+ tv) for all directions v
x
∗
is the global maximizer of f(x)
These theorems have variants for minimizers.
78
Variants of Theorems 1.31 and 1.32
Suppose f is a function with domain D and a is in D.
1 If
∇f(a) =
0
Hf (a) is positive definite
then a is a strict local minimizer of f.
2 If D is convex and
∇f(a) =
0
Hf (x) is positive definite for all x in D
then a is the only critical point of f and the unique global minimizer.
Minor determinants with the wrong sign produce the wrong sign of v
T
Mv for some v. This in turn
means the wrong second derivative in the direction of v. This relationship is formalized in the following
necessary condition.
Corollary 1.33
Let f(x) be a twice-differentiable function on a convex domain D. Let M = Hf(a).
1 If a is a local maximizer, then
(−1)
i
|M
i
| ≥ 0 for all 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
2 If a is local minimizer, then
|M
i
| ≥ 0 for all 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
1.3.8
Applying the Multivariable Second-Order Condition
Let f(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) = 3
3
√
x
1
x
3
+ln x
2
−
x
1
4
−
x
2
5
−2x
3
+15 on the domain D = {(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) : x
1
, x
2
, x
3
>
0}. Find the critical point of f. What does the Global Second-Order Condition say about this point?
79
1.3.8
Applying the Multivariable Second-Order Condition
Solution
We take all three partial derivatives of f. Since they are always defined on D, the gradient vector exists,
so the critical points must be where they all equal 0.
3
√
x
3
3
p
x
2
1
−
1
4
= 0
1
x
2
−
1
5
= 0
3
√
x
1
3
p
x
2
3
− 2 = 0
3
√
x
3
3
p
x
2
1
=
1
4
1
x
2
=
1
5
3
√
x
1
3
p
x
2
3
= 2
3
√
x
3
=
3
p
x
2
1
4
x
2
= 5
16
3
√
x
1
3
p
x
4
1
= 2
16
x
1
= 2
8 = x
1
3
√
x
3
=
3
√
8
2
4
x
3
= 1
The critical point is (8, 5, 1). We compute the Hessian by taking the second partial derivatives of f .
Hf (x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) =
−
2
3
√
x
3
3
3
√
x
5
1
0
1
3
3
√
x
2
1
x
2
3
0 −
1
x
2
2
0
1
3
3
√
x
2
1
x
2
3
0 −
2
3
√
x
1
3
3
√
x
5
3
To check that Hf(x) is negative definite for all x, we apply Theorem 1.30. There are three determinants
to calculate.
(−1)
1
|M
1
| = (−1)
−
2
3
√
x
3
3
3
p
x
5
1
=
2
3
√
x
3
3
3
p
x
5
1
(−1)
2
|M
2
| = (1)
−
2
3
√
x
3
3
3
√
x
5
1
0
0 −
1
x
2
2
=
2
3
√
x
3
3x
2
2
3
p
x
5
1
(−1)
3
|M
3
| = −|Hf(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
)|
= −
−
2
3
√
x
3
3
3
p
x
5
1
!
−
1
x
2
2
0
0 −
2
3
√
x
1
3
3
√
x
5
3
− 0 +
1
3
3
p
x
2
1
x
2
3
!
0 −
1
x
2
2
1
3
3
√
x
2
1
x
2
3
0
!
=
4
9x
2
2
3
p
x
4
1
x
4
3
−
1
9x
2
2
3
p
x
4
1
x
4
3
=
1
3x
2
2
3
p
x
4
1
x
4
3
80
Since x
1
, x
2
and x
3
are all positive in this domain, so are these three quantities. We conclude that
Hf (x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) is negative definite. By the global second-order condition, we conclude that (8, 5, 1) is
the only critical point (which we already knew from the FOC) and that it is the unique maximizer of f .
1.3.9
The Hessian and Concavity
Linear compositions play well with secants. The height of the secant above each t is the same
whether we are looking in ty-plane or in R
n+1
. We can state this relationship formally as a lemma.
Lemma 1.34
If y = s(t) is a secant of y = f (a + tv), then
x(t) = a + tv
y(t) = s(t)
is a secant of y = f(x).
Figure 1.30: A secant of y = f (a + tv) and the corresponding secant of y = f(x) over x(t) = a + tv
We determine whether a function f(x) is concave by whether its graph lies above its secant lines.
Every such secant line lies above some line a + tv. This secant stays below the graph y = f(x), if and
only if the corresponding secant stays below y = f(a + tv).
81
1.3.9 The Hessian and Concavity
Lemma 1.35
A function f(x) on a convex domain is concave, if and only if f(a + tv) is concave for every a in the
domain of f and every direction vector v.
f(a + tv) is concave
for all lines a + tv
y = f(a + tv) lies above
its secants (t, s(t))
for all lines a + tv
y = f(x) lies above the secants
x(t) = a + tv
y(t) = s(t)
for all lines a + tv
f(x) is concave
Def 1.16
Cor 1.34
Def 1.16
Variants of Lemma 1.35
Suppose f(x) is a function on a convex domain
1 f(x) is strictly concave if and only if f(x(t)) is strictly concave for every line x(t) in the domain
of f.
2 f(x) is convex if and only if f (x(t)) is convex for every line x(t) in the domain of f.
3 f(x) is strictly convex if and only if f(x(t)) is strictly convex for every line x(t) in the domain of
f.
The result of this lemma is that any test for concavity or convexity of the single-variable compositions
f(a + tv) becomes a test for the concavity of f(x) itself. If every composition passes, then f does.
If at least one composition fails, then so does f. Our natural next step is to take our theorems from
single-variable concavity and apply them to these compositions,
Theorem 1.22 showed that the graphs single-variable strictly concave functions lie below their tangent
lines. Tangent lines to a composition have the same heights as the tangent lines of the multivariable
graph. We can formalize this relationship with a lemma.
Lemma 1.36
If the line y = ℓ(t) is tangent to y = f (a + tv), then
x(t) = a + tv
y(t) = ℓ(t)
is a tangent line to y = f(x).
82
Figure 1.31: A tangent line of y = f (a + tv) and the corresponding tangent line of y = f(x) over
x(t) = a + tv
We can check whether tangent lines lie above or below a graph y = f(x) by checking whether
tangent lines lie above or below the compositions y = f(a + tv).
Theorem 1.37 [Multivariable version of Theorem 1.22]
A differentiable function f on a convex domain is strictly concave if and only if the graph y = f(x) lies
below each of its tangent lines (except at the point of tangency).
y = f(x) lies below
its tangent lines.
y = f(a + tv) lies below all
its tangent lines for any a + tv.
f(a + tv) is strictly concave
for any a + tv
f(x) is strictly concave
Cor 1.36
Thm 1.22
Lem 1.35
This theorem allows us to update our corollary on critical points of strictly concave functions.
Corollary 1.38 [Multivariable Version of Corollary 1.23]
If x
∗
is a critical point of a differentiable, strictly concave function f(x), then it is the only critical
point and is the unique global maximizer.
83
1.3.9 The Hessian and Concavity
We can also use compositions to update our theorems about second derivatives and concavity.
Theorem 1.39 [Multivariable Version of Theorem 1.24]
If f is a function on a convex domain D ⊂ R
n
and
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) < 0 for all lines a + tv in D, then
f(x) is strictly concave.
Corollary 1.40 [Multivariable Version of Corollary 1.25]
A twice differentiable function f(x) on a convex domain D is concave, if and only if
d
2
dt
2
f(a + tv) ≤ 0
on all lines a + tv in D.
As we have seen, the sign of these second derivatives depends on the Hessian matrix. This gives us
our most useful computational test for the concavity of a multivariable function.
Theorem 1.41
Let f(x) be a twice-differentiable function on a convex domain D. If Hf (x) is negative definite for all
x in D, then f is strictly concave.
This means that concavity plays the same role in multivariable optimization as in single-variable
optimization. For some functions, we can identify a maximizer by concavity even though they do not
satisfy the second-order condition. On the other hand, the most convenient way to identify concave
functions is still the second derivatives.
84
1.3.10
Negative Semi-Definite Matrices
Changing the condition f
′′
(x) < 0 to f
′′
(x) ≤ 0 was a natural approach to generalizing Theorem
1.24. As a bonus, we obtained Corollary 1.25, which is both a necessary and sufficient condition
for concavity. The same is possible for multivariable functions, but the condition on the Hessian is
surprisingly complicated.
We might expect the multivariable analogue to be that (−1)
i
|M
i
| ≥ 0 for each i. Consider a
function like f(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) = x
2
3
. In the x
3
direction this function is a parabola which is strictly convex.
Unfortunately, its Hessian passes our expected test for concavity.
Hf (x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) =
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 2
.
This has |M
i
| = 0 for each i. The determinant cannot detect the curvature of later variables, if the
earlier variables produce a row of zeroes in Hf(x). Our expected test is not a correct test. To avoid
this problem, we must consider different orders of variables. Which orders? All of them.
Theorem 1.42
Let f(x) be a twice-differentiable function on a convex domain D ⊆ R
n
. let σ be any reordering of
the coordinates of R
n
. Let σM = Hf(σx).
1 f is concave if and only if
(−1)
i
|σM
i
| ≥ 0 for all σ and all 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
If so, then v
T
Hf (x)v ≤ 0 for all nonzero v. We say Hf(x) is negative semidefinite
2 f is convex if and only if
|σM
i
| ≥ 0 for all σ and all 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
If so, then v
T
Hf (x)v ≥ 0 for all nonzero v. We say Hf(x) is positive semidefinite
To give a sense of the amount of computation required, we will consider an example. Suppose
Hf (x) =
0 2 5
2 −6 0
5 0 −3
.
We check the determinants
|M
1
| = |0| ≤ 0 |M
2
| =
0 2
2 −6
≥ 0 |M
3
| =
0 2 5
2 −6 0
5 0 −3
≤ 0
85
1.3.10 Negative Semi-Definite Matrices
But then we must do the same for all possible reorderings of x
1
, x
2
and x
3
meaning we must check
the same three minors for each of
0 2 5
2 −6 0
5 0 −3
original Hf(x)
−6 2 0
2 0 5
0 5 −3
σ switches x
1
and x
2
−3 0 5
0 −6 2
5 2 0
σ switches x
1
and x
3
0 5 2
5 −3 0
2 0 −6
σ switches x
2
and x
3
−6 0 2
0 −3 5
2 5 0
σ : (x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) 7→ (x
2
, x
3
, x
1
)
−3 5 0
5 0 2
0 2 −6
σ : (x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) 7→ (x
3
, x
1
, x
2
)
This is a significant amount of work, though linear algebra knowledge lets us avoid some. For
instance, all the |σM
3
| are equal. As the dimension increases, there are more symmetries to exploit.
With these shortcuts, the main driver in complexity is computing the n×n determinant, not the number
of re-ordered smaller determinants. Checking whether a matrix is negative semidefinite takes about twice
as many operations as checking that it is negative definite.
1.3.11
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The multivariable first-order condition (Theorem 1.27)
The Hessian matrix (Definition 1.28)
Positive and negative definite (Definition 1.29)
The determinant test for a negative definite matrix (Theorem 1.30)
The multivariable global second-order condition (Theorem 1.32)
The Hessian test for strict concavity (Theorem 1.41)
Here is a summary of which conditions and statements from this section imply which others.
86
Hf (x) negative
definite for all x
Hf (x) negative semi-
definite for all x
Hf (a) negative
definite
f is strictly concave
f is concave
a is the
unique global max
and only critical point
a is a
global max
a is a strict
local max
∇f(a) =
0
∇f(a) =
0
Hf (a) negative
semidefinite
Thm 1.41
Thm 1.42
SOC
GSOC
GSOC
FOC
FOC
Thm 1.33
Thm 1.33
Figure 1.32: Relationships between the conditions of multivariable optimization
87
1.3.11
Section Summary
88
Chapter 2
Constrained Optimization
2.1
Equality Constraints
Goals:
1 Use logic to reason about the effects of a constraint on optimization problems.
2 Visually identify maximizers and minimizers using level sets.
3 Compute the maximizer subject to an equality constraint using the Lagrangian.
4 Use paths and the chain rule to understand the reasoning behind the Lagrangian.
2.1.1
Constrained Optimization
Given a function f (x) with domain D, we have so far performed unconstrained optimization, trying
to compute
max
x∈D
f(x) or min
x∈D
f(x)
In a constrained optimization problem, we restrict our attention to a subset of the domain. For some
subset S ⊆ D, we want to know
max
x∈S
f(x) or min
x∈S
f(x)
A maximizer in S is a vector a such that f(a) ≥ f(x) for all x ∈ S. Geometrically, it is the highest
point on the part of the graph y = f(x) that lies above S. In constrained optimization, the function we
are maximizing is called a objective function. The set S is called the feasible set.
The notation above is flexible enough to apply to many different kinds of constraints, producing
many different kinds of subset S.
Figure 2.1: The graph y = f (x) over a two-dimensional subregion S
90
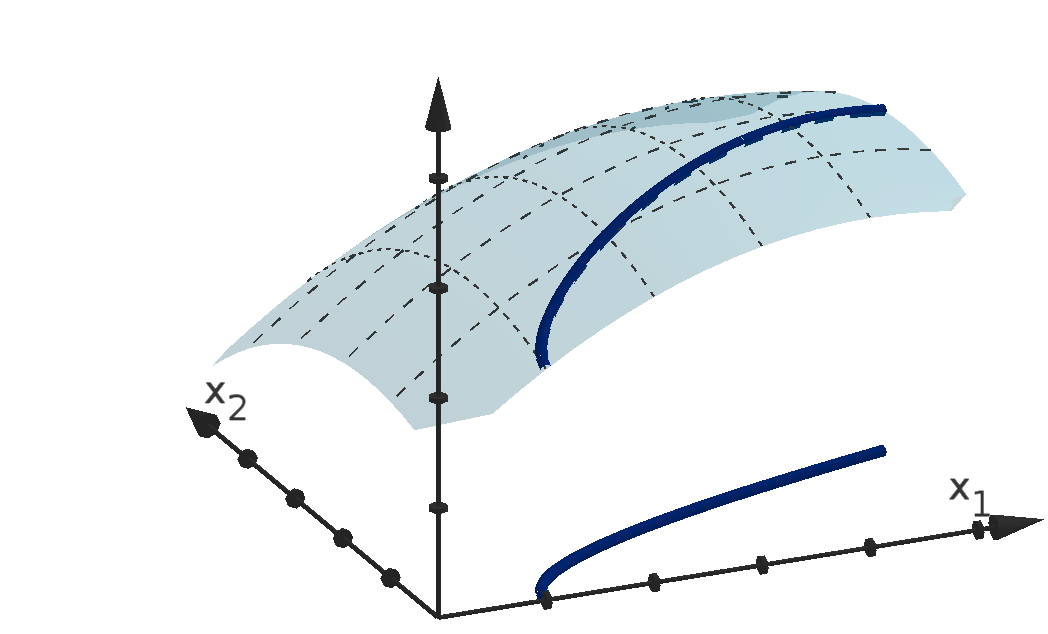
Figure 2.2: The graph y = f (x) over a curve S
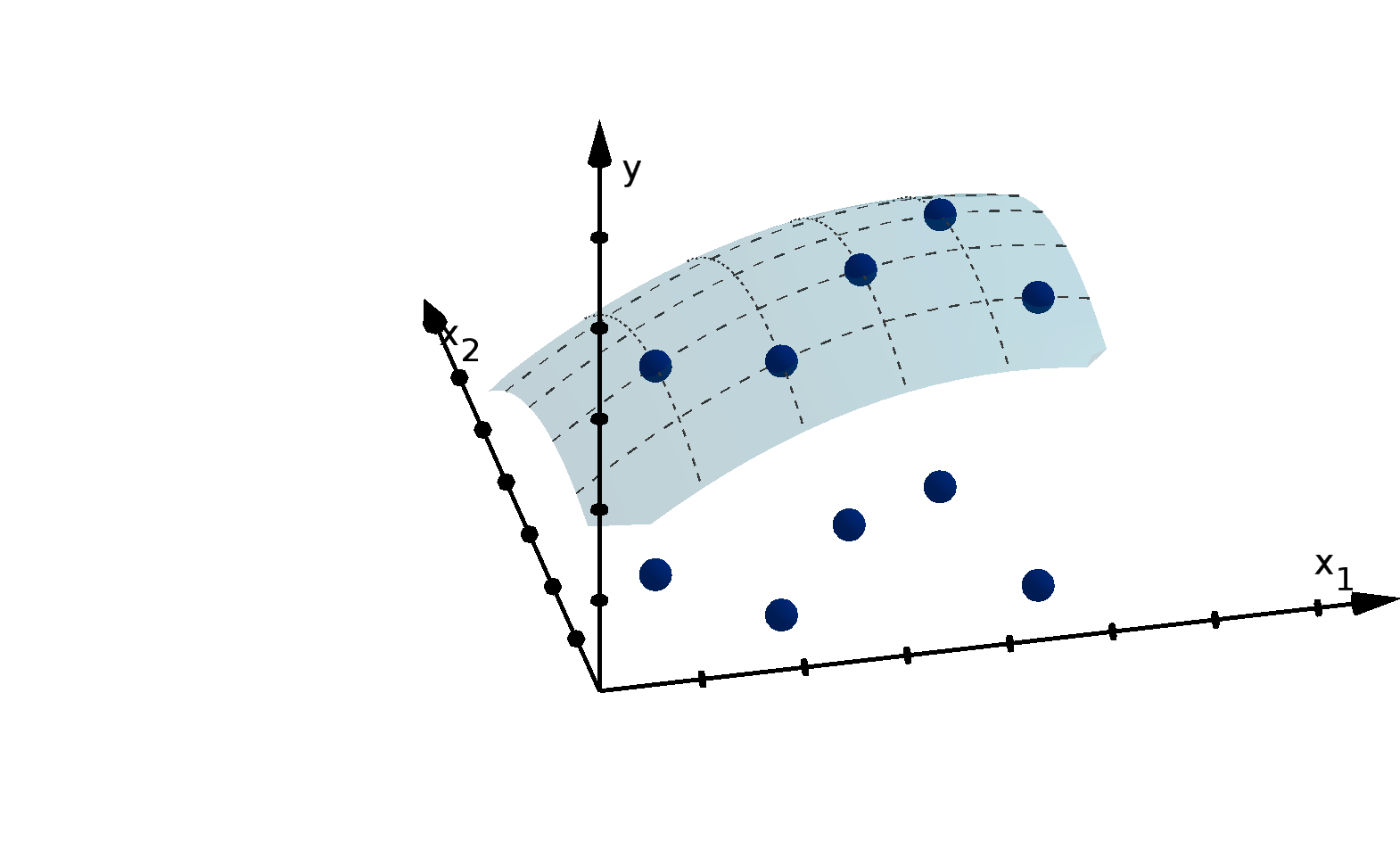
Figure 2.3: The graph y = f (x) over a finite set S
Constraints arise naturally in economics. Here are two familiar examples recast in the abstract form
that we just introduced.
Example
What is the maximum utility one can attain given a budget constraint?
max
x∈S
u(x)
where S is the set of purchases one can afford.
91
2.1.1
Constrained Optimization
Example
How cheaply can a firm produce 500 units?
min
x∈S
c(x)
Here, S is the set of inputs that produce 500 units.
Without knowing the specific nature of the constraint, we can still deduce some basic facts about
constrained optimization using logic and set theory.
Tightening a constraint can only reduce the value of the maximum.
Lemma 2.1
For a function f(x) with domain D and a two subsets T ⊆ S ⊆ D,
max
x∈T
f(x) ≤ max
x∈S
f(x)
Sometimes finding a maximum over S is computationally easier than finding a maximum over T . If
we are lucky, the maximizer of f(x) in S might also lie in T . We can apply the following reasoning.
Corollary 2.2
Suppose x
∗
is a maximizer of f(x) over a set S. If T ⊆ S and x
∗
∈ T then x
∗
is also a maximizer of
f(x) over T and
max
x∈T
f(x) = max
x∈S
f(x)
Remark
Why do we make the distinction between the domain and a subset? If we want to constrain x to values
in S, we could redefine f to have a domain of S. This is generally not a good idea. We will want to
use the derivatives of f to solve constrained optimization problems. For example, we may need to know
lim
h→0
f(a + he
i
) − f (a)
h
If a is on the boundary of S and we declare everything outside S to no longer be in the domain of
f, then we may not be able to evaluate f(a + he
i
) in a neighborhood of h = 0.
92
2.1.2
Equality Constraints and Level Sets
The first type of constraint we will examine is an equality constraint.
Definition 2.3
An equality constraint is a constraint of the form g(x) = 0. With such a constraint we are solving
max
x∈D
f(x) subject to g(x) = 0 or
max
x∈S
f(x) where S = {x ∈ D : g(x) = 0}
To contrast g with the objective function f, we call it a constraint function.
Remark
We can rewrite any equation in the variables of x to have the form g(x) = 0. For example:
x
2
=
16
x
1
=⇒ 16 − x
1
x
2
= 0
An equality constraint is an equation, a condition that a point can satisfy or fail to satisfy. In order
to maximize f among such points, we want to be able to visualize the entire set of points that satisfy
the constraint. Mathematics has a term for this set.
Definition 2.4
Given a function g(x) a level set of g is the set of points that, for some number c, satisfy g(x) = c.
Example
Given the function g(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
, here are four different level sets of g:
{(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
x
2
= 9}
{(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
x
2
= 17.32}
{(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
x
2
= 0}
{(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
x
2
= −4}
93
2.1.2
Equality Constraints and Level Sets
Remark
Commonly, people refer to a level set by its defining equation, rather than using set notation. Thus “the
level set x
2
1
+ x
2
2
= 16” refers to the set {(x
1
, x
2
) : x
2
1
+ x
2
2
= 16}.
Level sets have several applications in economics you may be familiar with:
Example
If we are choosing to buy quantities x
1
and x
2
of goods priced at p
1
and p
2
, then the goods we can buy
with a budget constraint I is the level set (often called a budget line):
p
1
x
1
+ p
2
x
2
= I
Example
Given a utility function u(x
1
, x
2
), the level set u(x
1
, x
2
) = c is called an indifference curve. The
chooser will be equally happy with any point on the curve.
For a two-variable function, a level set is the intersection of the graph y = g(x
1
, x
2
) with a horizontal
plane y = c. These are often curves, so we call them level curves.

Figure 2.4: The level curves x
1
x
2
= c
Notice that x
1
x
2
= c is not always a curve. When c = 0, the level set is the x
1
- and x
2
-axes. At
the origin, this is two curves (lines) intersecting.
94
For a three-variable function, the level sets are called level surfaces because for most values of c,
they are 2-dimensional.
Figure 2.5: The level surfaces x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ x
2
3
= c
Notice x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ x
2
3
= 0 is not a surface, it is a point. x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ x
2
3
= −5 is the empty set.
It can be difficult to determine the shape and structure of a level set. A powerful mathematical
theorem can tell us when to expect good behavior.
Corollary 2.5 [Corollary to the Implicit Function Theorem]
Let g(x) be a continuously differentiable function at a. If a lies on the level set g(x) = c and ∇g(a) =
0,
then the level set g(x) = c is a (n −1)-dimensional shape in some neighborhood of a. Specifically, it is
the graph of a differentiable function of n − 1 of the variables of R
n
.
This means that for smooth functions we can generally expect the level set to be a space of one
dimension lower than the domain, except at the occasional points where ∇g(x) =
0. We can see this
in our previous examples.
For g(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
the nonempty level sets are curves, except for x
1
x
2
= 0. Even x
1
x
2
= 0
looks like a curve in any neighborhood that does not include (0, 0).
For g(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ x
2
3
the nonempty level sets are surfaces (spheres), except for
x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ x
2
3
= 0
We will give an argument for this corollary once we have seen the implicit function theorem in chapter
4.
95
2.1.3
Finding the Maximizer and Minimizer Graphically
The level set g(x) = 0 is obviously important to a constrained optimization problem. We can also
use level sets to understand the shape of the objective function. Level sets have the advantage that
they live in R
n
, not R
n+1
, making them easier to draw than the graph y = f(x),
Consider the objective function f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
subject to x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0.
a
What are the level curves of f (x
1
, x
2
)?
b
How can we use a diagram of the level curves of f to argue that (1, −3) is not a local maximizer
or minimizer?
c
Where do the local maximizer(s) and local minimizer(s) of f on x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0 appear to lie?
d
Are any of the local maximizers and minimizers also global maximizers or minimizer?
Solution
a
The level sets have the form x
2
1
+x
2
2
= c these are circles centered at the origin, with higher values
the farther from the origin we go.
b
(1, −3) lies on the level set x
2
1
+x
2
2
= 10. We can see from a sketch that the curve x
2
1
−x
2
−4 = 0
passes through this level set from higher values to lower values. Thus (1, −3) is not a local
maximizer or minimizer.
c
(0, −4) appears to be a local maximizer, because x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0 meets the x
2
1
+ x
2
2
= 16 and
travels back to smaller-values in both directions. There also appear to be local minimizers in the
third and fourth quadrant where x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0 touches a smallest level set and then travels
back to larger-valued level sets.
d
There is no global maximizer. As we travel upwards in x
2
1
−x
2
−4 = 0, we cross larger and larger
valued level sets. There is no upper bound to the values of f(x
1
, x
2
) that we can attain on the
constraint. On the other hand, the local minimizers are global minimizers. The only smaller-valued
level curves are inside that circle, and the constraint does not enter that region.
96
c = 1
c =?
c = 10
c = 16
c = 25
(1, −3)
global min global min
local max
x
1
x
2
Figure 2.6: Level curves of x
2
1
+ x
2
2
and the level curve x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0
Figure 2.7: The graph of y = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
over the constraint x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0
When the level set g(x) = 0 crosses a level set f(x) = c at a, this usually means that it intersects
97
2.1.3
Finding the Maximizer and Minimizer Graphically
both larger-valued and smaller-valued level sets on either side. If it does, then a cannot be a local
maximizer or minimizer of f on the constraint.
Main Idea
We expect to find local maximizer and minimizers only where the level set g(x) = 0 is tangent to a level
set of f.
We can base our intuition on the following narrative: g(x) = 0 crosses higher and higher-valued level
sets of f as it approaches f(x) = c. When it reaches f (x) = c, rather than crossing it to even higher
values, it brushes against it (tangency) and backs away toward lower-valued level sets.
This does not describe every possible version of tangency. The curve x
2
− x
3
1
= 0 is tangent to
the level set x
2
= 0, but still crosses onto both sides. Furthermore level sets can behave unpredictably
when their gradient vector is
0. A rigorous argument for a maximizer using tangency generally needs to
appeal to the algebraic properties of f (x) and g(x) in some way.
2.1.4
The Lagrangian
Looking for tangency is a valuable method for approximating the maximizer, but we cannot expect it
to be precise enough to determine exact coordinates. For an exact position, we need a set of equations
to solve. These equations take the form of a necessary condition for a maximizer subject to an equality
constraint. We first form a new function from both the objective function and the constraint.
Definition 2.6
Given an n-variable objective function f(x) and a constraint g(x) = 0, the Lagrangian is an (n + 1)-
variable function of the x
i
and λ (lambda). Its equation is
L(x, λ) = f(x) + λg(x)
98
Theorem 2.7
Let f(x) and g(x) be continuously differentiable functions. If a is a local maximizer or minimizer of
f(x) subject to the constraint g(x) = 0, then either
1 there is some number λ such that (a, λ) satisfies the first-order condition of L or
2 ∇g(a) = 0.
We will call these the points that satisfy these conditions critical points or stationary points of
the constrained optimization problem. The value of λ is called a Lagrange multiplier.
Remark
Notice that this theorem is a necessary condition for a maximizer or minimizer, not a sufficient one.
2.1.5
Using the Lagrangian
We expect that the objective function f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
has a minimizer on the constraint
x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0 somewhere in the fourth quadrant. Find it.
Solution
Letting g(x
1
, x
2
) = x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 we have the Lagrangian:
L(x
1
, x
2
, λ) = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ λ(x
2
1
− x
2
− 4)
∇g(x
1
, x
2
) = (2x
1
, −1). This is never
0, so any minimizer must satisfy the first-order condition of L.
99
2.1.5
Using the Lagrangian
We set the partial derivatives equal to 0 and solve.
∂L
∂x
1
= 0
∂L
∂x
2
= 0
∂L
∂λ
= 0
2x
1
+ 2x
1
λ = 0 2x
2
− λ = 0 x
2
1
− x
2
− 4 = 0
2x
1
(1 + λ) = 0
if x
1
= 0 0
2
− x
2
− 4 = 0
x
2
= −4
if λ = −1 2x
2
+ 1 = 0
x
2
= −
1
2
x
2
1
+
1
2
− 4 = 0
x
1
= ±
r
7
2
The only possible local maximizers and minimizer are (0, −4),
q
7
2
, −
1
2
and
−
q
7
2
, −
1
2
. Since we
are looking for a minimizer in the fourth quadrant, it must be
q
7
2
, −
1
2
.
2.1.6
Proving the First-Order Condition of the Lagrangian
The partial derivatives of the Lagrangian are
∂L
∂x
i
=f
i
(x) + λg
i
(x)
∂L
∂λ
=g(x)
Any solution (a, λ) to the first-order condition on L satisfies
1 f
i
(a) = −λg
i
(a) for all i, so ∇f (a) = −λ∇g(a).
2 g(a) = 0, so a lies on the constraint.
The necessity of 2 is easy to explain. If a does not lie on the constraint, then it cannot be a
maximizer or minimizer subject to that constraint.
In order to understand 1 , we need to investigate the relationship between gradient vectors and
level sets. Like with multivariable unconstrained optimization, we use compositions over paths to study
maximizers on constraints. We need to alter our approach in three important ways.
100
We are only comparing f(a) to f(
b) for other
b in the level set g(x) = 0. Thus we only consider
paths x(t) that stay in the level set.
Unless the level set is linear, we cannot assume the paths x(t) are straight lines. They likely need
to curve to stay in the level set.
The tangent vectors x
′
(t) generally cannot point in all directions. Most directions of travel would
cause the path to leave the level set.
Now we examine the composition f(x(t)) where x(t) is a path in the level set g(x) = 0.
Figure 2.8: The composition f(x
1
(t), x
2
(t)) for a path (x
1
(t), x
2
(t)) in the level set g(x
1
, x
2
) = 0 and
its realization as the heights of y = f(x
1
, x
2
)
If a is a local maximizer or minimizer of f(x) among the points on g(x) = 0 then it must be a local
maximizer or minimizer of the composition f(x(t)) for all paths x(t) in the level set g(x) = 0. This
means the t-value corresponding to a (we will call it t
0
) must satisfy the first-order condition of f(x(t)).
To compute the derivative of the composition, we apply the chain rule.
df
dt
(t
0
) = 0 (first-order condition)
∇f(x(t
0
)) · x
′
(t
0
) = 0 (chain rule)
∇f(a) · x
′
(t
0
) = 0
In the unconstrained case, ∇f(a) · v = 0 for all v allowed us to conclude that ∇f(a) = 0. Our
conclusion cannot be so restrictive here. x(t) must be a path in the level set. We are thus only
considering vectors x
′
(t
0
) that are tangent to the level set at a.
To make a conclusion about ∇f (a), we appeal to the geometric properties of the dot product. ∇f (a)
and x
′
(t
0
) must be orthogonal for all paths in the level set that pass through a at t
0
. We introduce the
following vocabulary to describe this relationship between ∇f(a) and the level set.
101
2.1.6 Proving the First-Order Condition of the Lagrangian
Definition 2.8
A vector v is normal to a set at a, if v orthogonal to all tangent vectors of that set at a.
To avoid having to mention it as a separate case, we consider
0 to be orthogonal to every vector.
Lemma 2.9
If a is a local maximizer or local minimizer of a continuously differentiable function f(x) subject to
g(x) = 0, then ∇f(a) is normal to the level set g(x) = 0.
This gives us a good characterization of the gradient of the objective function at a local maximizer
or minimizer. We can now visually rule out a potential maximizer, if its gradient does not point in the
right direction. We now need to connect this to our computational tool. The Lagrangian compares ∇f
to ∇g. What can we say about ∇g?
Again, we consider a path x(t) in the level set g(x) = 0. This time we study the composition g(x(t)).
If you think carefully about what we have done, you will notice that this is a silly composition. We can
evaluate this composition at any value of t, and we will always get 0 (make sure you see why).
We can now apply the chain rule to g(x(t)), the zero function. This time the derivative is zero
because we are differentiating a constant function.
dg
dt
(t
0
) = ∇g(x(t
0
)) · x
′
(t
0
)
0 = ∇g(a) · x
′
(t
0
)
We conclude that ∇g(x(t)) is orthogonal to x
′
(t) for all paths x(t) in the level set g(x) = 0.
Remark
This argument did not rely on a being any special point on the level set. Nor did it matter that the level
set had value 0. Any level set g(x) = c will have this relationship to the gradient, since the composition
will still be a constant function.
The result of this argument is the one of the most important geometric facts about gradient vectors.
We will use it over and over again.
102
Theorem 2.10
If g is a continuously differentiable function, and g(a) = c, then ∇g(a) normal to the level set g(x) = c.
In R
2
, this means that ∇g(a) points either 90
◦
degrees clockwise or 90
◦
counterclockwise from
x
′
(t
0
).
Figure 2.9: Two possible ∇g(x(a)) orthogonal to x
′
(t
0
)
In the case of a level surface, there are many paths through a. In order to be normal to the level
set, there are only two possible directions for ∇g(a).
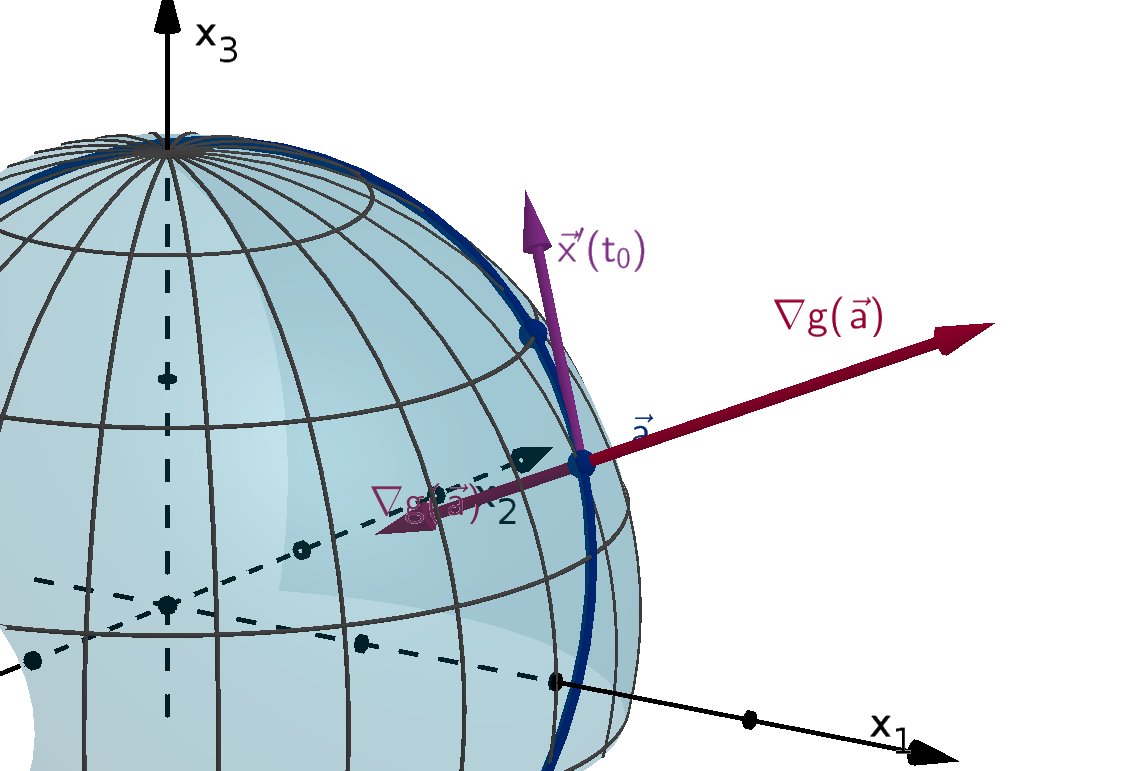
Figure 2.10: Two possible ∇g(a) orthogonal to all possible tangent vectors x
′
(t
0
) in the level set
g(x) = 0.
We can use Corollary 2.5 to generalize this to an n-variable function. The level set is an (n − 1)
dimensional graph in n-space (as long as the gradient is nonzero). It has two normal directions, pointing
in opposite directions.
We can summarize what we have learned about the gradients of f and g as follows.
103
2.1.6 Proving the First-Order Condition of the Lagrangian
∇f(a) is normal to the level set g(x) = 0 at a local maximizer a.
∇g(x) is normal to the level set g(x) = 0 at all points on the level set.
If ∇g(a) =
0, then there are only two normal directions to the level set g(x) = 0, pointing in
opposite directions.
Vectors in the same or opposite directions are parallel. Algebraically, they are scalar multiples of each
other. We conclude that at any local maximizer or local minimizer, f(a) = −λ∇g(x) for some λ. This
is exactly what the first-order condition of the Lagrangian requires.
Figure 2.11: Parallel vectors ∇f(x) and ∇g(x) at a minimizer of f(x) subject to g(x) = 0
This line of reasoning is complex. It is also important. We will revisit and generalize it later. Here
is a reminder of the steps of our argument.
a is a local maximizer
of f(x) on g(x) = 0
t
0
is a local maximizer of f(x(t))
on any path x(t) through a in g(x) = 0
d
dt
f(x(t)) = 0 at t
0
∇f(a) · x
′
(t
0
) = 0
∇f(a) is normal to g(x) = 0
∇g(x) is always
normal to g(x) = 0
There are only two
normal directions to g(x) = 0
∇f(a) and ∇g(a) are parallel
∇f(x) = −λ∇g(a) for some λ
(λ,a) satisfies the FOC
of the Lagrangian
FOC
chain rule
104
2.1.7
The Tangency Method
This argument also validates the tangency method of locating a maximizer. Theorem 2.10 applies
to f as well as to g. ∇f(a) is normal to the level set f(x) = c where c = f(a). At a local maximizer,
where ∇f (a) and ∇g(a) are parallel, it must follow that the level sets g(x) = 0 and f (x) = c have the
same normal directions. This implies that g(x) = 0 and f (x) = c are tangent to each other.
Corollary 2.11
Suppose both ∇f(a) and ∇g(a) exist and are not
0. If a is a maximizer of f(x) subject to g(x) = 0,
then the level sets of f and g that contain a are tangent to each other at a.
Figure 2.12: Parallel ∇f and ∇g and their tangent level curves at a local maximizer
2.1.8
Section Summary
The important definitions and results from this section were
The effect of strengthening a constraint (Lemma 2.1)
The definition of a level set (Definition 2.4)
The Lagrangian (Definition 2.6)
The first-order condition of the Lagrangian (Theorem 2.7)
The direction of the gradient (Theorem 2.10)
The tangency of level curves (Corollary 2.11)
105
2.2
Inequality Constraints
Goals:
1 Identify maximizers subject to inequality constraints.
2 Use the Lagrange multiplier to identify points that cannot be maximizers or minimizers.
3 Recognize several notations for complementary slackness.
2.2.1
Inequality Constraints and Upper Level Sets
Definition 2.12
An inequality constraint is a constraint of the form g(x) ≥ 0. With such a constraint we are solving
max
x∈D
f(x) subject to g(x) ≥ 0 or
max
x∈S
f(x) where S = {x ∈ D : g(x) ≥ 0}
Remark
Like with an equality constraint, just about any non-strict inequality can be rewritten in the form
g(x) ≥ 0. Even an expression g(x) ≤ k is equivalent to k − g(x) ≥ 0.
Here are two prototypical applications of inequality constraints in economics.
Example
If you have a budget to buy two types of goods, but you are not required to spend all of it, then your
constraint is
I − p
1
x
1
− p
2
x
2
≥ 0
106
Example
If x
1
denotes a physical quantity then it is often appropriate to assume
x
1
≥ 0.
Inequalities like these define the familiar shape of the budget set.
I/p
2
I/p
1
x
1
x
2
Figure 2.13: The region constrained by I − p
1
x
1
− p
2
x
2
≥ 0, x
1
≥ 0 and x
2
≥ 0
The set of points that satisfies an inequality constraint generally lies on one side of the level set
g(x) = 0. Graphically, it is the subset of the domain over which the graph y = g(x) is above the plane
y = 0. We therefore adopt the following terminology.
Definition 2.13
Given a multivariate function f(x) a upper level set of f is the set of points that, for some number
c, satisfy f(x) ≥ c. The points that satisfy f (x) ≤ c are a lower level set.
107
2.2.1
Inequality Constraints and Upper Level Sets
Figure 2.14: The upper level set where y = f (x) lies above y = c
We can use the chain rule to determine whether a path travels into an upper level set or lower level
set.
Lemma 2.14
Suppose a lies in the level set f(x) = c, ∇f(a) =
0, and x(t) is a path that passes through a at t
0
.
If x
′
(t
0
) makes an acute angle with ∇f(a), then immediately after t
0
, x(t) travels into the upper
level set f(x) ≥ c.
If x
′
(t
0
) makes an obtuse angle with ∇f(a), then immediately after t
0
, x(t) travels into the lower
level set f(x) ≤ c.
Figure 2.15: The gradient vector, the upper level set and the lower level set of f
108
The gradient vector makes an acute angle with itself, so we obtain the following characterization
immediately.
Corollary 2.15
Suppose f(a) = c. If ∇f(a) =
0, then ∇f(a) points into the upper level set f(x) ≥ c.
We can visualize the reasoning behind Lemma 2.14. Here is the case where the angle is acute.
x
′
(t
0
) makes an acute
angle with ∇f(a)
∇f(a) · x
′
(t
0
) > 0
df
dt
(t
0
) > 0
In some nbhd of t
0
,
f(x(t)) > f(x(t
0
)) for t > t
0
.
In some nbhd of t
0
,
x(t) is in the upper level set
f(x) ≥ c for t > t
0
.
chain rule
Lem 1.2
2.2.2
Binding and Nonbinding Constraints
We already have the tools to impose necessary conditions on a maximizer subject to an inequality
constraint. Our strategy is to consider two cases and to apply the appropriate first-order conditions to
each one.
Suppose a is a local maximizer of f(x) subject to g(x) ≥ 0.
1 If g(a) = 0 we say that the constraint is binding.
a
x
1
x
2
Figure 2.16: A maximizer a on g(x) = 0
109
2.2.2
Binding and Nonbinding Constraints
If a is a maximizer subject to g(x) ≥ 0, then it also maximizes f subject to g(x) = 0. It must
satisfy the FOC of the Lagrangian.
2 If g(a) > 0 then the constraint is non-binding.
x
′
(t)
a
x
1
x
2
Figure 2.17: A maximizer a in g(x) > 0 and some directions of travel through a
We can travel in all directions x
′
(t) through a without immediately leaving the upper level set.
To ensure ∇f(a) · x
′
(t) = 0, ∇f(a) must be the zero vector.
At an interior point, the boundary is not relevant to local measurements like the derivative. The
conditions of optimization are those of an unconstrained optimization, as if the constraint did not exist.
2.2.3
The Sign of λ at a Maximizer
If the inequality constraint g(x) = 0 binds at local maximizer a, then a will satisfy the first-order
condition of the Lagrangian
L(x, λ) = f(x) + λg(x)
What can we say about the λ that goes with a?
Any path in the direction of ∇f(a) points toward higher values of f. If ∇f(a) points into the region
g(x) ≥ 0, then a cannot be a local maximizer subject to g(x) ≥ 0. This can be tested by the sign of λ.
∇g
∇f
a
x
1
x
2
Figure 2.18: A non-maximizing critical point a on g(x) = 0
110
The first-order condition of the Lagrangian requires that ∇f (a) = −λ∇g(a). ∇g(a) points into the
upper level set g(x) ≥ 0. If λ is negative then ∇f (a) points into this set as well.
Lemma 2.16
Suppose that (a, λ) satisfies the first-order condition of the Lagrangian of f subject to g(x) = 0. If a
is a local maximizer of f(x) subject to g(x) ≥ 0, then either
1 λ ≥ 0 or
2 ∇g(a) =
0
Understanding the intuition behind this result is probably more important than knowing a formal
proof. Still, here is a proof. Like the argument we have already given, it is a proof of the contrapositive.
Proof
If ∇g(a) =
0 then the lemma is satisfied. We will consider the case where ∇g(a) =
0 and λ < 0. We
will show that a is not a local maximizer.
Consider the line through a in the direction of ∇g(a). Its equation is x(t) = a + t∇g(a) and
x
′
(0) = ∇g(a). By Lemma 2.14, since ∇g(a) · x
′
(0) = ∇g(a) · ∇g(a) > 0, this line travels into the
upper level set g(x) ≥ 0 at t = 0.
What happens to values of f along this line? Consider the composition f(a+ t∇g(a)). Its derivative
at t = 0 is
df
dt
(0) = ∇f(a) · ∇g(a)
= (−λ∇g(a)) · ∇g(a)
= −λ(∇g(a) · ∇g(a))
> 0
By Lemma 1.2, there is a neighborhood of 0 where for t > 0, f(x(t)) > f(x(0)) = f(a). We have seen
that these points lie in the upper level set, so a cannot be a maximizer of f(x) subject to g(x) ≥ 0.
Since a cannot be a maximizer when λ < 0, we conclude that if a is a maximizer, then λ ≥ 0.
Remark
Showing that a is not a maximizer required us to compare it to points in the upper level set g(x) ≥ 0.
This reasoning does not work when maximizing subject to an equality constraint. The line we used does
not lie in g(x) = 0. We can thus pout no restriction on λ when maximizing subject to g(x) = 0. λ can
be positive, negative, or zero at a maximizer.
111
2.2.4
Complementary Slackness
Whenever we have an inequality constraint, there are two cases to check: it can be binding or non-
binding. We could keep track of this manually, but there is an easier way to organize our search. We
can use the Lagrangian
L(x, λ) = f(x) + λg(x)
to test for both the binding and non-binding case.
g(x) ≥ 0 binding:
A maximizer a satisfies the first-order
condition of the Lagrangian.
This automatically checks g(a) = 0.
We can check that λ ≥ 0.
g(x) ≥ 0 nonbinding:
We can set λ = 0
Now a maximizer a satisfies the first-
order condition of L(x, λ) = f(x).
We can check that g(a) ≥ 0.
There is an interesting algebraic symmetry between the role of λ and g(a). The following definition
allows us to combine both these cases into one statement.
Definition 2.17
A point satisfies two non-strict inequalities with complementary slackness, if at least one of them
holds with equality.
We can cover both cases of an inequality constraint by demanding that g(x) ≥ 0 and λ ≥ 0 hold
with complementary slackness. Here are a few different ways to denote complementary slackness.
Notations for Complementary Slackness
1 g(x) ≥ 0 and λ ≥ 0 hold with complementary slackness
2 g(x) ≥ 0, λ ≥ 0 and λg(x) = 0
3 λ ≥ 0 and g(x) ≥ 0, = 0 if λ > 0
112
2.2.5
Conditions for a Maximizer Subject to an Inequality Constraint
With complementary slackness in hand, we can write a necessary condition for a maximizer on an
inequality constraint. This theorem is written using notation 2 , but we could rewrite it with one of the
other notations.
Theorem 2.18
Let f(x) and g(x) be continuously differentiable functions. If a is a local maximizer of f(x) subject to
the constraint g(x) ≥ 0, then one of the following must be true
1 there is some number λ such that (a, λ) satisfies
∂L
∂x
i
(a, λ) = 0 for all i
g(a) ≥ 0, λ ≥ 0, and λg(a) = 0.
2 g(a) = 0 and ∇g(a) = 0.
2.2.6
Opimization Subject to an Inequality Constraint
Find the maximizer of f(x
1
, x
2
) = 10 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
subject to 3x
1
+ 4x
2
≥ 25.
Solution
First we write our constraint in the correct form. g(x
1
, x
2
) = 3x
1
+4x
2
−25 ≥ 0. Note that ∇g(x
1
, x
2
)
is never
0, so any critical point must satisfy our complementary slackness conditions. The Lagrangian is
L(x
1
, x
2
, λ) = 10 − x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ λ(3x
1
+ 4x
2
− 25)
The conditions are
∂L
∂x
1
= 0
∂L
∂x
2
= 0
λ ≥ 0 3x
1
+ 4x
2
− 25 ≥ 0 λ(3x
1
+ 4x
2
− 25) = 0
113
2.2.6
Opimization Subject to an Inequality Constraint
First consider the λ = 0 case. The constraint is nonbinding. We solve the equations then check the
inequality.
∂L
∂x
1
= 0
∂L
∂x
2
= 0 λ = 0
−2x
1
+ 3λ = 0 −2x
2
+ 4λ = 0
−2x
1
= 0 −2x
2
= 0
x
1
= 0 x
2
= 0
check 3(0) + 4(0) − 25 ≥ 0
The only critical point we found failed the check. There is no maximizer where the constraint is
nonbinding. Now consider the g(x) = 0 case.
∂L
∂x
1
= 0
∂L
∂x
2
= 0 g(x) = 0
−2x
1
+ 3λ = 0 −2x
2
+ 4λ = 0 3x
1
+ 4x
2
− 25 = 0
x
1
=
3
2
λ x
2
= 2λ
9
2
λ + 8λ − 25 = 0
25
2
λ = 25
λ = 2
x
1
=
3
2
(2) x
2
= 2(2)
x
1
= 3 x
2
= 4
check λ ≥ 0
2 ≥ 0
The point (3, 4, 2) passes all of these conditions. We conclude that (3, 4) is the only possible maximizer.
Since this is not a sufficient condition, we cannot conclude (3, 4) is a maximizer. There may be no
maximizer at all.
Main Idea
To solve for the maximizer over an inequality constraint
1 Pick a case from complementary slackness
2 Set up and solve the system of equations
3 Check whether the solutions satisfy the inequalities
4 Repeat for the other case from complementary slackness
114
2.2.7
Section Summary
The important definitions and results from this section were
The notation of an inequality constraint (Definition 2.12)
The definition of an upper or lower level set (Definition 2.13)
The sign of λ at a maximizer subject to an inequality constraint (Lemma 2.16)
Complementary slackness (Definition 2.17)
Conditions for a maximizer on an inequality constraint (Theorem 2.18)
115
2.3
The Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
Goals:
1 Solve for maximizers on multiple constraints using the Kuhn-Tucker conditions
2 Recognize what each case of the Kuhn-Tucker conditions is checking
2.3.1
Multiple Equality Constraints
In economics, it is easy to imagine a firm is constrained by more than one equation:
A budget for capital and labor
Availability of labor or other inputs
A government regulation
You can’t purchase or produce a negative amount
What if we want to maximize an n-variable function f(x) subject to more than one equality con-
straint?
g
1
(x) = g
2
(x) = ··· = g
m
(x) = 0
The feasible set, is the intersection of the level sets g
j
(x) = 0. We have seen that a single level set
is usually one dimension less than the space it lies in. The intersection of m level sets will usually be an
(n − m)-dimensional shape.
Notation
The g
i
are different functions, not partial derivatives of g. Whenever we have multiple g’s around, we
will need to write our partial derivatives using ∂ notation, for instance
∂
∂x
2
g
3
(x) not g
3
2
(x)
116
Figure 2.19: Two level sets intersecting at a pair of (one-dimensional) curves
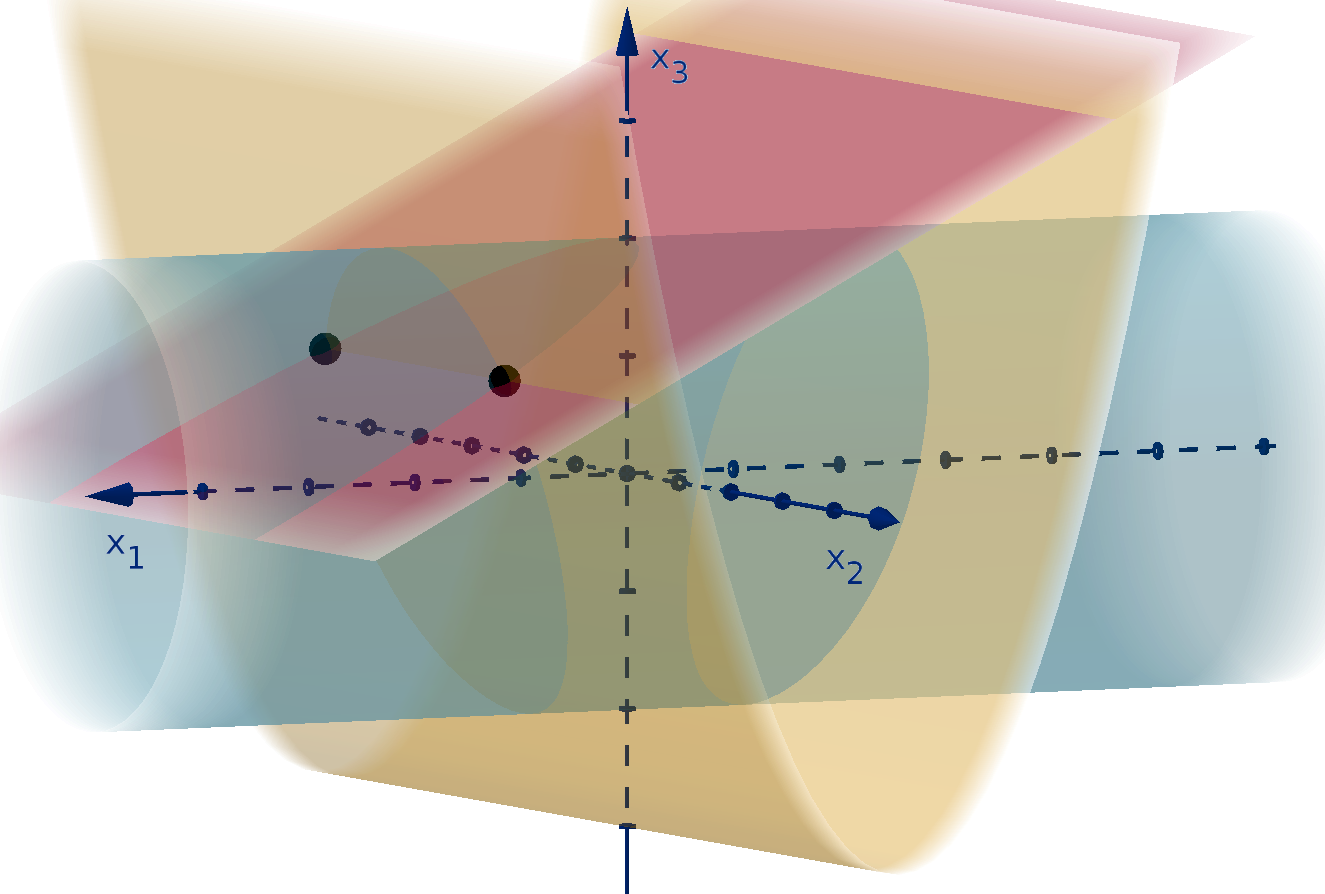
Figure 2.20: Three level sets intersecting at a pair of (zero-dimensional) points
Like with a single constraint, there are exceptions. Also like a single constraint, these exceptions
rely on the inadequacy of the gradient vector(s). The following definition come from linear algebra. A
corollary of the multivariable implicit function theorem characterizes the intersection of the level sets.
Definition 2.19
Vectors v
1
, v
2
, . . .v
m
are linearly dependent if there are constants k
j
, not all 0, such that
m
X
j=1
k
j
v
j
=
0
If no such k
j
exist then they are linearly independent
117
2.3.1 Multiple Equality Constraints
Equivalently, vectors are linearly dependent, if one of them is a linear combination of the others.
Corollary 2.20
Let g
1
(x), g
2
(x), . . . g
m
(x) be a continuously differentiable functions at a. If a lies on the level sets
g
j
(x) = c
j
and the ∇g
j
(a) are linearly independent, then the intersection of the level sets g
j
(x) = c
j
is
a (n −m)-dimensional shape in some neighborhood of a. Specifically, it is the graph of m differentiable
functions on R
n−m
.
Remark
Any set containing the zero vector is linearly dependent. Thus this corollary agrees with our criterion
for a single constraint. If the vector ∇g(a) =
0, then it is linearly dependent.
Two vectors are linearly dependent if they are parallel. With parallel gradients, the intersection of
m level sets can have fewer than (n − m) dimensions.
Figure 2.21: Two level sets with parallel gradients intersecting at a point
Parallel gradients can also occur when the level sets overlap, in this case the intersection can have
more than (n − m) dimensions.
Figure 2.22: Two (overlapping) level sets whose intersection is a plane
118
Three vectors are linearly dependent if they are coplanar. Coplanar gradient vectors can also lead to
intersections of unexpected dimension.
Figure 2.23: Three level sets with coplanar gradients intersecting on a line
Main Idea
Each additional equality constraint reduces the dimension of the feasible set by 1, unless its gradient
vector is a linear combination of the existing gradient vectors.
2.3.2
The Lagrangian for Multiple Equality Constraints
For multiple constraints, we write a Lagrangian that uses all of the constraints. We need a different
variable λ for each one. The first-order condition of this Lagrangian is a necessary condition for a local
maximizer or local minimizer.
Definition 2.21
Given the problem of maximizing an n-variable objective function f(x) subject to constraints g
j
(x) = 0
for 1 ≤ j ≤ m, the Lagrangian is a function of the n components of x and m variables
λ = (λ
1
, . . . , λ
m
).
L(x,
λ) = f(x) +
m
X
j=1
λ
j
g
j
(x)
119
2.3.2 The Lagrangian for Multiple Equality Constraints
Theorem 2.22
If a is a local maximizer or local minimizer of f(x) subject to constraints g
j
(x) = 0, all continuously
differentiable at a, then either
1 (a,
λ) satisfies the first-order condition of L for some
λ or
2 The ∇g
j
(a) are linearly dependent
Notation
When developing the theory, we write our constraint functions and our Lagrange multipliers using a
common letter and an index variable
g
1
(x), g
2
(x), . . . λ
1
, λ
2
, . . .
This makes it easier to generalize to any number of constraints, because can use Σ notation in the
Lagrangian. For a small number of constraints, using an index is inconvenient. Economists often use
different letters for each constraint and multiplier.
g(x), h(x), . . . λ, µ, . . .
2.3.3
A Multi-Constraint Optimization
Find the maximizer of f(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) = 3x
2
on the constraints x
2
1
+x
2
3
−50 = 0 and x
1
+x
2
+x
3
= 0.
Solution
The Lagrangian is
L(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
, λ
1
, λ
2
) = 3x
2
+ λ
1
(x
2
1
+ x
2
3
− 50) + λ
2
(x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
)
The first-order condition is
120
∂L
∂x
1
= 0
∂L
∂x
2
= 0
∂L
∂x
3
= 0
∂L
∂λ
1
= 0
∂L
∂λ
2
= 0
2λ
1
x
1
+ λ
2
= 0 3 + λ
2
= 0 2λ
1
x
3
+ λ
2
= 0 x
2
1
+ x
2
3
− 50 = 0 x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
= 0
λ
2
= −3
x
1
=
3
2λ
1
x
3
=
3
2λ
1
x
1
= x
3
x
2
1
+ x
2
1
− 50 = 0
x
1
= ±5
±5 = x
3
±5 + x
2
± 5 = 0
x
2
= ∓10
We conclude that (±5, ∓10, ±5). The value f(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) = 3x
2
is larger when x
2
= 10. We conclude
that no point besides (−5, 10, 5) can be the maximizer of f on these constraints. Because this is not a
sufficient condition, we cannot be sure that this is the maximizer. It may be that no maximizer exists
at all.
We can visualize the maximizer of f(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) = 3x
2
by looking for the point in the level sets that
is farthest in the x
2
direction. It appears that such a point exists at (−5, 10, −5).
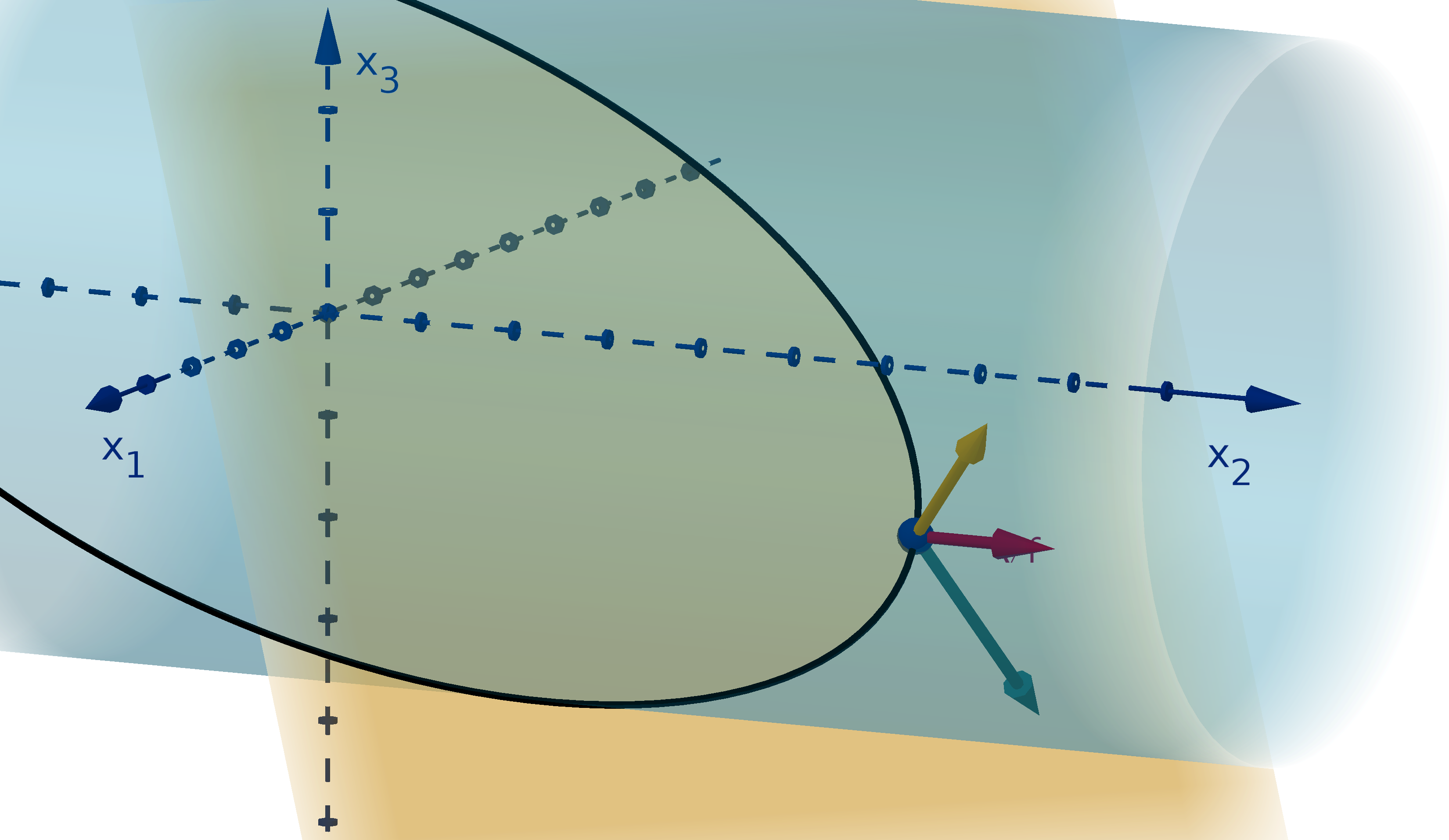
Figure 2.24: The gradients of x
2
1
+ x
2
3
− 50, x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
= 0, and f(x) = 3x
2
at the maximizer
121
2.3.4
The Reasoning for the Multi-Constraint Lagrangian
The partial derivatives of the Lagrangian are
L
x
i
=
∂f
∂x
i
(x) +
m
X
j=1
λ
j
∂g
j
∂x
i
(x)
L
λ
j
=g
j
(x)
Any solution (a,
λ) to the first-order condition on L satisfies
f
x
i
(a) = −
m
X
j=1
λ
j
∂g
j
∂x
i
(a) for all i, so ∇f (a) = −
P
λ
j
∇g
j
(a).
g
j
(a) = 0 for all j so a lies on all the constraints.
We can examine the relationship between the gradients using the same procedure we used for a
single constraint. We take a path x(t) through a at t
0
. We assume that x(t) lies in the feasible set.
This means it lies in all of the level sets g
j
(x) = 0.
If a is a local maximizer or minimizer of f(x) on the feasible set then it must be a local maximizer
or minimizer of the composition f(x(t)) for all paths x(t) in the feasible set. This means the t-value
corresponding to a (we will call it t
0
) must satisfy the first-order condition of f(x(t)). The derivative
calculation should be familiar:
0 =
df
dt
(t
0
)
0 = ∇f(x(t
0
)) · x
′
(t
0
)
0 = ∇f(a) · x
′
(t
0
)
Thus ∇f(a) is normal to the feasible set.
When we had a single constraint, we argued that there were two opposite normal directions to the
feasible set, and ∇g(a) pointed in one of them. This relied on the fact that our feasible set was a level
set and had dimension (n −1). If we assume that the ∇g
j
(a) are linearly independent, then the feasible
set has dimension (n − m) at a.
There is an entire m-dimensional space of vectors normal to the feasible set at a. If a is a maximizer,
∇f(a) must be a vector in this space.
122
Figure 2.25: The gradient vector of the objective function and the normal plane of the feasible set at a
local maximizer of the composition: f(x(t))
The feasible set lies in each level set g
j
(x) = 0. The gradient of each g
j
is normal its level set. We
can put together what we know about the gradients and the shape of the feasible set.
f(a) is normal to the feasible set at a local maximizer a.
Each ∇g
j
(x) is normal to the feasible set at all points in the level set.
If the ∇g
j
(a) are linearly independent, then the normal space is m-dimensional.
m independent vectors in a m-dimensional space must span the space. We conclude that ∇f(a) is a
linear combination of the ∇g
j
(a). This is what the first-order condition of the Lagrangian requires.
Example
If a is a maximizer of a three-variable function subject to two equality constraints, then ∇f (a) must lie
in the normal plane, which is spanned by ∇g
1
(a) and ∇g
2
(a).
123
2.3.4 The Reasoning for the Multi-Constraint Lagrangian
Figure 2.26: Two gradients spanning the normal plane of the feasible set
2.3.5
An Optimization with Dependent Gradients
When the gradients of the g
j
(x) are linearly dependent, the feasible set may not have the expected
dimension of (n − m). Even if it does, the gradient vectors need not span the normal space. In this
case, calculus arguments cannot rule out a point from being a maximizer. Here is an example where
insisting upon the first-order condition of the Lagrangian would incorrectly rule out a maximizer.
Consider the smooth function f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
and the constraints x
2
+ 2 = 0 and x
2
− (x
1
−
3)
2
+ 2 = 0. If we attempt to apply the first-order condition we obtain the following.
The constraints intersect only at (3, −2).
At (3, −2) the gradients are
∇g
1
(3, −2) = (0, 1) ∇g
2
(3, −2) = (0, 1) ∇f(3, −2) = (6, −4).
∇f cannot be written as a linear combination of ∇g
1
and ∇g
2
Even though it doesn’t satisfy the first-order condition, (3, −2) must be the maximizer (and mini-
mizer), since it is the only point that satisfies both constraints.
124
Figure 2.27: (3, 2) is a maximizer, but ∇f cannot be written λ
1
∇g
1
+ λ
2
∇g
2
.
If we count dimensions, the feasible set is a 0-dimensional subspace of R
n
. Its normal space is
2 − 0 = 2-dimensional, which suggests that ∇f(3, −2) can be any vector in R
2
. This sounds bizarre
but actually makes sense. (3, −2) is the entire feasible set. It must be a maximizer, no matter what
∇f(3, −2) is. The exception for dependent gradients in Theorem 2.22 exists to avoid ruling out a
maximizer in a situation like this.
2.3.6
The Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
The Kuhn-Tucker conditions are a robust set of necessary conditions for constrained optimizations
with inequality constraints, potentially in addition to some number of equality constraints. They combine
all of the ideas we have developed in this chapter. We will use the same Lagrangian that we would for
equality constraints.
A Lagrangian For Multiple Equality and Inequality Constraints
Given an objective function f(x) and constraints of the forms g
j
(x) ≥ 0 or g
j
(x) = 0 the Lagrangian
is
L(x,
λ) = f(x) +
m
X
j=1
λ
j
g
j
(x).
Like with a single inequality constraint, complementary slackness will remove the λ
j
g
j
(x) when g
j
(x)
does not bind.
125
2.3.6 The Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
Theorem 2.23 [The Kuhn-Tucker Conditions]
Given the objective function f (x) and constraints of the forms g
j
(x) ≥ 0 or g
j
(x) = 0, then at any
local maximizer a one of the following must be true
1 There is some vector
λ such that (a,
λ) satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker conditions:
For each variable x
i
,
L
x
i
(a,
λ) = 0
For each equality constraint function g
j
,
g
j
(a) = 0
For each inequality constraint function g
j
,
g
j
(a) ≥ 0 and λ
j
≥ 0 and λ
j
g
j
(a) = 0
2 The binding ∇g
j
(a) are linearly dependent
2.3.7
Solving the Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
According to Kuhn-Tucker, what points (x
1
, x
2
) could be maximizers of f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
2
given the
constraints
12 − x
1
− 4x
2
≥ 0 9 − x
1
− x
2
≥ 0
Solution
The Lagrangian is L(x
1
, x
2
, λ
1
, λ
2
) = x
1
x
2
2
+ λ
1
(12 −x
1
−4x
2
) + λ
2
(9 −x
1
−x
2
). The Kuhn-Tucker
conditions are
∂L
∂x
1
= x
2
2
− λ
1
− λ
2
= 0
∂L
∂x
2
= 2x
1
x
2
− 4λ
1
− λ
2
= 0
12 − x
1
− 4x
2
≥ 0 9 − x
1
− x
2
≥ 0
λ
1
≥ 0 λ
2
≥ 0
λ
1
(12 − x
1
− 4x
2
) = 0 λ
2
(9 − x
1
− x
2
) = 0
The final equations carry our complementary slackness conditions. There are two ways to choose which
factor is 0 for each, giving us 2 × 2 = 4 cases to check.
126
1 λ
1
= 0, λ
2
= 0
x
2
2
− λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 2x
1
x
2
− 4λ
1
− λ
2
= 0
x
2
2
= 0 2x
1
x
2
= 0
x
2
= 0
check 12 − x
1
− 4x
2
≥ 0 6 − x
1
− x
2
≥ 0
12 − x
1
≥ 0 6 − x
1
≥ 0
x
1
≤ 12 x
1
≤ 9
So (k, 0, 0, 0) satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker conditions for k ≤ 9.
2 λ
1
= 0, 9 − x
1
− x
2
= 0
x
2
2
− λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 2x
1
x
2
− 4λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 9 − x
1
− x
2
= 0
x
2
2
− λ
2
= 0 2x
1
x
2
− λ
2
= 0
x
2
2
= 2x
1
x
2
x
2
2
− 2x
1
x
2
= 0
x
2
(x
2
− 2x
1
) = 0
x
2
= 0 covered in case 1
or x
2
= 2x
1
9 − x
1
− 2x
1
= 0
x
1
= 3
x
2
= 6
6
2
− λ
2
= 0
λ
2
= 36
check 12 − x
1
− 4x
2
≥ 0 λ
2
≥ 0
12 − 3 − 4(6) ≥ 0 36 ≥ 0
−15 ≥ 0
(3, 6, 0, 36) does not satisfy the inequalities.
127
2.3.7
Solving the Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
3 12 − x
1
− 4x
2
= 0, λ
2
= 0
x
2
2
− λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 2x
1
x
2
− 4λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 12 − x
1
− 4x
2
= 0
x
2
2
− λ
1
= 0 2x
1
x
2
− 4λ
1
= 0
4x
2
2
= 4λ
1
2x
1
x
2
= 4λ
1
4x
2
2
= 2x
1
x
2
4x
2
2
− 2x
1
x
2
= 0
2x
2
(2x
2
− x
1
) = 0
x
2
= 0 covered in case 1
or 2x
2
= x
1
12 − 2x
2
− 4x
2
= 0
x
2
= 2
x
1
= 4
2
2
− λ
1
= 0
λ
2
= 4
check 9 − x
1
− x
2
≥ 0 λ
1
≥ 0
9 − 4 − 2 ≥ 0 4 ≥ 0
(4, 2, 4, 0) satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker conditions
4 12 − x
1
− 4x
2
= 0, 9 − x
1
− x
2
= 0
x
2
2
− λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 2x
1
x
2
− 4λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 12 − x
1
− 4x
2
= 0 9 − x
1
− x
2
= 0
12 − x
1
− 4x
2
= 0
−(9 − x
1
− x
2
) = −0
3 − 3x
2
= 0
x
2
= 1
9 − x
1
− 1 = 0
x
1
= 8
1 − λ
1
− λ
2
= 0 16 − 4λ
1
− λ
2
= 0
−(16 − 4λ
1
− λ
2
) = −0
−15 + 3λ
1
= 0
λ
1
= 5
16 − 4(5) − λ
2
= 0
λ
2
= −4
check λ
1
≥ 0 λ
2
≥ 0
5 ≥ 0 −4 ≥ 0
(8, 1, 5, −4) does not satisfy the Kuhn-Tucker conditions.
The Kuhn-Tucker conditions are necessary. No point except (4, 2) or (k, 0) for k ≤ 9 can be a maximizer.
128
By evaluating we see
f(4, 2) = 16 f(k, 0) = 0
So only (4, 2) could be a maximizer. We cannot conclude that it is a maximizer, until we learn a relevant
sufficient condition.
Strategy
In general our method for solving the Kuhn Tucker conditions is
Pick an equality from a factor of each complementary slackness condition.
Solve the resulting system of equations.
Discard any solutions that violate the remaining inequalities.
Repeat for a different choice of equalities.
With m inequality constraints, we will need to repeat for all 2
m
combinations of equalities.
2.3.8
Visualizing the Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
Each choice of equalities mutates the Kuhn-Tucker conditions into the necessary conditions from
Theorem 2.22, where the binding g
j
(x) ≥ 0 are treated as equality constraints. The following diagram
shows how each choice corresponds to a different piece of the feasible set, where different constraints
bind.
∇g
1
∇g
2
x
1
x
2
g
1
(x) ≥ 0 and λ
1
= 0
g
2
(x) = 0 and λ
2
≥ 0
L(x,
λ) = f(x) + λ
2
g
2
(x)
∇f(x) = −λ
2
∇g
2
(x)
g
1
(x) ≥ 0 and λ
1
= 0
g
2
(x) ≥ 0 and λ
2
= 0
L(x,
λ) = f(x)
∇f(x) =
0
g
1
(x) = 0 and λ
1
≥ 0
g
2
(x) = 0 and λ
2
≥ 0
L(x,
λ) = f(x) + λ
1
g
1
(x) + λ
2
g
2
(x)
∇f(x) = −λ
1
∇g
1
(x) −λ
2
∇g
2
(x)
g
1
(x) = 0 and λ
1
≥ 0
g
2
(x) ≥ 0 and λ
2
= 0
L(x,
λ) = f(x) + λ
1
g
1
(x)
∇f(x) = −λ
1
∇g
1
(x)
Figure 2.28: The four regions covered by two pairs of inequalities with complementary slackness
129
2.3.8 Visualizing the Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
In the case of multiple binding inequality constraints, the condition that λ
j
≥ 0 forces ∇f(a) to lie
in the cone made by −∇g
j
(x).
∇g
1
∇g
2
−∇g
1
−∇g
2
∇f
x
1
x
2
Figure 2.29: The cone where ∇f must lie if both constraints bind at a maximizer
2.3.9
Proving the Necessity of the Kuhn-Tucker Conditions
To justify the necessity of the Kuhn-Tucker conditions, we can list each condition and describe why
it must apply.
1 A given a will satisfy some binding equations g
j
(x) = 0.
2 For the constraints that do not bind, setting λ
j
= 0 turns L(x,
λ) into the Lagrangian for f with
only the binding equality constraints. If a is a local maximizer, it must satisfy Theorem 2.22,
specifically,
∂L
∂x
i
(a) = 0.
3 For each inequality constraint, a maximizer must satisfy g
j
(a) ≥ 0 to be feasible.
4 Finally, if every path from a into the feasible region decreases f , then all λ
j
≥ 0.
We have not given a convincing argument for the last statement yet. A formal proof is just below,
but it may be more illuminating to convince yourself graphically. Try drawing a few ∇f that lie outside
the cone between −∇g
1
and −∇g
2
in the previous figure. For each one, you should be able to identify
a vector x
′
(t) that points into the feasible region but makes an acute angle with ∇f.
Here is a formal proof that λ
j
≥ 0 at a maximizer.
Proof
Pick any inequality constraint g
k
(x) ≥ 0. If g
k
(x) ≥ 0 is not binding at a, then λ
k
= 0 and we are
done.
130
We will therefore consider the case where g
k
(a) ≥ 0 is binding and show λ ≥ 0. Let S be the inter-
section of all the binding constraints except g
k
(x) = 0. Since the gradients of the binding constraints
a linearly independent, we can conclude:
The gradients of the binding constraints other than ∇g
k
(a) span the normal space of S at a
∇g
k
(a) is not a linear combination of these gradients, so it does not lie in the normal space of S
at a
There must be a path x(t) in S through a such that x
′
(t
0
) is not orthogonal to ∇g
k
(a). We can pick
such a path so that ∇g
k
(a) · x
′
(t
0
) > 0. If the first path we try produces a negative dot product, just
traverse x(t) backwards instead. First we show that, in some neighborhood of t
0
, x(t) lies in the feasible
region for all t > t
0
. We check that it satisfies each constraint.
a lies in the interior of each upper level set g
j
(x) ≥ 0 for each nonbinding g
j
. x(t) will travel for
some distance before leaving the upper level set.
Since x(t) was chosen to lie in S it lies in the level set g
j
(x) = 0 for all binding g
j
except g
k
.
Since ∇g
k
(a) · x
′
(t
0
) > 0, x(t) must travel into the upper level set g
k
(x) ≥ 0.
Thus in some neighborhood of t
0
, x(t) lies in the feasible set for t > t
0
. Since a is a local maximizer,
f(x(t
0
)) ≥ f(x(t)) for t > t
0
in this neighborhood. Thus
df
dt
(t
0
) ≤ 0. We use the chain rule to examine
this inequality.
df
dt
(t
0
) ≤ 0
∇f(a) · x
′
(t
0
) ≤ 0
−
m
X
j=1
λ
j
∇g
j
(a) · x
′
(t
0
) ≤ 0
We pause to examine the terms of this summation. Most are 0. Here is the reasoning.
For nonbinding g
j
(x), λ
j
= 0.
For binding g
j
(x) except j = m, we have ∇g
j
(a) ·x
′
(t
0
) = 0, since ∇g
j
(a) is a normal vector of
S and x(t) lies in S.
Finally, ∇g
k
(a) · x
′
(t
0
) > 0 by our choice of x(t).
We apply these to our inequality.
−
m
X
j=1
λ
j
∇g
j
(a) · x
′
(t
0
) ≤ 0
−λ
k
∇g
k
(a) · x
′
(t
0
) ≤ 0
λ
k
≥ 0
131
2.3.10
Kuhn-Tucker with Non-Negativity Constraints
If we demand that x
i
≥ 0 for each i, then we have added n new constraints to our Langrangian.
We will use µ
i
for the Lagrange multipliers of the x
i
.
L(x,
λ, µ) = f(x) +
m
X
j=1
λ
j
g
j
(x) +
n
X
i=1
µ
i
x
i
This is unwieldy. If we are clever, we can do better.
For 1 ≤ k ≤ n, the inequality conditions for µ
k
are
∂L
∂µ
k
= x
k
≥ 0 and µ
k
≥ 0
If the constraint x
k
≥ 0 is not binding, then µ
k
= 0. The µ
k
x
k
term is 0 in L and its partial
derivatives. We can remove it, but we will still need to verify that x
k
≥ 0 is satisfied.
If the constraint is binding, then we can still remove the µ
k
x
k
term from L.
The term goes to 0 anyway in L
x
i
for i = k.
In L
x
k
, there is a single +µ
k
term. L
x
k
is supposed to be 0, whereas µ
k
≥ 0. We can
replicate this effect by removing µ
k
x
k
from L, but requiring that the remaining terms of L
x
k
have a sum less than or equal to 0.
For each k, we can remove the variable µ
k
and the µ
k
x
k
term from our Lagrangian in exchange for
some new conditions.
132
Corollary 2.24 [The Kuhn-Tucker Conditions with Non-Negativity]
Given the objective function f (x) and constraints of the forms g
j
(x) ≥ 0 or g
j
(x) = 0, along with
x
i
≥ 0 for each i, then at any local maximizer a one of the following must be true.
1 There is some vector
λ such that (a,
λ) satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker Conditions with Non-
Negativity Constraints:
For each i,
a
i
≥ 0 and
∂L
∂x
i
(a,
λ) ≤ 0 and a
i
∂L
∂x
i
(a,
λ) = 0
For each equality constraint function g
j
,
g
j
(a) = 0
For each inequality constraint function g
j
,
g
j
(a) ≥ 0 and λ
j
≥ 0 and λ
j
g
j
(a) = 0
2 The binding constraints (including any x
i
= 0) have linearly dependent gradients at a.
2.3.11
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The shape of an intersection of level sets (Corollary 2.20)
The Lagrangian for multiple constraints (Definition 2.21)
First-order condition for multiple equality constraints (Theorem 2.22)
The Kuhn-Tucker conditions (Theorem 2.23)
The Kuhn-Tucker conditions with non-negativity (Corollary 2.24)
133
2.3.11
Section Summary
134
Chapter 3
Comparative Statics
3.1
The Implicit Function Theorem
Goals:
1 Identify when one variable of an implicit equation can be written as a function of the other(s)
2 Compute the derivative of one variable with respect to another
3 Determine how the optimal choice responds to changes in an exogenous parameter
3.1.1
Comparative Statics
Comparative statics study situations with one or more choice variables x
i
and one or more exoge-
nous parameters α
j
.
Example
A consumer maximizing her utility has the choice variable
q: the quantity of a product they buy
and the exogenous parameter
p: the price of that product
136
Example
From the point of view of a producer, the choice variables might be
q: the quantity of a product they produce
p: the price they sell for
the exogenous parameters may include
w, r: the price of labor or capital
t, s: a tax or subsidy imposed by the government
some aspect of the demand function
Remark
The choice variables are the variables whose value is chosen by the agent who wants to maximize the
function.
In economics, we assume that choosers are rational and well-informed. We assume they will learn the
value of the parameters. After that, they will pick the value of the choice variables that maximizes their
objective function. Comparative statics ask how the outcome changes as the value of the parameter
changes. We will present the tools to compute two types of comparative statics
1 How does the optimal value of a choice variable change as a parameter changes?
2 How does the value of the objective function change as a parameter changes?
Notation
Given an objective function f(x, α), with choice variable x and parameter α, we expect that different
values of α will lead the chooser to pick different values of x. The chooser’s optimal choice is a function
of α that we write x
∗
(α).
The first-order condition tells us that for each α, x
∗
(α) must satisfy the first-order condition:
f
x
(x
∗
(α), α) = 0
Without an expression for x
∗
(α), trying to understand its rate of change raises a sequence of questions.
1 What is
dx
∗
(α)
dα
?
137
3.1.1
Comparative Statics
2 How do we know that x
∗
(α) is differentiable?
3 How do we know that x
∗
(α) is even a function?
Given a specific f, we can solve the first-order condition algebraically. If we can tell which solution
is the maximizer (assuming one exists), then we can write an expression for x
∗
as a function of α and
answer all these questions. In the case of a general or abstract f, this may not be possible. Fortunately,
mathematics has the vocabulary to describe these questions in abstract. It also has a powerful tool to
answer them.
3.1.2
Explicit Functions and Implicit Equations
Definition 3.1
An explicit function equates a function or dependent variable to an expression entirely in terms of the
independent variables.
Example
The following equations describe explicit functions.
f(x) = x
3
−
√
x + 7
y = sin(x
2
)
z = 3xy + x
2
− 2
g(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) = e
x
1
cos(x
2
x
3
)
Since each input has at most one output, graphs of explicit functions pass the vertical line test. We
also have a variety of tools for differentiating explicit functions (though not all are differentiable).
We do not have the luxury of always working with explicit functions. We use the following vocabulary
when we wish to draw a contrast with explicit functions.
Definition 3.2
An implicit equation in two or more variables does not necessarily have any dependent variable which
is equated to an expression in the others.
Sometimes we can solve an implicit equation to obtain an explicit function, but other times we
cannot.
138
Example
2x + 3y = 12 =⇒ y = 4 −
2
3
x
x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ x
2
3
= 25 =⇒ x
3
= ±
q
25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
(multiple outputs for each input, not a function)
13 − 3y
3
+ xy
4
= y
5
=⇒ x =
y
5
− 13 + 3y
3
y
4
(can solve for x but not for y)
x
3
+ y
3
= 6xy =⇒ y = ??? (requires the cubic formula, not a function)
The solutions to any implicit equation form a level set of some function. We obtain the function by
rewriting the equation in a form like:
F (x, y) = c or F (x) = c
3.1.3
An Implicit Equation
Consider the implicit equation x
3
+ y
3
= 6xy
a
Write the equation in the form F (x, y) = c.
b
Does this equation have a graph?
c
Can we solve it to obtain an explicit function?
Solution
a
We can write x
3
+ y
3
− 6xy = 0
b
Yes. The graph is the set of points (x, y) that satisfy the equation. Every equation has a graph,
though some graphs are the empty set.
139
3.1.3
An Implicit Equation
c
We could look up the cubic formula and solve this. The cubic formula, like the quadratic formula,
returns multiple values for the variable. The result is not a function. We can see this in the graph,
which fails the vertical line test.
Figure 3.1: The graph of x
3
+ y
3
− 6xy = 0
Sometimes we cannot write y as an explicit function of x in a way that describes the whole graph.
If we are only interested in rates of change, we can restrict our attention to a small neighborhood of the
graph. At most points, this neighborhood does look like the graph of some function y = f (x).
Figure 3.2: A neighborhood in which the graph x
3
+ y
3
− 6xy = 0 is the graph of an explicit function
This is not always possible. Consider the part of x
3
+ y
3
−6xy = 0 near (0, 0). In any neighborhood
we choose, there are three branches of the graph that extend to the right. No matter how small a
neighborhood we choose around (0, 0), the graph will fail the vertical line test and cannot be written as
y = f(x).
140
3.1.4
The Implicit Function Theorem
The implicit function theorem tells us when a point on the graph of an implicit equation has a
neighborhood that is identical to the graph of an explicit function. The basic version takes an implicit
equation in two variables and writes a function that expresses one (the dependent variable) in terms of
the other (the independent variable).
Theorem 3.3 [The Implicit Function Theorem]
Suppose F (x, y) is a continuously differentiable function and (a, b) is a point on F (x, y) = c. If
F
y
(a, b) = 0, then there exists a differentiable function f (x) such that y = f(x) and F (x, y) = c
describe the same graph in some neighborhood of (a, b).
The theorem does not tell us what the function f(x) is, only that it exists. Even so, we can express
its derivatives in terms of F .
Corollary 3.4
The derivative of f with respect to x at a is given by
f
′
(a) = −
F
x
(a, b)
F
y
(a, b)
The derivation of this formula is famous and not too difficult. To compute the derivative of f, we
parameterize a path in the graph y = f(x). Unlike our previous parametrizations, we will use x as the
parameter. Differentiating x with respect to x is most palatable with Leibniz notation.
x = x
dx
dx
= 1
y = f(x)
dy
dx
= f
′
(x)
The points (x, f(x)) lie in F (x, y) = c near (a, b). Thus the composition F (x, f(x)) is the constant
function c. Differentiating F (x, f(x)) = c with respect to the parameter x to produces an equation that
contains f
′
(x). We solve this equation to obtain an expression for f
′
(x).
141
3.1.4 The Implicit Function Theorem
F (x, f(x) = c (y = f (x) lies in F (x, y) = c)
dF (x, f(x))
dx
= 0 (derivative of a constant is 0)
F
x
(x, f(x))
dx
dx
+ F
y
(x, f(x))
df(x)
dx
= 0 (chain rule)
F
x
(x, f(x))(1) + F
y
(x, f(x))f
′
(x) = 0 (evaluate derivative of x)
f
′
(x) = −
F
x
(x, f(x))
F
y
(x, f(x))
(solve for f
′
(x))
f
′
(a) = −
F
x
(a, b)
F
y
(a, b)
(evaluate at x = a)
The implicit function theorem guarantees that f exists and is differentiable in a neighborhood of a.
Since we don’t know how big this neighborhood is, x = a is the only point at which we can be sure
f
′
(x) exists.
We often apply this formula before checking whether the implicit function theorem applies. Assuming
F is continuously differentiable, the theorem will only fail when F
y
(a, b) = 0. Conveniently, this formula
will be undefined in that case.
We can also determine the derivative of f geometrically. Near (a, b), the graph y = f(x) is the level
set F (x, y) = c. We know the ∇F (a, b) = (F
x
(a, b), F
y
(a, b)) is normal to the level set.
The gradient has a slope of
F
y
(a,b)
F
x
(a,b)
. The tangent line, which is perpendicular, has a negative
reciprocal slope: −
F
x
(a,b)
F
y
(a,b)
. The slope of the tangent line is also the derivative f
′
(a).
Figure 3.3: The gradient of F and the tangent line whose slope is f
′
(a)
142
3.1.5
Applying the Implicit Function Theorem
If x and y satisfy x
3
− 2xy
2
+ 3y = −13, show that y can be written as a function f(x) of x near
(2, 3) and compute f
′
(2)
Solution
We may first want to check that (2, 3) satisfies the implicit equation.
(2)
2
− 2(2)(3)
2
+ 3(3) = −13
In order to apply the implicit function theorem, we need to know that F (x, y) = x
3
− 2xy
2
+ 3y has
continuous partial derivatives. It is a polynomial, so it does. Finally, we need to show F
y
(2, 3) = 0.
F
y
(x, y) = −4xy + 3
F
y
(2, 3) = −4(2)(3) + 3
F
y
(2, 3) = −21 = 0
Therefore, by the implicit function theorem, there is a function f (x) such that y = f(x) and x
3
−2xy
2
+
3y = −13 describe the same graph near (2, 3). The derivative of f at x = 2 is given by Corollary 3.4.
f
′
(2) = −
F
x
(2, 3)
F
y
(2, 3)
= −
3(2)
2
− 2(3)
2
−4(2)(3) + 3
= −
−6
−21
= −
2
7
Figure 3.4: The graph of x
3
− 2xy
2
+ 3y = −13 and its tangent line at (2, 3)
143
3.1.6
The Derivative of the Optimal Choice
In comparative statics, we are interested in the function x
∗
(α), which is a solution to the equation
f
x
(x, α) = 0. We apply the implicit function theorem where:
α takes the role of the independent variable “x”.
x takes the role of the dependent variable “y”.
f
x
(x, α) takes the role of the two-variable function “F ”.
(b, a) is a point on the graph f
x
(x, α) = 0.
The derivatives of F are second derivatives of f .
The implicit function theorem requires that
F
x
(b, a) = f
xx
(b, a) = 0.
It concludes there is a differentiable function x
∗
(α) such that x = x
∗
(α) matches the graph of f
x
(x, α) =
0 in a neighborhood of (b, a).
Corollary 3.5
Given a function f(x, α), suppose that
1 a is a value of α and b = x
∗
(a)
2 x
∗
(α) satisfies f
x
(x
∗
(α), α) = 0 near (b, a)
3 f(x, α) has continuous second derivatives near (b, a)
4 f
xx
(b, a) = 0
Then
dx
∗
(a)
dα
= −
f
xα
(b, a)
f
xx
(b, a)
This computes the derivative at a point. If, in some interval of α values, every point (x
∗
(a), a)
satisfies these conditions, then we can extend this to a derivative function for x
∗
(α).
dx
∗
(α)
dα
= −
f
xα
(x
∗
(α), α)
f
xx
(x
∗
(α), α)
144
Remark
When working with comparative statics, we can reasonably assume the requirements of the implicit
function theorem.
1 If an optimal choice exists, then it must satisfy the first-order condition.
2 It makes sense to work with smooth functions when modeling empirical data.
3 At a maximizer, f
xx
is likely (though not required) to be negative. Alternately, assuming f
xx
< 0
on the entire domain guarantees that x
∗
(α) is actually the global maximizer for each α.
3.1.7
The Construction of f(x)
Here we will give a construction of the function y = f(x) that matches the graph of F (x, y) = c
near a point (a, b). The same argument works for more variables, but the pictures are harder to draw.
Constructing f(x) requires the following tools:
1 Lemma 1.11: If f
′
(x) > 0 then f is increasing.
2 Definition of continuity: The values of F can be kept arbitrarily close to F (a, b) by restricting to
points sufficiently close to (a, b).
3 The intermediate value theorem: If f(x) is continuous and f(a
−
) < c < f(a
+
) then there is a
value k between a
−
and a
+
such that f(k) = c.
The implicit function theorem requires that F
y
(a, b) = 0. There are two cases to consider, but the
arguments are analogous. We will consider the case F
y
(a, b) > 0.
145
3.1.7 The Construction of f(x)
1 F is continuously differentiable, so
there is a neighborhood of (a, b) where
F
y
(x, y) > 0.
2 Within this neighborhood, we can travel
h units in the y-direction from (a, b). Let
F (a, b + h) = c
+
and F (a, b − h) = c
−
3 Since F
y
(x, y) > 0, we have c
+
> c and
c
−
< c.
4 Since F is continuous, there is a neigh-
borhood of (a, b + h) where F (x, y) > c.
There is a neighborhood of (a, b − h)
where F (x, y) < c.
5 We consider segments from (x, b + h)
to (x, b − h), with one endpoint in each
neighborhood.
6 Apply the intermediate value theorem,
since F (x, b − h) < c < F (x, b + h),
there is a k between b−h and b +h such
that F (x, k) = c.
7 Since F
y
(x, y) > 0, F is increasing along
the segment, so it cannot take the value
c more than once. The k in the previous
step is unique.
8 Repeat this for every segment of the form
(x, b+h) to (x, b−h), and define f(x) =
k.
F
y
(x, y) > 0
F (a, b + h) = c
+
> c
F (a, b − h) = c
−
< c
(a, b)
F
y
(x, y) > 0
F (x, y) > c
F (x, y) < c
(a, b)
n some in
F
y
(x, y) > 0
F (x, b + h) > c
F (x, b − h) < c
(x, b + h)
(x, b − h)
(a, b)
(x, k)
F
y
(x, y) > 0
y = f(x)
146
3.1.8
The Implicit Function Theorem with More Variables
We can also apply the implicit function theorem to an implicit equation of n > 2 variables. In this
case, one dependent variable can be expressed as a function of n − 1 independent variables.
Theorem 3.6 [The Multivariable Implicit Function Theorem]
Suppose F (x, y) is a continuously differentiable function and F (a, b) = c. If F
y
(a, b) = 0, then there
exists a differentiable function f(x) such that y = f(x) and F (x, y) = c describe the same graph in
some neighborhood of (a, b).
Since f (x) is an n − 1 variable function, the derivatives we can compute are the partial derivatives.
The formula for these derivatives is analogous to the single-variable version.
Corollary 3.7
For each variable x
k
, the partial derivative of f with respect to x
k
at a is given by
f
x
k
(a) = −
F
x
k
(a, b)
F
y
(a, b)
We can now justify our earlier characterization of level sets. At the time we made no mention
of dependent and independent variables. This lack of distinction actually makes the implicit function
theorem easier to apply.
Remark
There is nothing special about the letter y, nor the fact that it is the last variable of F . The variable
“y” in the implicit function theorem can apply to any variable of an implicit equation, so long as the
partial derivative with respect to that variable is not zero.
147
3.1.8 The Implicit Function Theorem with More Variables
Figure 3.5: A point where x
3
+ y
3
− 6xy = 0 cannot be written in the form y = f(x) because it fails
the vertical line test but can be rewritten as x = f(y)
If we are not picky about which variable is written as a function of the others, then the implicit
function theorem only fails when all the partial derivatives are 0. As long as the gradient of the function
is not the zero vector, one component can play the role of the dependent variable. This is exactly what
our corollary requires.
Corollary 2.5
Let g(x) be a continuously differentiable function at a. If a lies on the level set g(x) = c and ∇g(a) =
0,
then the level set g(x) = c is a (n −1)-dimensional shape in some neighborhood of a. Specifically, it is
the graph of a differentiable function of n − 1 of the variables of R
n
.
The “differentiable function” is the function f produced by the implicit function theorem.
We can also apply this version of the implicit function theorem and its corollary to comparative
statics. Consider a function of one choice variable and multiple parameters. We write this objective
function as f(x, α). The implicit function theorem and its corollary can compute the partial derivatives
of x
∗
(α).
148
Corollary 3.8
Given a function f(x, α), suppose that
1 a is a value of α and b = x
∗
(a).
2 x
∗
(α) satisfies f
x
(x
∗
(α), α) = 0 near (b, a)
3 f(x, α) has continuous second derivatives near (b,a)
4 f
xx
(b,a) = 0
Then
∂x
∗
(a)
∂α
k
= −
f
xα
k
(b,a)
f
xx
(b,a)
.
We can justify the multivariable implicit function and Corollary 3.7 using arguments similar to the
single-variable versions. The construction of f is the same for both versions, except that x replaces x.
The computation of the partial derivatives of f requires more adaptation.
Since f
k
(x) is a partial derivative, we treat x
k
as a parameter. The other x
i
are constants, held
equal to the corresponding components of a.
x
i
=
(
a
i
if i = k
x
k
if i = k
dx
i
dx
k
=
(
0 if i = k
1 if i = k
y = f(x)
dy
dx
k
= f
x
k
(x)
The strategy is the same. We differentiate F (x, f(x)) with respect to x
k
, solve for f
x
k
(x), and evaluate
at x
k
= a
k
.
F (x, f(x)) = c ((x, f(x)) lies in F (x, y) = c)
dF (x, f(x))
dx
k
= 0 (derivative of a constant is 0)
n
X
i=1
F
x
i
(x, f(x))
dx
i
dx
k
+ F
y
(x, f(x))f
x
k
(x) = 0 (chain rule)
F
x
k
(x, f(x))
dx
k
dx
k
+ F
y
(x, f(x))f
x
k
(x) = 0 (
dx
i
dx
k
= 0 for i = k)
F
x
k
(x, f(x))(1) + F
y
(x, f(x))f
x
k
(x) = 0 (evaluate derivative of x
k
)
f
x
k
(x) = −
F
x
k
(x, f(x))
F
y
(x, f(x))
(solve for f
x
k
(x))
f
x
k
(a) = −
F
x
k
(a, b)
F
y
(a, b)
(evaluate at x = a)
149
3.1.9
The Implicit Function Theorem for Multiple Equations
We have seen two instances previously where the solution to multiple implicit equations was relevant.
1 The feasible set of multiple equality constraints is the intersection of multiple level sets.
2 Critical points of a multivariable function satisfy f
x
i
(x) = 0 for each i.
A graph of the form y = f(x) in R
n+1
will have dimension n. In general, each equation we wish
to satisfy lowers the dimension of our space of solutions by 1. If we want to express an intersection of
level sets, y = f(x) will not have the right dimension.
The way to handle this loss of dimension in an explicit function is to increase the number of dependent
variables. Specifically, if we have n-variables x and m-variables y then the graph of a family of functions
y
j
= f
j
(x) will have dimension n in R
n+m
The most general version of the implicit function theorem states when a family of implicit equations
can be expressed as a family of explicit functions instead.
Notation
Given a family of functions
F(x, y) = (F
1
(x, y), F
2
(x, y), . . . , F
m
(x, y))
the derivative of F with respect to y
j
is the family of functions
∂F
∂y
j
(x, y) =
∂F
1
∂y
j
(x, y),
∂F
2
∂y
j
(x, y), . . . ,
∂F
n
∂y
j
(x, y)
Note that we are using subscripts here to indicate different components of the vector F, not as
partial derivatives.
Theorem 3.9 [The Implicit Function Theorem for Multiple Dependent Variables]
Suppose y is an m-vector and F(x, y) is a family of m continuously differentiable functions such that
F(a,
b) = (c
1
, . . . , c
m
). If the vectors
∂F
∂y
j
(a,
b) are linearly independent, then there exists a family
of differentiable functions (f
j
(x)) such that the equations y
j
= f
j
(x) describe the same graph as
F(x, y) = (c
1
, . . . , c
m
) in some neighborhood of (a,
b).
We can use the chain rule to solve for partial derivatives
∂f
j
(a,
b)
∂x
k
, but the derivative of any equation
F
j
(x, y) = c
j
with respect to x
k
will contain the derivatives of all the f
j
. To compute the derivative
we want, we need to differentiate all of the implicit equations and solve a system of equations. Here is
the simplest example.
150
Example
Consider two implicit equations F
1
(x, y
1
, y
2
) = c
1
and F
2
(x, y
1
, y
2
) = c
2
. Assuming F
y
1
and F
y
2
are
linearly independent, the implicit function guarantees differentiable explicit functions y
1
= f
1
(x) and
y
2
= f
2
(x). Differentiating the original implicit equations with respect to x gives
∂F
1
∂x
dx
dx
+
∂F
1
∂y
1
f
′
1
(x) +
∂F
1
∂y
2
f
′
2
(x) = 0
∂F
2
∂x
dx
dx
+
∂F
2
∂y
1
f
′
1
(x) +
∂F
2
∂y
2
f
′
2
(x) = 0
We can use this system to solve for f
′
1
(x) and f
′
2
(x).
3.1.10
The Derivative of Optimal Choice with Multiple Choice Variables
Suppose your utility is a function of two choice variables and one exogenous parameter.
u(x
1
, x
2
, α)
Your optimal choices x
∗
1
(α) and x
∗
2
(α) satisfy the following implicit equations:
u
1
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) = 0
u
2
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) = 0.
By the implicit function theorem, we can write x
∗
1
(α) and x
∗
2
(α) as differentiable explicit functions of α
if their derivatives with respect to x
1
and x
2
are linearly independent. Here are those derivatives.
∂(u
1
, u
2
)
∂x
1
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) = (u
11
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α), u
21
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α))
∂(u
1
, u
2
)
∂x
2
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) = (u
12
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α), u
22
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α))
These are the columns of the second upper left square minor of the Hessian of u. Columns of a matrix
are independent, if the matrix has a nonzero determinant.
|Hu(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
2
| =
u
11
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
12
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
u
21
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
22
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
= 0
Assuming this holds, we can use the chain rule to differentiate both implicit equations with respect to
α. We obtain
u
11
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dx
∗
1
(α)
dα
+ u
12
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dx
∗
2
(α)
dα
+ u
1α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dα
dα
= 0
u
21
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dx
∗
1
(α)
dα
+ u
22
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dx
∗
2
(α)
dα
+ u
2α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dα
dα
= 0
151
3.1.10
The Derivative of Optimal Choice with Multiple Choice Variables
In a concrete example we could solve for
dx
∗
1
(α)
dα
and
dx
∗
2
(α)
dα
directly using algebra. If that seems difficult
or the problem is abstract, we can borrow an approach from linear algebra. We write this system of
equations as a matrix product.
u
11
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
12
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
u
21
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
22
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dx
∗
1
(α)
dα
dx
∗
2
(α)
dα
=
−u
1α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
−u
2α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
Cramer’s rule writes the solution to a matrix equation as a ratio of determinants.
dx
∗
1
(α)
dα
=
−u
1α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
12
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
−u
2α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
22
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
u
11
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
12
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
u
21
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
22
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
dx
∗
2
(α)
dα
=
u
11
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) −u
1α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
u
21
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) −u
2α
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
u
11
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
12
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
u
21
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α) u
22
(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
Notice the denominator in each formula is |Hu(x
∗
1
(α), x
∗
2
(α), α)
2
|. We replace the corresponding column
with the right side of the equation to obtain the numerator.
Cramer’s rule can apply to any number of variables, so we can extend this procedure to more than
two choice variables. We can also handle multiple parameters. This method would compute partial
derivatives of x
∗
i
(α) with respect to some α
j
.
Main Ideas
The optimal choice of multiple variables satisfies the multivariable first-order condition.
The implicit function theorem applies to the optimal choice variables, if the Hessian minor cor-
responding to the choice variables has a nonzero determinant. If the optimal choice satisfies the
second-order condition, this is automatic.
We can differentiate the multivariable first-order condition with respect to a parameter and obtain
a linear system of equations in the derivatives of the choice variables.
Cramer’s rule is a reliable way to solve such systems.
152
3.1.11
Section Summary
The key definitions and results from this section were
Explicit functions and implicit equations (Definitions 3.1 and 3.2)
The implicit function theorem (Theorem 3.3)
The derivative of the function guaranteed by the implicit function theorem (Corollary 3.4)
The derivative of the function x
∗
(α) (Corollary 3.5)
153
3.2
The Envelope Theorem
Goals:
1 Use the envelope theorem to compute the derivative of value functions.
3.2.1
Value Functions
Definition 3.10
Suppose we have
f(x, α), a differentiable function.
x is a choice variable
α is a parameter
x
∗
(α) is the x that maximizes f(x, α) for a given α.
Then the outcome that will occur for each α is the value function
V (α) = f(x
∗
(α), α)
Vocabulary
In the case that f has an economic meaning, we sometimes use the term indirect, along with the ∗
notation, to refer to its value function of f.
If u(x, α) is a utility function then u
∗
(α) = u(x
∗
(α), α) is the indirect utility function.
If π(x, α) is a profit function then π
∗
(α) = π(x
∗
(α), α) is the indirect profit function.
x
∗
(α) is a solution to f
x
(x, α) = 0. Assuming f is continuously differentiable, the implicit function
guarantees that x
∗
(α) is a differentiable function. This means that V is a differentiable function. If we
want to understand how a change in α affects the value of V , we want to compute V
′
(α).
154
V
′
(α) computes how a change in a parameter affects the an outcome, assuming the agents involved
make the optimal choices. This derivative can answer a variety of questions in economics.
Example
How will increasing a tax impact company profits?
Will increasing a subsidy increase consumer well-being?
In the case that we have an expression for f, computing V
′
(α) is not difficult:
1 Solve for x
∗
(α)
2 Substitute x
∗
(α) into f(x, α) to obtain an expression for V (α)
3 Differentiate V (α)
But is there a better way?
3.2.2
The Envelope Theorem
The envelope theorem gives us an alternative method. We compute V
′
(α) by parametrizing the
values of α and x
∗
in a neighborhood where x
∗
(α) is differentiable. We use α as the parameter.
α = α
dα
dα
= 1
x = x
∗
(α)
We can apply the chain rule to V (α) = f(x
∗
(α), α). We use the fact that x
∗
(α) satisfies the first-order
condition for all α. Specifically, have f
x
(x
∗
(α), α) = 0.
V
′
(α) =
df(x, α)
dα
= f
x
(x
∗
(α), α)
dx
∗
(α)
dα
+ f
α
(x
∗
(α), α)
dα
dα
(chain rule)
= (0)
dx
∗
(α)
dα
+ f
α
(x
∗
(α), α)(1) (FOC)
= f
α
(x
∗
(α), α)
155
3.2.2 The Envelope Theorem
Remark
This computation requires us to know that x
∗
(α) is a differentiable function. Here are two ways to
verify this.
1 For a concrete function, compute x
∗
(α). Verify directly that it is differentiable.
2 In more abstract settings, apply the implicit function theorem. Check that
f has continuous second derivatives
f
xx
(x
∗
(α), α) = 0 for all α.
.
Theorem 3.11 [The Envelope Theorem, Single-Variable]
Suppose
f(x, α) is a differentiable function, and
x
∗
(α) that maximizes f for each α is a differentiable function.
The following two derivatives are equal:
V
′
(α)
|{z}
derivative of
value function
= f
α
(x
∗
(α), α)
| {z }
partial derivative
of original function
The envelope theorem allows us to compute a partial derivative of f instead of the total derivative
of V . In some sense, the envelope theorem is saying that the change in x
∗
does not matter. This makes
sense, because at a maximizer, we cannot increase the value of the function by changing x.
This is an interesting insight into the behavior of value functions, but all we have done is traded one
derivative for another. We still need to compute x
∗
(α) to evaluate the partial derivative. It is natural
to ask: does the envelope theorem save us any work in practice?
Compare the following methods of computing V
′
(α):
Without the envelope theorem
1 Compute x
∗
(α)
2 Substitute into f(x, α) to get V (α)
3 Differentiate V (α)
With the envelope theorem
1 Compute x
∗
(α)
2 Partially differentiate f(x, α)
3 Substitute x
∗
(α)
156
Remark
In concrete situations, the first method gives us a more complicated function to differentiate. In abstract
situations, the first method may be impossible or give us an answer in a less useful form.
The envelope theorem can also be justified visually. If we pick a specific a, we can compare two
functions
1 The value function: V (α) = f(x
∗
(α), α), which uses the best x for each α
2 The stubborn function: V
0
(α) = f(x
∗
(a), α), which sticks with the best x for a, even if α
changes.
The stubborn function has the following properties
Since its x-coordinate is constant, the derivative of V
0
is equal to the partial derivative f
α
.
V
0
(a) = V (a)
For any other α, x
∗
(a) cannot be a better choice than x
∗
(α). Thus V
0
(α) ≤ V (α).
The graph y = V
0
(α) meets y = V (α) at a but does not go above it. They must be tangent, which
means their derivatives are equal.
V
′
(a) = V
′
0
(a) = f
α
(x
∗
(a), a)
Figure 3.6: The graphs of the value function and stubborn function and their tangent line
The envelope theorem gets its name from the fact that y = V (α) envelopes all of the stubborn
functions y = V
0
(α), generated by choosing different values of a.
157
3.2.3
Generalizations of the Envelope Theorem
There are several ways to generalize the envelope theorem. First we can consider a function of more
choice variables or more parameters.
1 If f is a function of n choice variables, then each choice variable has an optimal value that depends
of α. We obtain a family of functions x
∗
i
(α). We can write them as a vector x
∗
(α). The value
function is
V (α) = f(x
∗
(α), α)
2 If f is a function of m parameters α
j
, we can express the parameters as a vector α. The optimal
choice of each choice variable is a function of all the α
j
. The value function also a function of all
the α
j
.
V (α) = f(x
∗
(α), α)
Since the x
∗
i
(α) satisfy the family of equations f
x
i
(x, α) = 0, we need the multi-equation version of the
implicit function theorem to justify their existence and differentiability.
The value function is a function of multiple parameters, so the envelope theorem computes its partial
derivatives.
Theorem 3.12 [The Envelope Theorem, Multivariable]
Suppose
f(x, α) is a differentiable function
x
∗
(α) that maximizes f for each α is a differentiable function
For any region of R
m
where x
∗
(α) is differentiable and any coordinate α
k
of α we have:
V
α
k
(α) = f
α
k
(x
∗
(α), α)
We can again show this with a parametrization. Since we need the partial derivative, we treat α
k
as
a parameter. The other α
j
are constants, held equal to the corresponding components of some fixed a.
This parametrization will not cover the entire domain of α, only those that lie in the α
k
-direction from
a.
α
j
=
(
a
j
j = k
α
k
j = k
dα
j
dα
k
=
(
0 if j = k
1 if j = k
x = x
∗
(α)
In general, x
∗
i
is a multivariable function of α. In this parametrization, x
i
is a function only of the
parameter α
k
. By the first-order condition, x
∗
(α) satisfies f
x
i
(x
∗
(α), α) = 0 for each x
i
. We can apply
158
the chain rule to V (α) = f(x
∗
(α), α) to compute V
α
k
(α).
V
α
k
(α) =
df(x
∗
(α), α)
dα
k
=
n
X
i=1
f
x
i
(x
∗
(α), α)
dx
∗
i
(α)
dα
k
+
m
X
j=1
f
α
j
(x
∗
(α), α)
dα
j
dα
k
=
n
X
i=1
(0)
dx
∗
i
(α)
dα
k
+
X
j=k
f
α
j
(x
∗
(α), α)(0) + f
α
k
(x
∗
(α), α)(1)
= f
α
k
(x
∗
(α), α)
This is valid for any α that lies on our path through a in the α
k
-direction. We can apply this
reasoning to any a though, so the computation holds for the entire domain of x
∗
(α).
Our final generalization of the envelope theorem assumes that x
∗
(α) is the optimal choice given an
equality constraint, g(x, α) = 0.
Theorem 3.13 [The Envelope Theorem, Constrained]
Suppose
f(x, α) is a differentiable objective function
g(x, α) is a differentiable constraint function
x
∗
(α) that maximizes f subject to g(x, α) = 0 for each α is a differentiable function
λ
∗
(α) is the value of λ that solves the first-order conditions of L along with x
∗
(α) and α.
For any region of R
m
where x
∗
(α) and λ
∗
(α) are differentiable and any coordinate α
k
of α we have:
V
α
k
(α) = L
α
k
(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))
Proving this version requires us to use the fact that g(x
∗
(α), α) = 0 for all α. This means that
L(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α)) = f(x
∗
(α), α) + λ
∗
(α)g(x
∗
(α), α)
= f(x
∗
(α), α) + λ
∗
(α)(0)
= V (α)
x
∗
(α) does not necessarily satisfy the first-order condition of f, but for a fixed α it does satisfy the first
order condition of L(x
∗
(α), λ
∗
(α)). Specifically:
L
x
i
(x
∗
(α), λ
∗
(α)) = 0
L
λ
(x
∗
(α), λ
∗
(α)) = 0
159
3.2.3 Generalizations of the Envelope Theorem
We can use the same parametrization as the unconstrained case, with the understanding that x
∗
(α)
now describes the maximizer of the constrained optimization and with λ
∗
(α) the corresponding λ value.
V
α
k
(α) =
df(x
∗
(α), α)
dα
k
=
dL(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))
dα
k
=
n
X
i=1
L
x
i
(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))
dx
∗
i
(α)
dα
k
+
m
X
j=1
L
α
j
(x
∗
(α, α, λ
∗
(α))
dα
j
dα
k
+ L
λ
(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))
dλ
∗
(α)
dα
k
=
n
X
i=1
(0)
dx
∗
i
(α)
dα
k
+
X
j=k
L
α
j
(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))(0) + L
α
k
(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))(1) + (0)
dλ
∗
(α)
dα
k
= L
α
k
(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))
Further Generalizations
We can extend this reasoning to multiple equality constraints without any trouble.
We can also also extend the envelope theorem to inequality constraints, where we set λ
∗
(α) = 0 for
any α such that the constraint is not binding at the maximizer x
∗
(α). If x
∗
and λ
∗
are differentiable
functions of α in this setting, we can still conclude that
V
α
k
(α) = L
α
k
(x
∗
(α), α, λ
∗
(α))
However, we expect x
∗
(α) will not be differentiable at the transition between the binding and
nonbinding cases.
Proving the inequality case is identical to the equality case, except
L
λ
(x(t), α(t), λ(t))
| {z }
=0 if binding
λ
′
(t)
|{z}
=0 if
nonbinding
= 0
Remark
The generalizations of the envelope theorem require that x
∗
(α) is a differentiable function. Like in the
single-variable case, it usually makes sense to solve for x
∗
(α) and directly verify that it is differentiable. If
we need to use the implicit function theorem instead, we need the multivariable version. The requirement
for that is
|Hf
x
(x, α)| = 0 or |HL
x,λ
(x, α)| = 0
depending on whether there is a constraint.
160
3.2.4
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The definition of a value function (Definition 3.10)
Three versions of the envelope theorem (Theorems 3.11, 3.12 and 3.13)
161
3.2.4
Section Summary
162
Chapter 4
Sufficient Conditions
4.1
The Extreme Value Theorem
Goals:
1 Recognize when the extreme value theorem applies.
2 Apply the extreme value theorem to identify a maximizer.
4.1.1
The Extreme Value Theorem
In previous examples, we often found that only one point satisfied the necessary conditions for a
maximizer. Still we did not conclude that this point was a maximizer. We would have found it very
useful to know that a maximizer existed in these circumstances. We then could have identified our point
as that maximizer. Even if we only narrowed our search down to two or three potential maximizers, the
information that one of them is in fact the maximizer would have been helpful.
This is what the extreme value theorem does for us.
Theorem 4.1 [The Extreme Value Theorem]
If f(x) is a continuous function and S is a closed and bounded subset of the domain of f, then there
exists an x
∗
that maximizes f(x) subject to x ∈ S.
In order to apply this theorem, we need to be able to identify when a region S is closed and bounded.
Here are the definitions of those terms.
Definition 4.2
Let S be a subset of R
n
.
S is closed if it contains all of the points on its boundary.
S is bounded if there is some upper limit to how far its points get from the origin (or any other
fixed point). If there are points of S arbitrarily far from the origin, then S is unbounded.
164
For one-variable functions, we can use the fact that a union of finitely many closed intervals (or
isolated points) is closed. If the intervals are each finite length, then the union is also bounded.
x
−4 −2 0 2 4
Figure 4.1: A finite union of closed intervals
The same holds for curves. A curve must include its endpoints, or have no endpoints to be closed.
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.2: A closed curve
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.3: The graph x
2
1
+ x
2
2
= 9 is
closed.
Generally, a region defined by a strict inequality will not contain its boundary points and thus will
not be closed.
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.4: x
2
1
+ x
2
2
≤ 9 is closed.
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.5: x
2
1
+ x
2
2
< 9 is not closed.
If multiple inequalities are involved and relevant, they must all be nonstrict in order to avoid removing
boundary points. An interesting case is the removal of a single interior point. If we exclude that point
from S, then that point becomes a boundary point. Any neighborhood of it contains points in S and a
point not in S.
165
4.1.1
The Extreme Value Theorem
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.6: −2 ≤ x
1
≤ 2 and
−3 < x
2
< 3 is not closed.
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.7: −2 ≤ x
1
≤ 2 and
−3 ≤ x
2
≤ 3 and (x
1
, x
2
) = (1, 2) is not
closed.
Boundedness is a simpler concept and easy to check. If you can draw a circle around S, it is bounded.
If no circle is big enough, it is unbounded.
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.8: −2 ≤ x
1
≤ 2 and
−3 ≤ x
2
≤ 3 is bounded.
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.9: −2 ≤ x
1
≤ 2 is unbounded.
The examples above are a good way to visually recognize a closed and bounded set. What if we have
an equation or inequality instead of a graph? The following theorems answer some of these questions.
Theorem 4.3
If f(x) is a continuous function, then any level set or upper level set of f is closed.
166
Theorem 4.4
1 The intersection of any number of closed sets is closed.
2 The union of any finite number of closed sets is closed.
The second theorem is specifically useful for feasible sets defined by multiple constraints. Under our
formulation of constrained optimization, the feasible set is an intersection of level sets and upper level
sets. As long as the constraint functions are continuous, the feasible set will be closed.
The extreme value theorem is a standard result in analysis. While we will not prove it, we can at
least demonstrate that each hypothesis is necessary.
Example
Consider f(x) = x
2
on the region S = {x : x ≥ 0}. f(x) is continuous and S is closed but not
bounded. f(x) grows without bound in S and has no maximum.
2 4
2
4
x
y
Figure 4.10: The graph of y = x
2
over [0, ∞)
Example
Consider
f(x) =
(
x
2
if x < 2
0 if x ≥ 2
on the region S = {x : 0 ≤ x ≤ 2}. S is closed and bounded, but f (x) is not continuous. f (x)
approaches a value of 4 but never reaches it. There is no maximizer a. For any a < 2, there is a b closer
to 2 with f(b) > f(a).
167
4.1.1
The Extreme Value Theorem
2 4
2
4
x
y
Figure 4.11: The graph of y = f (x) over [0, 2]
Example
Consider f(x) = x
2
on the region S = {x : 0 ≤ x < 2}. f(x) is continuous and S is bounded but not
closed. Again f(x) approaches a value of 4 but never reaches it. There is no maximizer a. For any a
in S, there is a b closer to 2 with f(b) > f (a).
2 4
2
4
x
y
Figure 4.12: The graph of y = x
2
over [0, 2)
168
4.1.2
Applying the Extreme Value Theorem
Find the maximizer(s) of f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
2
1
+ x
2
1
x
2
+ 2x
2
2
subject to 8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0.
−4 −2 2 4
−4
−2
2
4
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.13: The feasible set
Solution
Apply the necessary conditions for maximizers subject to an inequality. The Lagrangian is
L(x
1
, x
2
, λ) = x
2
1
+ x
2
1
x
2
+ 2x
2
2
+ λ(8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
)
The conditions are
L
x
1
(x
1
, x
2
, λ) = 2x
1
+ 2x
1
x
2
− 2λx
1
= 0
L
x
2
(x
1
, x
2
, λ) = x
2
1
+ 4x
2
− 2λx
2
= 0
8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0, λ ≥ 0 and λ(8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
) = 0
We solve each case of the complementary slackness.
1 Set λ = 0
2x
1
+ 2x
1
x
2
= 0 x
2
1
+ 4x
2
= 0
2x
1
(1 + x
2
) = 0
if x
1
= 0 0
2
+ 4x
2
= 0
x
2
= 0
if x
2
= −1 x
2
1
+ 4(−1) = 0
x
1
= ±2
Check that (0, 0, 0) and (±2, −1, 0) satisfy 8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0. They do.
2 Set 8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
= 0. We need to solve
2x
1
+ 2x
1
x
2
− 2λx
1
= 0 x
2
1
+ 4x
2
− 2λx
2
= 0 8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
= 0
169
4.1.2
Applying the Extreme Value Theorem
One good approach is to factor
2x
1
+ 2x
1
x
2
− 2λx
1
= 0
2x
1
(1 + x
2
− λ) = 0
x
1
= 0 or λ = 1 + x
2
We treat these two cases separately.
a If x
1
= 0,
8 − (0)
2
− x
2
2
= 0
x
2
= ±2
√
2 (0)
2
+ 4(±2
√
2) − 2λ(±2
√
2) = 0
±8
√
2 = ±4
√
2λ
2 = λ
b If λ = 1 + x
2
,
x
2
1
+ 4x
2
− 2(1 + x
2
)x
2
= 0
x
2
1
= 2x
2
2
− 2x
2
8 − (2x
2
2
− 2x
2
) − x
2
2
= 0
3x
2
2
− 2x
2
− 8 = 0
−(3x
2
+ 4)(x
2
− 2) = 0
if x
2
= 2
λ = 1 + 2 x
2
1
= 8 − (2)
2
λ = 3 x
1
± 2
if x
2
= −
4
3
λ = 1 −
4
3
x
2
1
= 8 −
4
3
2
λ = −
1
3
x
1
= ±
2
√
14
3
We verify that (0, ±2
√
2, 2), (±2, 2, 3) and
±
2
√
14
3
,
4
3
, −
1
3
satisfy λ ≥ 0. The third one does
not.
Now we can apply the extreme value theorem. The function f(x
1
, x
2
) is continuous. The feasible
set is the upper level set of a continuous function: 10 − x
2
1
−x
2
2
≥ 0, so it is closed. The feasible set is
a disk, so it is bounded. The extreme value theorem tells us a maximizer must exist.
Only a point that satisfies our necessary condition can be that maximizer. To determine which one,
170
we evaluate f (x
1
, x
2
) at each.
f(0, 0) = (0)
2
+ (0)
2
(0) + 2(0)
2
= 0
f(±2, −1) = (±2)
2
+ (±2)
2
(−1) + 2(−1)
2
= 2
f(0, ±2
√
2) = (0)
2
+ (0)
2
(±2
√
2) + 2(±2
√
2)
2
= 16
f(±2, 2) = (±2)
2
+ (±2)
2
(2) + 2(2)
2
= 20
Because they produce the greatest values among the candidates, the maximizers are (2, 2) and (−2, 2).
Figure 4.14: The maximizers of y = x
2
1
+ x
2
1
x
2
+ 2x
2
2
subject to 8 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0
Main Ideas
The algebraic expressions tell us when the objective function is continuous and the feasible set is
closed.
Draw the feasible set to decide whether it is bounded.
If the EVT applies, we can evaluate f at all of the points that passed our necessary conditions.
The one that attains the greatest value is the maximizer.
171
4.1.3
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The extreme value theorem (Theorem 4.1)
The meaning of closed and bounded (Definition 4.2)
Level sets, upper level sets, and their intersections are closed (Theorems 4.3 and 4.4)
172
4.2
The Bordered Hessian
Goals:
1 Use the bordered Hessian to identify local maximizers of a function subject to a constraint.
4.2.1
The Bordered Hessian
We used the Hessian matrix to recognize maximizers and minimizers in unconstrained optimization.
This worked because the Hessian computed the second derivative over a straight line a+ tv. An equality
constraint does not usually contain straight lines. The test for the second derivative will need to take
account of the shape of the level set g(x) = 0.
Definition 4.5
Given a constrained optimization problem with Hessian L, the matrix HL(λ, x) is called the bordered
Hessian of the constrained optimization problem.
Example
The 2-variable bordered Hessian has the form
HL(λ, x
1
, x
2
) =
L
λλ
L
λ1
L
λ2
L
λ1
L
11
L
12
L
λ1
L
12
L
22
=
0 g
1
g
2
g
1
f
11
+ λg
11
f
12
+ λg
12
g
2
f
21
+ λg
21
f
22
+ λg
22
Why is this called “bordered?”
The bottom right 2 × 2 minor looks like a Hessian.
It is bordered to the left and above by ∇g.
Notice that we have switched the order of variables in our Lagrangian. This is common when writing
the bordered Hessian. Placing the border on the top allows us to write our condition for a local maximizer
in a familiar way. If we instead prioritized consistency, we could keep the λ last and modify our condition.
173
4.2.1 The Bordered Hessian
Theorem 4.6
Let f(x) be an n-variable function and g(x) = 0 be a constraint. If (ℓ,a) satisfies the first-order
condition of the Lagrangian and the upper left square minors of HL(ℓ,a) satisfy
(−1)
i
|M
i
| < 0 2 ≤ i ≤ n + 1,
then a is a strict local maximizer of f among points on the constraint.
Remark
We do not test |M
1
|, since M
1
= [0].
We generally do not need to worry about M
2
either, since
|M
2
| =
0 g
1
g
1
f
11
+ λg
11
= −(g
1
)
2
Notice the inequality is reversed from the unconstrained second-order condition.
Variant of Theorem 4.6
Let f(x) be an n-variable function and g(x) = 0 be a constraint. If (ℓ,a) satisfies the first-order
condition of the Lagrangian and the upper left square minors of HL(ℓ,a) satisfy
|M
i
| < 0 2 ≤ i ≤ n + 1,
then a is a strict local minimizer of f among points on the constraint.
Remark
We might hope to quickly extend this to a global condition, but unfortunately, HL only tells us about
the second derivatives at a critical point. Deriving a condition that works for all points on the constraint
is possible but more complicated.
174
4.2.2
Using the Bordered Hessian
Let f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
on the domain
D = {(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
> 0, x
2
> 0}
Find the critical point of f on the constraint x
4
1
+ x
4
2
= 2. Classify it as a local maximizer or local
maximizer of f (or neither) on the constraint.
Solution
The Lagrangian is
L(x
1
, x
2
, λ) = x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ λ(2 − x
4
1
− x
4
2
)
Here are the first-order conditions. We can solve them, using the fact that x
1
> 0 and x
2
> 0.
2x
1
− 4λx
3
1
= 0 2x
2
− 4λx
3
2
= 0 2 − x
4
1
− x
4
2
= 0
x
2
1
=
1
2λ
x
2
2
=
1
2λ
x
2
1
= x
2
2
x
1
= x
2
2 − x
4
1
− x
4
1
= 0
2 = 2x
4
1
1 = x
1
1 = x
2
1 =
1
2λ
λ =
1
2
The critical point is
1, 1,
1
2
. Switching the order of the variables, we compute
HL(λ, x
1
, x
2
) =
0 −4x
3
1
−4x
3
2
−4x
3
1
2 − 12λx
2
1
0
−4x
3
2
0 2 − 12λx
2
2
HL
1
2
, 1, 1
=
0 −4 −4
−4 −4 0
−4 0 −4
The determinants of the upper left square minors are
|M
2
| =
0 −4
−4 −4
= −16
|M
3
| =
0 −4 −4
−4 −4 0
−4 0 −4
= 0 + 4
−4 0
−4 −4
− 4
−4 −4
−4 0
= 128
175
4.2.2
Using the Bordered Hessian
(−1)
2
(−16) < 0 and (−1)
3
(128) < 0. According to Theorem 4.6, (1, 1) is a strict local maximizer.
∇f(1, 1)
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.15: The level sets of x
2
1
+ x
2
2
and the constraint x
4
1
+ x
4
2
= 2
4.2.3
The Multi-Constraint Bordered Hessian
For more variables, the test requires more determinants.
Theorem 4.7
Let f (x) be an n-variable function and {g
j
(x) = 0} be a set of m constraint equations. If (
ℓ,a) satisfies
the first-order condition of the Lagrangian and the upper left square minors of HL(
ℓ,a) satisfy
(−1)
i
|M
i
| < 0 2m ≤ i ≤ n + m,
then a is a strict local maximizer of f(x) among the feasible points.
176
4.2.4
The Bordered Hessian and Inequality Constraints
If we combine the determinant of the bordered Hessian with the requirement that ℓ > 0, then we can
guarantee that f(x) < f(a) on the equality constraint and in the direction of ∇g(a) from the equality
constraint. This guarantees a neighborhood of some size in which a is a maximizer among feasible
points.
4.2.5
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The definition of the bordered Hessian (Definition 4.5)
The bordered Hessian determinant test for a maximizer (Theorems 4.6)
177
4.3
Separation
Goals:
1 Use normal vectors to describe half-spaces of a hyperplane.
2 Apply optimization by separation arguments.
4.3.1
Upper Level Sets and Optimization
Recall our necessary conditions for a maximizer of f(x) subject to g(x) ≥ 0. If the constraint is
binding, we learned to check that ∇f(a) is parallel to ∇g(a), meaning the level sets are parallel. We
also check that λ ≥ 0, meaning that ∇f(a) points away from the feasible set. However, these checks
are not sufficient. We will construct an example that passes these conditions but isn’t a maximizer.
Recall the following definition
Definition 2.13
The upper level sets of a function f(x) with domain D are the sets
{x ∈ D | f(x) ≥ c} for some number c
The lower level sets are
{x ∈ D | f(x) ≤ c} for some number c
The following characterization will be important to our arguments.
Lemma 2.14
Suppose ∇f(x) =
0, and x(t) is a path that passes through a in the level set f(x) = c at t
0
If x
′
(t
0
) makes an acute angle with ∇f (a), then x(t) travels into the upper level set f (x) ≥ c.
If x
′
(t
0
) makes an obtuse angle with ∇f (a), then x(t) travels into the lower level set f (x) ≤ c.
178
Consider the following diagram of a feasible set and an upper level set. The point a satisfies
∇f(a) = −λ∇g(a) and λ ≥ 0, but we can see that there are also feasible points in the interior of the
upper level set, like
b. f(
b) may be greater than f (a).
∇f(a)
∇g(a)
a
b
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.16: An upper level set and feasible set for which a is not a maximizer
We would like a condition to rule out this behavior. Suppose that a line separates the upper level
set f(x) ≥ c from the feasible set. This prevents any higher values of f from appearing in the feasible
set.
a
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.17: The upper level set of f, a feasible set, and a separating line
4.3.2
Hyperplanes and Half-Spaces
To formalize this reasoning, we first present the notation for a separating line and generalize it to
higher dimensions. Every line h in R
2
has a normal vector v. h divides R
2
into two half-planes:
h
+
on the side of v
h
−
on the other side.
179
4.3.2
Hyperplanes and Half-Spaces
h
h
+
h
−
v
a
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.18: A line, its normal vector v, and its half spaces
For any point x, the vector that points from a to x is
x −a.
The angle of this vector with v tells us which half-plane contains x. The dot product tells us whether
this angle is acute, obtuse or right.
Lemma 4.8
Suppose h is a line in R
2
with normal vector v, and a is a point on h. For any point x
v · (x −a)
> 0 if x lies in h
+
= 0 if x lies on h
< 0 if x lies in h
−
Figure 4.19: The angle between a vector and the normal vector of a line
180
The analogous object in R
3
is a plane h. It has a normal vector and divides R
3
into two half-spaces
h
+
and h
−
. The sign of v · (x −a) tests which half-space x lies in. Specifically, x lies on the plane, if
v · (x −a) = 0.
Figure 4.20: A plane, its normal vector v, and a vector on it
This reasoning works in any dimension to define a set of points whose displacement from a known
point a is orthogonal to a normal vector v.
Definition 4.9
In R
2
, v · (x −a) = 0 defines a line.
In R
3
, v · (x −a) = 0 defines a plane.
In R
n
, v · (x −a) = 0 defines a hyperplane, a linear (n − 1)-dimensional subspace.
When dimension is general or ambiguous, we use the term hyperplane as a catch-all term. We can
rewrite our dot product lemma to reflect the n-dimensional case.
Variant of Lemma 4.8
Suppose h is a hyperplane with normal vector v and a is a point on h. For any point x
v · (x −a)
> 0 if x lies in h
+
= 0 if x lies on h
< 0 if x lies in h
−
181
4.3.2
Hyperplanes and Half-Spaces
For a more concise test, we can let k = v ·a. We can rewrite our dot product
v · (x −a) = v · x −v ·a = v · x − k
and the lemma
v ·x
> k if x lies in h
+
= k if x lies on h
< k if x lies in h
−
4.3.3
Optimization by Separation
In Figure 4.17, a line separates the upper level set of f and the feasible set. The point where they
meet appears to be a maximizer of f. We now have the notation to formalize this argument.
Theorem 4.10
Suppose we have a continuous objective function f(x) and some constraint(s). Suppose x
∗
is in the
feasible set and let f(x
∗
) = c. If there is a hyperplane h such that
1 the upper level set f(x) ≥ c has no points in h
−
2 the feasible set has no points in h
+
then x
∗
is a maximizer of f(x) subject to the constraint(s).
This method is called optimization by separation and h is a separating hyperplane. It is a
sufficient condition, but it requires us to know the proper hyperplane h.
Notice both the upper level set and the feasible set may contain have points on h. In fact, x
∗
is
one of them. What if they share an additional point a in h? a must lie on the boundary of the upper
level set, arbitrarily close to points for which f(x) < c. Since f(x) is continuous, f(a) = c. We can still
conclude that x
∗
is a maximizer, but not a unique maximizer.
182
h
a
b
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.21: An upper level set of f and the feasible set intersecting multiple times along their
separating line
We can modify this theorem by stipulating that x
∗
is either
1 the only point of the upper level set on h or
2 the only feasible point on h.
In this case we can conclude that x
∗
is the unique maximizer.
If we want to avoid talking directly about the hyperplane h, we can think of v ·x as a function of x.
Its level sets are the hyperplanes v ·x = k. The value of v ·x increases as we travel in the direction of v.
k > k< k
v
x
∗
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.22: Some level sets of v ·x that intersect an upper level set of f and a feasible set
Our separation argument can be rephrased to require that the upper level set meets only higher
values of v ·x while the feasible set meets only lower values of v · x. We can verify this algebraically.
Suppose x be a point in the upper level set of f(x). Lemma 4.8 states that x does not lie in h
−
, if
v · (x − x
∗
) ≥ 0
v ·x ≥ v · x
∗
183
4.3.3 Optimization by Separation
This inequality indicates that the value of v · x at x
∗
is less than or equal to the value at any other
point in the upper level set. In other words, x
∗
minimizes the function v · x subject to the constraint
f(x) ≥ c.
To show that the feasible set has no points in h
+
we can check that for each feasible x:
v · (x − x
∗
) ≤ 0
v ·x ≤ v · x
∗
This means that the value of v · x at x
∗
is greater than or equal to the value at any other x in the
feasible set. In other words, x
∗
maximizes the function v · x subject to the constraints of the original
optimization problem. We can restate Theorem 4.10 in terms of this new vocabulary.
Alternate Formulation of Theorem 4.10
Suppose we have a continuous objective function f and some constraints. If f(x
∗
) = c and for some
v =
0 we have
1 x
∗
minimizes v ·x subject to f(x) ≥ c
2 x
∗
maximizes v ·x subject to the constraints
Then x
∗
maximizes f(x) given the constraints.
We can see that this is a condition for a maximizer without knowing much about hyperplanes. If
the feasible points all have values of v ·x less than or equal to k and the upper level sets all have values
greater than or equal to k, then the feasible set and the upper level can only meet where v · x = k.
4.3.4
The Tangent Hyperplane
An observant reader will have noticed that our separating lines have always been tangent to the level
curve f(x) = c. This is not a coincidence. It occurs in higher dimensions as well, where the tangent
lines become tangent hyperplanes.
Definition 4.11
Suppose a point a lies on level set f (x) = c, and ∇f(a) =
0. The tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c
at a is the hyperplane containing of all the tangent lines to f (x) = c at a. Its normal vector is ∇f(a).
Its equation is
∇f(a) · (x −a) = 0
184
If ∇f(a) = 0, the only candidate for a separating hyperplane is the tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c.
Any other hyperplane would contain some vector w such that ∇f(a) · w > 0, meaning it would cut into
the upper level set of f at a.
On the other hand, we have seen examples where a tangent line fails to keep the upper level set out
of h
−
.
∇f(a)
a
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.23: An upper level set that crosses its own tangent line
For this reason, optimization by separation is only realistic for functions with nicely shaped level sets.
We will discover a class of such functions in the next section.
4.3.5
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
Hyperplanes and the dot product test (Definition 4.9 and Lemma 4.8)
Optimization by separation, both formulations (Theorem 4.10 and its variant)
Equation of a tangent hyperplane to a level set (Definition 4.11)
185
4.4
Concave Programming
Goals:
1 Understand the geometric consequences of concavity on constrained optimizations.
2 Apply sufficient conditions for maximizers of concave functions with concave constraints.
4.4.1
Kuhn-Tucker Sufficiency
When is a separation argument possible? When does the tangent hyperplane separate the upper level
set from the feasible set? Concavity is one way to guarantee this. There is an a rich theory and toolset
for optimization that is specific to concave functions. This is the field of concave programming. Here
is our main result.
Theorem 4.12
Given an objective function f(x) and constraints g
j
(x) ≥ 0, suppose (x
∗
,
λ
∗
) satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker
conditions:
L
x
i
(x
∗
,
λ
∗
) = 0 for all i
g
j
(x
∗
) ≥ 0 and λ
∗
j
≥ 0 with complementary slackness for each j
If f(x) and the g
j
(x) are all concave functions, then x
∗
maximizes f(x), subject to the constraints.
It is worth understanding the full argument of this theorem that follows, but the essential ideas are:
1 The upper level sets of a concave function are convex sets. This applies not only to f (x) ≥ c but
also to the feasible set, which is an intersection of the upper level sets: g
j
(x) ≥ 0.
2 Using this convexity, we can show that the tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c separates the upper
level set f(x) ≥ c from the feasible set.
186
∇f(x
∗
)
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.24: A feasible region defined by multiple concave inequalities separated from the upper level
set of f by a tangent line
Remark
This sufficient condition is especially powerful because once we find a point that satisfies Kuhn-Tucker,
we can stop looking. If, by luck or cleverness, we find a solution in the first case of complementary
slackness we try, then we have found the maximizer. We need not examine the other cases at all.
4.4.2
Applying the Kuhn-Tucker Sufficient Condition
Find the maximum value of f(x
1
, x
2
) = 4x
1
+ x
2
on the region
S = {(x
1
, x
2
) : 25 − 7x
1
− x
2
≥ 0, x
2
≥ 0, x
2
+ x
2
1
− 5 ≥ 0, and 25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0}
x
2
+ x
2
1
− 5 = 0
25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
= 0
25 − 7x
1
− x
2
= 0
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.25: The feasible set S
187
4.4.2
Applying the Kuhn-Tucker Sufficient Condition
Solution
Increasing x
1
seems to be the most important factor in increasing f , but larger x
2
helps too. We should
draw and examine the region S. The set x
2
+ x
2
1
−5 ≥ 0 appears to be nonconvex. On the other hand,
based on our diagram, that inequality appears not to bind. We will instead maximize f over the region
T = {(x
1
, x
2
) : 25 − 7x
1
− x
2
≥ 0, x
2
≥ 0, and 25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0}
S is a subset of T so a maximizer in T that lies in S is a maximizer in S. This modified problem has
the following Lagrangian:
L(x
1
, x
2
, λ
1
, λ
2
, λ
3
) = 4x
1
+ x
2
+ λ
1
(25 − 7x
1
− x
2
) + λ
2
x
2
+ λ
3
(25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
).
The Kuhn-Tucker conditions are
L
x
1
= 4 − 7λ
1
− 2λ3x
1
= 0
L
x
2
= 1 − λ
1
+ λ
2
− 2λ
3
x
2
25 − 7x
1
− x
2
≥ 0 λ
1
≥ 0 λ
1
(25 − 7x
1
− x
2
) = 0
x
2
≥ 0 λ
2
≥ 0 λ
2
x
2
= 0
25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0 λ
3
≥ 0 λ
3
(25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
) = 0
We might guess that 25 −7x
1
−x
2
= 0 and 25−x
2
1
−x
2
2
= 0 are binding at the maximizer and x
2
≥ 0 is
not. Based on that guess, we first consider the case where λ
2
= 0. Next we use the binding constraints
to solve for x
1
and x
2
.
25 − 7x
1
− x
2
= 0 25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
= 0
25 − 7x
1
= x
2
25 − x
2
1
− (25 − 7x
1
)
2
= 0
25 − x
2
1
− 49x
2
1
+ 350x
1
− 625 = 0
−50x
2
1
+ 350x
1
− 600 = 0
−50(x
1
− 3)(x
1
− 4) = 0
x
1
= 3 or 4
25 − 7(3) = 4 = x
2
or
25 − 7(4) = −3 = x
2
We can look ahead and see that x
2
= −3 will not satisfy our inequalities, so we set (x
1
, x
2
) = (3, 4).
We use the remaining equations to solve for the λ
1
and λ
3
.
4 − 7λ
1
− 2λ
3
x
1
= 0 1 − λ
1
− 2λ
3
x
2
= 0
4 − 7λ
1
− 6λ
3
= 0 1 − λ
1
− 8λ
3
= 0
1 − 8λ
3
= λ
1
4 − 7 + 56λ
3
− 6λ
3
= 0
50λ
3
= 3
λ
3
=
3
50
1 −
24
50
= λ
1
13
25
= λ
1
188
Our solution is
3, 4,
13
25
, 0,
3
50
. We check, and it satisfies the remaining inequalities.
λ
1
=
13
25
≥ 0
x
2
= 4 ≥ 0
λ
3
=
3
50
≥ 0
There are 7 other cases of complementary slackness to check, but we can avoid them. Our sufficiency
theorem applies to (3, 4). We only need to check for concavity of the relevant functions.
4x
1
+ x
2
is concave because it is linear.
25 − 7x
1
− x
2
is concave because it is linear.
x
2
is concave because it is linear.
25 −x
2
1
−x
2
2
is strictly concave because its hessian is
−2 0
0 −2
, which is negative definite for
all (x
1
, x
2
).
We ignored the constraint x
2
+ x
2
1
− 5 ≥ 0.
Based on these checks, the theorem applies, and (3, 4) must be a maximizer of f on T . Since (3, 4)
satisfies
x
2
+ x
2
1
− 5 = 4 + 9 − 5 ≥ 0
it lies in S as well. Since S ⊆ T , we conclude (3, 4) is also a maximizer of f in S. The maximum value
is f(3, 4) = 4(3) + (4) = 16.
Main Idea
The most common methods to check concavity are
linear functions are concave
functions with negative definite Hessians are strictly concave
If the functions are concave, and we guess the right combination of binding constraints, then we only
need to check the Kuhn-Tucker conditions for that case.
189
4.4.2
Applying the Kuhn-Tucker Sufficient Condition
Remark
The underlying separation argument was between the convex upper level set f(x
1
, x
2
) ≥ 16 and the
convex set
T = {(x
1
, x
2
) : 25 − 7x
1
− x
2
≥ 0, x
2
≥ 0 and 25 − x
2
1
− x
2
2
≥ 0}
Since (3, 4) is a maximizer on T , it is a maximizer on S.
∇f(3, 4)
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.26: A convex set T containing S, an upper level set, and a separating line
The reasoning of this example also suggests the following variant.
Variant of Theorem 4.12
Given an objective function f(x) and constraints g
j
(x) ≥ 0, suppose (x
∗
,
λ
∗
) satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker
conditions.
If f(x) and the binding g
j
(x) are all concave, then x
∗
maximizes f(x), subject to the constraints.
4.4.3
Proving Kuhn-Tucker Sufficiency
This will be an extensive argument with many parts, but there are two reasons to give it our attention.
1 Some of the lemmas along the way are useful or interesting in their own right.
2 There are many ways to modify this argument for different circumstances. If you understand the
original argument, you can understand or even generate these variants.
190
Our first step is to understand the upper level sets of concave functions.
Lemma 4.13
If f(x) is a concave function, then the upper level set f(x) ≥ c is a convex set.
We can argue this directly from the definition of an upper level set, the definition of a convex set,
and the following inequality for concave functions:
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ (1 − t)f(a) + tf(
b).
Figure 4.27: The segment from a to
b in the upper level set of f(x)
Proof
Let a and
b be points in the upper level set f(x) ≥ c. We will show that the segment between a and
b
also lies in this upper level set. The points on the segment from a to
b are parametrized by
(1 − t)a + t
b 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
If we evaluate f along these points we get
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ (1 − t)f(a) + tf(
b) (f is concave)
≥ (1 − t)c + tc (a and
b lie in the upper level set)
≥ c
Since f((1 −t)a + t
b) ≥ c, (1 −t)a + t
b lies in the upper level set. Since this is true for every t between
0 and 1, the entire segment from a to
b lies in the upper level set. Since this is true for all a and
b in
the upper level set, we conclude that the upper level set is convex.
191
4.4.3 Proving Kuhn-Tucker Sufficiency
We now know that if f is concave, then its upper level sets are convex. For a separation argument,
we also would like to know they do not cross their tangent hyperplane. Fortunately, this is the case.
Lemma 4.14
Let
f(x) be a continuously differentiable function
a be a point such that f(a) = c and ∇f (a) =
0
h be the tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c at a.
If upper level set f(x) ≥ c is convex, then it does not intersect h
−
.
Proof
Suppose
b is any point in the upper level set f(x) ≥ c. We want to show that
b does not lie in h
−
.
Since the upper level set is convex, the entire segment
x(t) = (1 − t)a + t
b 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
= a + t(
b −a)
must lie within it. This specifically requires that the direction vector x
′
(0) =
b −a points into the upper
level set at a. Lemma 2.14 tells us that if ∇f(a) · x
′
(0) < 0, then x(t) travels into the lower level set.
Thus ∇f · (
b −a) ≥ 0. By Lemma 4.8,
b does not lie in h
−
.
∇f(a)
a
b
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.28: The vector
b −a in a
convex upper level set making an acute
angle with ∇f(a)
∇f(a)
a
b
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.29: The vector
b −a leaving an
upper level set and making an obtuse
angle with ∇f(a)
Now we turn our attention to the constraint functions. Lemma 4.13 applies as well to each g
j
as it
does to f. If each function g
j
(x) is concave, then each upper level set g
j
(x) ≥ 0 is convex. With some
very familiar looking conditions on ∇g
j
(a), we can ensure that the feasible set stays on one side of the
tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c.
192
Corollary 4.15
Let f(a) = c and ∇f(a) =
0. Let h be the tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c at a. If
1 The upper level sets g
j
(x) ≥ 0 are convex
2 ∇f(a) = −
X
j
λ
j
∇g
j
(a) for some numbers λ
j
3 For each j, λ
j
≥ 0 if g
j
(a) = 0 and λ
j
= 0 otherwise
then the intersection of the upper level sets g
j
(x) ≥ 0 does not intersect h
+
.
The geometry is easiest to visualize if we consider a single constraint g(x) ≥ 0. In this case,
∇f(a) = −λ∇g(a). For any
b in g(x) ≥ 0, the vector
b −a makes an acute angle with ∇g(a). Thus it
makes an obtuse angle with ∇f (a), meaning
b lies in h
−
.
∇f(a)
∇g(a)
a
b
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.30: The vector
b −a in a convex feasible set making an obtuse angle with ∇f(a)
For multiple constraints, angles are too difficult to discern. The dot product provides a cleaner
argument.
Proof
Let
b be a point in the intersection of the upper level sets. For each g
j
(x) that is binding at a, we can
apply Lemma 4.14 to the convex upper level set g
j
(x) ≥ 0. As that proof argued, we can conclude that
∇g
j
· (
b −a) ≥ 0.
By Lemma 4.8, the sign of ∇f (a) · (
b −a) will tell us whether
b lies in h
+
. We can substitute as
193
4.4.3 Proving Kuhn-Tucker Sufficiency
follows:
∇f(a) · (
b −a) = −
X
j
λ
j
∇g
j
(a)
· (
b −a)
= −
X
j
λ
j
∇g
j
(a) · (
b −a)
We can determine the sign of each term of the summation.
1 For nonbinding g
j
, λ
j
= 0.
2 For binding g
j
, λ
j
≥ 0 and ∇g
j
(a) · (
b −a) ≥ 0.
We conclude that ∇f (a) · (
b −a) ≤ 0. Thus
b does not lie in h
+
.
We now have the ingredients to prove Theorem 4.12. There are two cases of complementary slackness
to consider when proving this theorem.
1 If all λ
∗
j
= 0 then ∇f(x
∗
) = 0. Since f is concave, a variant of Corollary 1.23 tells us that x
∗
is
an unconstrained maximizer of f. Corollary 2.2 tells us that since it lies in the feasible set, is also
a maximizer there.
2 If some λ
∗
j
> 0 then we can put together the results of this section to conclude the upper level
set of f and the feasible set lie on opposite sides of h. This is the requirement for optimization
by separation established in Theorem 4.10, so x
∗
is a maximizer.
Here is a diagram containing the reasoning for each case.
binding λ
∗
j
> 0
all λ
∗
j
= 0
∇f(x
∗
) =
0
f(x) is
concave
f(x) ≥ c is convex
f(x) ≥ c does not
intersect h
−
g
j
(x) are
concave
g
j
(x) ≥ 0
are convex
∇f(x
∗
) = −
P
λ
∗
j
∇g
j
(x
∗
)
feasible set does
not intersect h
+
x
∗
is a max
x
∗
is a max
in the feasible set
Lem 4.13
Lem 4.14
Lem 4.13
Cor 4.15
Thm 4.10
Cor 1.38
Cor 2.2
194
4.4.4
Variants of Kuhn-Tucker Sufficiency
In a separation argument, the upper level set and the feasible set may meet at many points in h. For
example, we could have an entire line segment of intersection, and every point on that segment would
satisfy Kuhn-Tucker.
h
∇f(x
∗
)
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.31: An upper level set of f and the feasible set intersecting along a separating line
This pathology only exists if both sets contain multiple points on the separating hyperplane. If one
of the sets is strictly convex, this will not happen. We can achieve this with strict concavity. Each
lemmas we used has a variant for strict concavity.
Variant of Lemma 4.13
If f(x) is a strictly concave function then the upper level set f(x) ≥ c is strictly convex.
Variant of Lemma 4.14
Suppose we have
a continuously differentiable function f(x)
a point a such that f(a) = c and ∇f (a) =
0
the tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c at a, denoted h.
If upper level set f(x) ≥ c is strictly convex, then it lies entirely within h
+
, except for the point a.
195
4.4.4 Variants of Kuhn-Tucker Sufficiency
Variant of Corollary 4.15
Let f(a) = c and ∇f(a) =
0. Let h be the tangent hyperplane to f(x) = c at a. If
1 The upper level sets g
j
(x) ≥ 0 are strictly convex
2 ∇f(a) = −
X
j
λ
j
∇g
j
(a) for some numbers λ
j
3 For each j, λ
j
≥ 0 if g
j
(a) = 0 and λ
j
= 0 otherwise
then the intersection of the upper level sets g
j
(x) ≥ 0 lies entirely within h
−
except the point a.
We can use these lemmas to guarantee a unique maximizer. We can either keep the upper level set
or the feasible set from having multiple points on h.
Theorem 4.12 for a Unique Maximizer
Given an objective function f(x) and constraints g
j
(x) ≥ 0, suppose (x
∗
,
λ
∗
) satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker
conditions. If f(x) and the binding g
j
(x) are concave, and additionally either
1 f(x) is strictly concave, or
2 at least one constraint binds and the binding g
j
(x) are strictly concave,
then x
∗
is the unique maximizer of f(x), subject to the constraints.
Another avenue of modification is to include equality constraints. One method is to treat the equality
constraint as an inequality constraint. The level set is a subset of the upper level set. By Corollary 2.2,
a maximizer over an inequality constraint that happens to bind is also a maximizer over the equality
constraint. This requires the constraint function to be concave and its λ
j
to be positive.
Alternately, if the equality constraint is linear, then its level set is a hyperplane, which is convex.
Thus the feasible set is still convex. Corollary 4.15 still holds regardless of the sign of λ
j
, because
∇g
j
(a) · (
b −a) = 0. We can formalize this possibility with the following variant.
Theorem 4.12 with Equality Constraints
Given an objective function f (x) and constraints of the forms g
j
(x) ≥ 0 and g
j
(x) = 0, suppose (x
∗
,
λ
∗
)
satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker conditions.
If f(x) and the binding g
j
(x) are all concave, and the equality constraints are linear, then x
∗
maximizes f(x), given the constraints.
196
This section contains just a few possibilities. There are other ways to modify our sufficiency theorems
that allow them to apply in more situations or to draw stronger conclusions.
4.4.5
Slater’s Condition
Concavity has produced a convenient sufficient condition for constrained optimization. It can also
help simplify our necessary conditions. Recall that the Kuhn-Tucker conditions are a necessary condition,
but they have an exception. Theorem 2.23 states that a maximizer a must either satisfy the Kuhn-Tucker
conditions or have binding ∇g
j
(a) that are linearly dependent.
Checking for linearly dependent gradient vectors is difficult, especially if we do not know where to
look for them. Slater’s condition allows us to skip that check in some situations.
Slater’s condition requires that the objective and constraint functions are concave. It also requires
the feasible set to have an interior, rather than collapsing to a lower dimensional set. Formally, it
demands the existence of a point
b in the interior. This point is not special. If the feasible region has
an interior, then you can identify infinitely many points inside it by looking at a diagram.
Theorem 4.16 [Slater’s Condition]
Suppose that the functions f(x) and g
j
(x) satisfy Slater’s condition:
1 f(x) and the g
j
(x) are all concave functions
2 there is at least one point
b in the interior of the feasible set, meaning
g
j
(
b) > 0 for all j
If a is a local maximizer of f(x) subject to g
j
(x) ≥ 0, then a satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker conditions.
Remark
Slater’s condition checks for concavity, just like Theorem 4.12 (our sufficient condition). This means
that if f(x) and g
j
(x) satisfy Slater’s condition, then the Kuhn-Tucker conditions are both necessary
and sufficient for a maximizer.
Slater’s condition doesn’t prevent the gradient vectors of the binding g
j
from being linearly depen-
dent. Instead it argues that even if the gradient vectors are linearly dependent at a, the Kuhn-Tucker
conditions must still be satisfied in order for a to be a maximizer.
Slater’s condition can be strengthened to handle equality constraints in the case that those are linear.
197
4.4.5 Slater’s Condition
Variant of Theorem 4.16
Suppose that we are maximizing f(x) subject to constraints of the form g
j
(x) ≥ 0 or g
j
(x) = 0.
Suppose further that
1 f(x) and the inequality constraint functions g
j
(x) are concave
2 the equality constraint functions g
j
(x) are linear
3 there is at least one point
b in the relative interior of the feasible set, meaning
g
j
(
b) > 0 for all inequality constraints
g
j
(
b) = 0 for all equality constraints
If a is a local maximizer, then it satisfies the Kuhn-Tucker conditions.
4.4.6
The Separating Hyperplane Theorem
Throughout this section, we have used tangent hyperplanes to separate convex sets. It is possible to
make these arguments without separation, however. Here is a short alternative proof of Theorem 4.12.
Proof
x
∗
satisfies the first-order condition of a stubborn lagrangian, in which
λ is held constant at
λ
∗
.
L
∗
(x) = f(x) +
X
j
λ
∗
j
g
j
(x)
Since λ
∗
j
≥ 0, L
∗
is a sum of concave functions. By Theorem 1.20, L
∗
is concave. Thus x
∗
is a
maximizer of L
∗
. x
∗
also satisfies λ
∗
j
g
j
(x
∗
) = 0 by complementary slackness. If we compare x
∗
and
any other feasible point a, we have
L
∗
(x
∗
) ≥ L
∗
(a)
f(x
∗
) +
X
j
λ
∗
j
g
j
(x
∗
) ≥ f(a) +
X
j
λ
∗
j
g
j
(a)
f(x
∗
) + 0 ≥ f(a) +
X
j
λ
∗
j
|{z}
≥0
g
j
(a)
|{z}
≥0
f(x
∗
) ≥ f(a)
Since this holds for any feasible a, we can conclude that x
∗
is a maximizer of f(x) subject to g
j
(x) ≥ 0.
198
This argument does not establish a separating hyperplane, even though we know one exists from our
longer proof. It turns out that in any successful maximization argument for a concave function over a
convex feasible set, the hyperplane is there, whether we use it or not. The following famous theorem
guarantees that.
Theorem 4.17 [The Separating Hyperplane Theorem]
If S and U are two convex sets, at least one has a non-empty interior, and they share no interior points
in common, then there is a vector v and a number k such that
1 For all x in U, v · x ≥ k
2 For all x in S, v ·x ≤ k
Remark
This theorem tells us that if a convex upper level set U and a convex feasible set S meet only at their
boundaries, then the hyperplane v · x = k separates them. It does not tell us what v is or how to
construct it.
As you might infer from this remark, the applications of the separating hyperplane theorem tend to
be abstract. The proof requires ideas from analysis.
4.4.7
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
Upper level sets of concave functions are convex (Lemma 4.13)
Convex upper level sets lie in one half space of their tangent hyperplanes (Lemma 4.14)
Kuhn-Tucker sufficiency for concave functions (Theorem 4.12)
Slater’s condition (Theorem 4.16)
This is also a good time to summarize the sufficient conditions we have covered. They differ in when
they can be applied and what conclusion they draw.
199
4.4.7
Section Summary
Sufficient Conditions for Constrained Optimization
Condition Limited to Conclusion
EVT bounded sets one of the critical points
is a maximizer
Bordered Hessian binding constraint this critical point
is a local maximizer
KT Sufficiency concave functions this critical point
is a maximizer
200
4.5
Quasiconcavity
Goals:
1 Recognize a quasiconcave function from its graph or level sets
2 Apply quasiconcavity in sufficient conditions for a maximizer
3 Use concavity and nondecreasing compositions to test for quasiconcavity
4 Use a determinant test to verify quasiconcavity
4.5.1
Limitations of Concave Programming
Concave programming provided sufficient conditions for a maximizer on one or more constraints.
Our argument excluded functions with badly behaved level sets in order to guarantee separation, but
did it exclude too many?
The function f(x) =
3
x
2
−2x+2
has convex upper level sets, but it is not a concave function. Could
we make a separation argument for it?
Figure 4.32: The graph of y =
3
x
2
−2x+2
and a convex upper level set
Another example: f (x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
(restricted to x
1
, x
2
> 0) has strictly convex upper level sets.
It is not a concave function, because
Hf (x
1
, x
2
) =
0 1
1 0
.
201
4.5.1 Limitations of Concave Programming
∇f(x
1
, x
2
)
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.33: Several level sets and one upper level set of f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
4.5.2
Quasiconcave Functions
Theorem 4.12 requires that the objective function and constraint functions are concave, but the only
part of the proof that used their concavity was the first step: that concave functions have convex upper
level sets. We have now seen examples of other functions that have this property. These examples
belong to a broader class of functions, on which the main ideas of concave programming still apply. We
call them quasiconcave.
Definition 4.18
A function f(x) is quasiconcave if for any points a and
b in the domain of f(x),
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ min{f(a), f(
b)} for all 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
It is quasiconvex if
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≤ max{f(a), f(
b)} for all 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
Quasiconcavity is a statement about the height of the graph over a path that goes across and then
up.
f((1 − t)a + t
b
| {z }
line from a to
b
) ≥ min{f(a), f(
b)}
| {z }
horizontal line
for all 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
202
Figure 4.34: The graph of a quasiconcave function and the across and up path
Remark
“Across and up” is designed so that the path has a height that is the minimum of f(a) and f(
b) for
each x between them. If it lies below the graph then
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ min{f(a), f(
b)} for all 0 ≤ t ≤ 1.
Do not make an “across and down” or “up and across” path by mistake. Those will test a different
inequality.
The name quasiconcavity suggests that these functions should be similar to concave functions. In
fact, concavity is a stronger condition than quasiconcavity. A visual argument is best here. Theorem
1.19 showed that a function is concave, if and only if its graph lies above its secants.
The across and up path lies below the secant from (a, f(a)) to (
b, f(
b)). If y = f(x) lies above the
secant, then it also lies above the across and up path.
Theorem 4.19
If f(x) is a concave function, then it is also a quasiconcave function.
203
4.5.2
Quasiconcave Functions
Figure 4.35: The secant and the across and up path below y = f (x)
Quasiconcavity is easiest to recognize in single-variable functions. We can verify that across and up
paths stay below the graph y = f(x) for functions with the following shapes.
Lemma 4.20
Suppose f(x) is a one-variable function. f (x) is quasiconcave, if one of the following is true about
f(x):
1 f(x) is non-decreasing.
2 f(x) is non-increasing.
3 For some a, f(x) is non-decreasing before a and nonincreasing after a.
Functions that satisfy 1 or 2 are called monotone.
Remark
These conclusions only make sense for single-variable functions. Increasing and decreasing are not words
that describe multivariable functions.
204
Figure 4.36: The across and up path below a non-increasing y = f (x)
Our goal in defining quasiconcavity was to produce a large class of functions whose upper level sets
allowed for separation arguments. In fact, the quasiconcave functions are the broadest possible such
class. Every function with convex upper level sets is quasiconcave, and every quasiconcave function has
convex upper level sets.
Lemma 4.21
f(x) is a quasiconcave function, if and only if every upper level set f(x) ≥ c is a convex set.
Figure 4.37: The segment from a to
b in the upper level set of f(x)
The proof relies on combining the definitions of quasiconcavity, upper level sets, and convex sets.
205
4.5.2
Quasiconcave Functions
Proof
There are two directions of argument that we need to make.
1 Suppose that f (x) is quasiconcave. Let a and
b be in the upper level set f(x) ≥ c. By definition,
we know that f(a) ≥ c and f(
b) ≥ c. The points on the segment from a to
b are parametrized by
(1 − t)a + t
b 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
If we evaluate f along these points we get
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ min{f(a), f(
b)} (f is quasiconcave)
≥ c (a and
b lie in the upper level set)
Thus the segment lies in the upper level set f(x) ≥ c. Since this holds for any a and
b in any
upper level set, we conclude that every upper level set of f(x) is convex.
2 Now suppose that every upper level set of (x) is convex. Let a and
b be any points in the domain.
Let c = min{f(a), f(
b)}, so a and
b both lie in the upper level set f (x) ≥ c. Since the upper
level set is convex, the segment between them
(1 − t)a + t
b 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
lies in this set. Thus for 0 ≤ t ≤ 1,
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ c = min{f(a), f(
b)}
Since this holds for all a and
b, we conclude f(x) is quasiconcave.
4.5.3
Quasiconcave Programming
Quasiconcave programming describes the methods we use to solve constrained optimization when
the objective functions and constraint functions are quasiconcave. Most methods are analogs of results
for concavity, but because quasiconcavity is a weaker condition, they often need additional conditions
or draw weaker conclusions. We begin with a result for unconstrained optimization.
206
Theorem 4.22
If x
∗
is a strict local maximizer of a quasiconcave function f(x), then x
∗
is the unique global maximizer
of f(x).
a
b
x
∗
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.38: A segment, a neighborhood in which x
∗
is a maximizer, and a point a that lies in both
Proof
Let
b be any other point in the domain of f(x). x
∗
is the unique maximizer in some neighborhood, and
the segment from x
∗
to
b travels through this neighborhood. Let a = x
∗
be a point that lies both on
the segment and in the neighborhood.
f(a) ≥ min{f(x
∗
), f(
b)} (f(x) is quasiconcave)
f(x
∗
) > min{f(x
∗
), f(
b)} (f(x
∗
) > f(a))
f(x
∗
) > f(
b) (f(x
∗
) is not less than itself)
Since this holds for any
b, we conclude that x
∗
is the unique maximizer of f(x),
Remark
For a quasiconcave function, knowing a is a critical point is not enough to conclude that a is a maximizer.
For instance f(x) = x
3
is increasing, so it is quasiconcave. 0 is a critical point but not a maximizer.
This means that our Kuhn-Tucker sufficiency theorem cannot translate directly to quasiconcavity,
because there is no way to cover the ∇f (x) =
0 case. The simplest workaround is to write a theorem
that only applies when ∇f(x
∗
) =
0.
207
4.5.3 Quasiconcave Programming
Theorem 4.23
Given an objective function f(x) and constraints g
j
(x) ≥ 0, suppose ∇f(x
∗
) =
0 and (x
∗
,
λ
∗
) satisfies
the Kuhn-Tucker conditions. If f (x) and the g
j
(x) are all quasiconcave, then x
∗
maximizes f(x), subject
to the constraints.
We can use almost the same argument that we used for the λ
j
> 0 case with concave functions.
Only the first steps need to change. Once we establish that the upper level sets are convex, the rest of
the proof is identical to Theorem 4.12.
binding λ
∗
j
> 0
all λ
∗
j
= 0
f(x) is
quasiconcave
f(x) ≥ c is convex
f(x) ≥ c does not
intersect h
−
g
j
(x) are
quasiconcave
g
j
(x) ≥ 0
are convex
∇f(x
∗
) = −
P
λ
∗
j
∇g
j
(x
∗
)
feasible set does
not intersect h
+
x
∗
is a max
in the feasible set
Lem 4.21
Lem 4.14
Lem 4.21
Cor 4.15
Thm 4.10
4.5.4
Positive Transformations and Quasiconcavity
The condition of quasiconcavity is ordinal rather than cardinal in nature. We care that certain
points attain greater values than others, but not how much greater. Contrast this to concavity where
f((1 − t)a + t
b) has to be at least t(f(
b) − f (a)) greater than f (a).
For this reason, quasiconcavity is a relevant property of utility functions. The values of a utility
function reflect no inherent information beyond relative preferences. We can rescale a quasiconcave
function f(x) without affecting whether f (a) > f (
b). The following definition and theorem formalizes
this flexibility.
Definition 4.24
A function f(x) is a positive transformation of a function g(x) if there is an increasing function p(x)
such that g(x) = p(f(x))
208
Example
Consider the function f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
on the domain
R
2
+
= {(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
> 0, x
2
> 0}.
p(x) = ln x is an increasing function so
g(x
1
, x
2
) = p(f(x
1
, x
2
))
= ln x
1
+ ln x
2
is a positive transformation of f.
Positive transformation is a symmetric relation. If p(x) is increasing, then so is p
−1
(x). That means
that if g(x) = p(f(x)) is a positive transformation of f(x), then f(x) = p
−1
(g(x)) is also a positive
transformation of g(x).
Theorem 4.25
Let f (x) be a function, and let g(x) be a positive transformation of f(x). f(x) is quasiconcave if and
only if g(x) is quasiconcave.
Proof
Since p(x) is an increasing function, larger values of f(x) correspond to larger values of g(x). This
means that
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ f(a), if and only if g((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ g(a),
and f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ f(
b), if and only if g((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ g(
b).
Putting these together gives
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ min{f(a), f(
b)}, if and only if g((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ min{g(a), g(
b)}.
If f(x) is quasiconcave, then this inequality is satisfied for all a and
b in the domain and t in [0, 1]. This
means that g(x) is also quasiconcave. If f(x) is not quasiconcave, then this inequality is not satisfied
for some a,
b and t. That means that g(x) is also not quasiconcave.
We will use this theorem to verify that positive transformations of concave functions are quasiconcave.
Here is an example.
209
4.5.4 Positive Transformations and Quasiconcavity
Example
Consider the function f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
on the domain
R
2
+
= {(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
> 0, x
2
> 0}.
We can reason that f(x
1
, x
2
) is quasiconcave as follows:
1 g(x
1
, x
2
) = ln x
1
+ ln x
2
is a positive transformation of f(x
1
, x
2
).
2 Apply Theorem 1.41. g(x
1
, x
2
) is concave, because its Hessian is negative definite.
Hg(x
1
, x
2
) =
"
−
1
x
2
1
0
0 −
1
x
2
2
#
3 Apply Theorem 4.19. Since g(x
1
, x
2
) is concave, it is also quasiconcave.
4 Apply Theorem 4.25. Since g(x
1
, x
2
) is quasiconcave, f(x
1
, x
2
) is quasiconcave.
Remark
Notice this reasoning does not apply to concavity.
g(x
1
, x
2
) = ln x
1
+ ln x
2
is concave
f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
is not concave
To use this method, we must find a function g(x) that is a positive transformation of f(x) and is
also concave. If we do not have an obvious candidate, random guessing is not practical. We would like
a more straightforward procedure.
4.5.5
The Bordered Hessian and Quasiconcavity
We can verify quasiconcavity by direct computation. We will derive that method here.
Recall Lemma 4.14. It showed that convex upper level sets lie in the positive half-space of their
tangent hyperplanes. Another way to say this is that a is the maximizer of f(x) among points on the
tangent hyperplane to its level set.
210
∇f(a)
a
x
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.39: A maximizer of f(x) on the
tangent line to its level set
∇f(a)
a
x
x
1
x
2
Figure 4.40: A local minimizer of f(x)
on the tangent line to its level set
We can prove a reverse version of this lemma with some modifications.
1 We generalize the tangent hyperplane to “points that satisfy ∇f (a) · (x −a) = 0.”
2 We require that each point is a strict local maximizer subject to that constraint.
If this holds for all a, we can conclude that f(x) is quasiconcave.
Lemma 4.26
Suppose f(x) is a continuously differentiable function on a convex domain. If every a in the domain of
f(x) is a strict local maximizer of f(x) subject to ∇f(a) · (x −a) = 0, then f(x) is quasiconcave.
The proof shows that f(x) satisfies the inequality that defines quasiconcavity.
Proof
Let f(x) be a function and g(x) be a positive transformation of f(x). Let a and
b be points in the
domain of f(x). In order to show f(x) is quasiconcave, we need to evaluate f (x) along the segment
x(t) = (1 − t)a + t
b 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
Consider the composition f (x(t)). By the extreme value theorem, this has a minimizer on [0, 1]. Let
0 < t
0
< 1. We claim that t
0
is not a minimizer of f(x(t)), there are two cases:
1 If
df(x(t
0
))
dt
= 0 then t
0
does not satisfy the first-order condition, so it is not a minimizer.
2 If
df(x(t
0
))
dt
= 0 then by the chain rule
∇f(x(t
0
)) · x
′
(t
0
) = 0
∇f(x(t
0
)) · (
b −a) = 0
211
4.5.5 The Bordered Hessian and Quasiconcavity
For any t, the vector x(t) − x(t
0
) is parallel to
b − a. Thus every x(t) satisfies ∇f(x(t
0
)) ·
(x(t) − x(t
0
)) = 0. By the hypothesis of this lemma, x(t
0
) is a strict local maximizer subject to
∇f(x(t
0
)) · (x −x(t
0
)) = 0. We can conclude that t
0
is not a minimizer of f(x(t)).
Since there is a minimizer of f (x(t)) on [0, 1], and it cannot occur for 0 < t < 1, the minimizer
must be t = 0 or t = 1. That means that
f((1 − t)a + t
b) ≥ min{f(a), f(
b)} for all 0 ≤ t ≤ 1
Since this holds for any a and
b, we conclude f(x) is quasiconcave.
Figure 4.41: A critical point of the composition f(x(t)), its gradient, and its upper level set
According to thus lemma, we now have a new way to verify quasiconcavity. We must check that
every point a is a strict local maximizer of f(x) subject to ∇f (a) · (x − a) = 0. We use different
methods at different points a. Which method we use depends on ∇f (a).
1 If ∇f(a) =
0 then every point x satisfies the constraint, making it meaningless. We can check
that a is an unconstrained strict local maximizer by checking the determinants of the minors of
Hf (a) (Theorem 1.31).
2 If ∇f(a) =
0 then the Lagrangian of f(x) subject to ∇f(a) · (x −a) = 0 is
L(λ, x) = f(x) + λ(∇f(a) · (x −a))
= f(x) + λ
n
X
i=1
f
i
(a)(x
i
− a
i
)
We can check the determinants of the minors of HL(λ,a) (Theorem 4.6).
212
The Hessian of
L(λ, x) = f(x) + λ
n
X
i=1
f
i
(a)(x
i
− a
i
)
has a memorable form.
Example
For n = 2, the bordered Hessian is
HL(λ, x) =
0 f
1
(a) f
2
(a)
f
1
(a) f
11
(x) f
12
(x)
f
2
(a) f
21
(x) f
22
(x)
.
Evaluating at x = a gives
HL(λ, a) =
0 f
1
(a) f
2
(a)
f
1
(a) f
11
(a) f
12
(a)
f
2
(a) f
21
(a) f
22
(a)
.
Due to its importance in this test, we call HL(λ, x) the bordered Hessian of f . We denote it
BHf(x), since it does not depend on λ.
Theorem 4.27
Suppose f(x) is a continuously differentiable function on a convex domain. If for each x in the domain
either
1 Hf(x) satisfies (−1)
i
|M
i
| > 0 for 1 ≤ i ≤ n, or
2 BHf(x) satisfies (−1)
i
|M
i
| < 0 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n + 1,
then f(x) is a quasiconcave function.
Here is a diagram of the steps of the proof.
Hf (a) satisfies the
alternating condition
BHf(a) satisfies the
alternating condition
a is a strict local maximizer
subject to ∇f(a) · (x −a) = 0
f(x) is quasiconcave
either
Thm 4.6
Local SOC
Lem 4.26
213
4.5.5 The Bordered Hessian and Quasiconcavity
The requirement that a be a strict local maximizer of f (x) subject to ∇f(a) ·(x −a) = 0 is actually
stronger than we need. We could make a valid argument only requiring a nonstrict local maximizer.
This would add some extra complexity to the proof of Lemma 4.26. In exchange we would gain the
ability to use the test for a negative semidefinite matrix instead of negative definite (Theorem 1.42).
That test is unpleasant to perform, so such a result may not be worth the effort.
4.5.6
Verifying Qusiconcavity Using the Bordered Hessian
Let f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
on the domain
R
2
+
= {(x
1
, x
2
) : x
1
> 0, x
2
> 0}.
Show that f (x
1
, x
2
) is quasiconcave.
Solution
We need to check the Hessian where ∇f(x
1
, x
2
) = (x
2
, x
1
) = (0, 0). This only occurs at (0, 0), which
is not in the domain. Everywhere else we can check the bordered Hessian.
BHf(x) =
0 f
1
(x) f
2
(x)
f
1
(x) f
11
(x) f
12
(x)
f
2
(x) f
21
(x) f
22
(x)
=
0 x
2
x
1
x
2
0 1
x
1
1 0
The minor determinants we need to check are
|M
2
| =
0 x
2
x
2
0
= −x
2
2
< 0
|M
3
| =
0 x
2
x
1
x
2
0 1
x
1
1 0
= 0 − x
2
x
2
1
x
1
0
+ x
1
x
2
0
x
1
1
= 2x
1
x
2
> 0
For all x
1
, x
2
> 0, this satisfies (−1)
i
|M
i
| < 0 for 2 ≤ i ≤ 3. We conclude that f(x
1
, x
2
) = x
1
x
2
is
quasiconcave on R
2
+
.
214
4.5.7
Strict Quasiconcavity
Like with strict concavity, strict quasiconcavity is defined by taking the inequality condition of qua-
siconcavity and making the inequalities strict.
Definition 4.28
A function f(x) is strictly quasiconcave if for any points a and
b in the domain of f(x),
f((1 − t)a + t
b) > min{f(a), f(
b)} for all 0 < t < 1
It is strictly quasiconvex if
f((1 − t)a + t
b) < max{f(a), f(
b)} for all 0 < t < 1
We can see from this definition that it is stronger than quasiconcavity. Every strictly quasiconcave
function is quasiconcave.
The condition on the upper level sets is more complicated.
Variant of Lemma 4.21
f(x) is a strictly quasiconcave function, if and only if
1 every upper level set f(x) ≥ c is a strictly convex set, and
2 there are no neighborhoods on which f(x) is constant
A function with a thick level set will fail condition 2 .
215
4.5.7 Strict Quasiconcavity
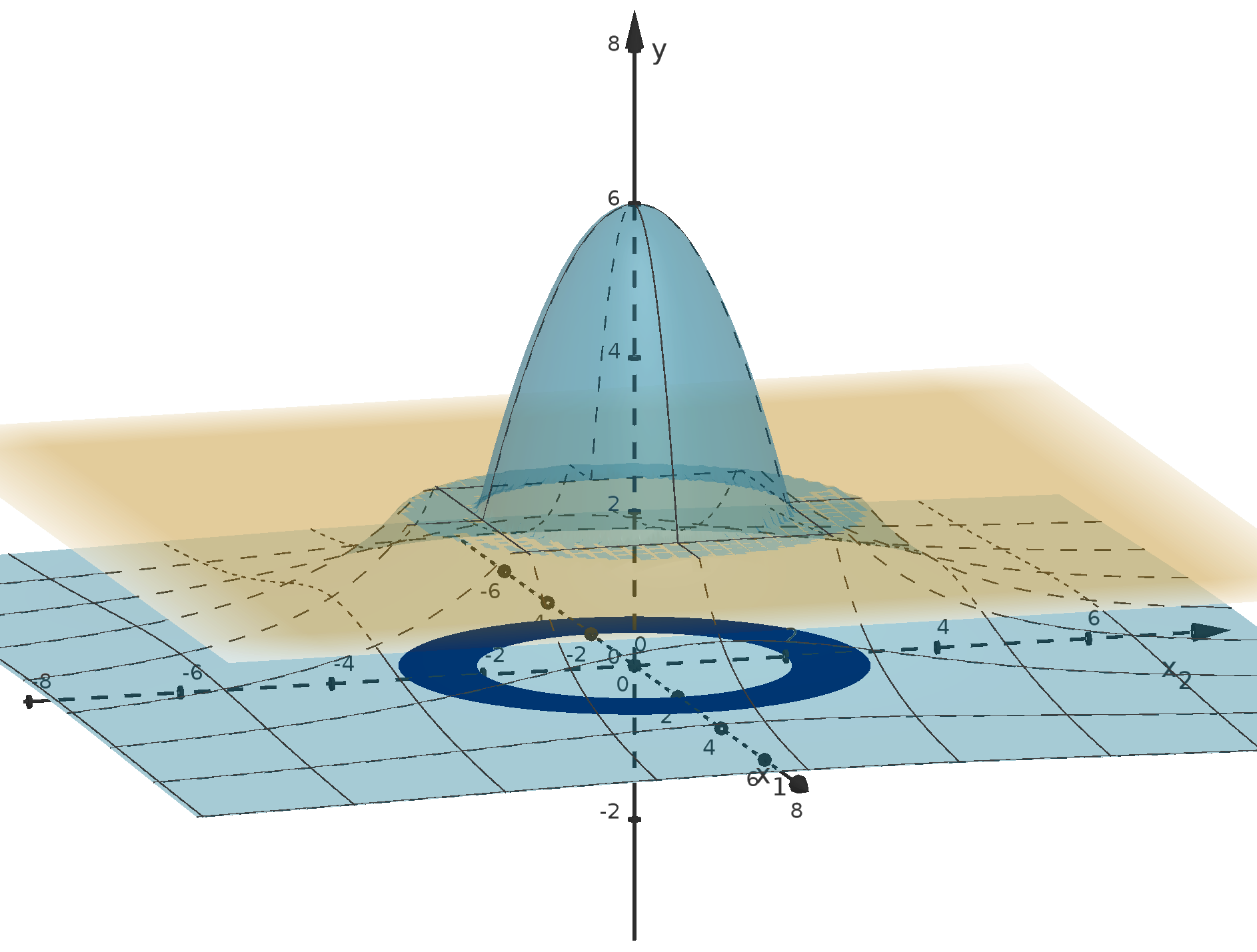
Figure 4.42: A thick level set of f(x)
As we might expect, strict quasiconcavity is a weaker condition than strict concavity.
Variant of Theorem 4.19
If a function f(x) is strictly concave, then it is also strictly quasiconcave.
We can summarize the relationships different forms of (quasi)-concavity in the following diagram.
f(x) is strictly concave
f(x) is concave
f(x) is strictly quasiconcave
f(x) is quasiconcave
Like with strict concavity, strict quasiconcavity can ensure that the Kuhn-Tucker conditions generate
a unique maximizer.
Variant of Theorem 4.23
Given an objective function f(x) and constraints g
j
(x) ≥ 0, suppose ∇f(x
∗
) =
0 and (x
∗
,
λ
∗
) satisfies
the Kuhn-Tucker conditions. If f (x) and the binding g
j
(x) are quasiconcave, and additionally either
1 f(x) is strictly quasiconcave or
2 the binding g
j
(x) are strictly quasiconcave,
then x
∗
is the unique maximizer of f(x), subject to the constraints.
216
Like regular quasiconcavity, strict quasiconcavity is preserved under positive transformation.
Variant of Theorem 4.25
Let f(x) be a function and g(x) be a positive transformation of f(x). f(x) is strictly quasiconcave if
and only if g(x) is strictly quasiconcave.
The proof of Lemma 4.26 could instead produce a strict inequality with no additional reasoning. As
a result we can strengthen our Hessian/bordered Hessian test to guarantee strict quasiconcavity with
no modifications.
Improvement on Theorem 4.27
Suppose f (x) is a continuously differentiable function on a convex domain. If for each a in the domain
either
1 Hf(x) satisfies (−1)
i
|M
i
| > 0 for 1 ≤ i ≤ n, or
2 BHf(x) satisfies (−1)
i
|M
i
| < 0 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n + 1,
then f(x) is strictly quasiconcave.
4.5.8
Section Summary
The most important definitions and results from this section were
The definition of quasiconcavity (Definition 4.18)
Concave functions are quasiconcave (Theorem 4.19)
The upper level sets of quasiconcave function are convex (Lemma 4.21)
Sufficient conditions for a maximizer of quasiconcave functions (Theorems 4.22 and 4.23)
Verifying quasiconcavity via composition (Theorem 4.25)
Verifying quasiconcavity with the bordered Hessian (Theorem 4.27)
Definition and variants for strict quasiconcavity (Definition 4.28 etc.)
217